|
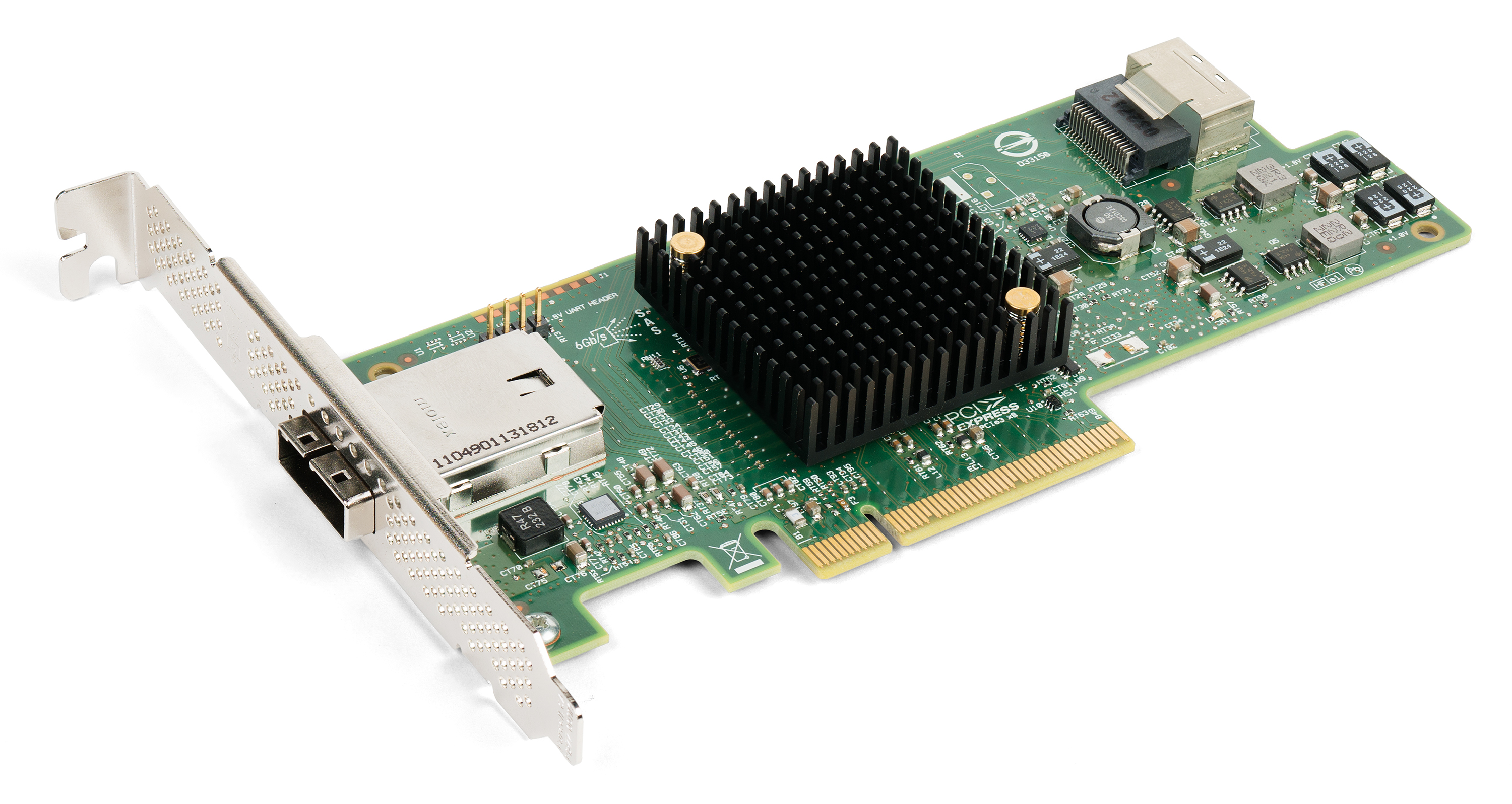
InfiniBand
InfiniBand (IB) is a computer networking communications standard used in high-performance computing that features very high throughput and very low latency. It is used for data interconnect both among and within computers. InfiniBand is also used as either a direct or switched interconnect between servers and storage systems, as well as an interconnect between storage systems. It is designed to be scalable and uses a switched fabric network topology. Between 2014 and June 2016, it was the most commonly used interconnect in the TOP500 list of supercomputers. Mellanox (acquired by Nvidia) manufactures InfiniBand host bus adapters and network switches, which are used by large computer system and database vendors in their product lines. As a computer cluster interconnect, IB competes with Ethernet, Fibre Channel, and Intel Omni-Path. The technology is promoted by the InfiniBand Trade Association. History InfiniBand originated in 1999 from the merger of two competing designs: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mellanox
Mellanox Technologies Ltd. () was an Israeli-American multinational supplier of computer networking products based on InfiniBand and Ethernet technology. Mellanox offered adapters, switches, software, cables and silicon for markets including high-performance computing, data centers, cloud computing, computer data storage and financial services. On March 11, 2019, Nvidia announced its intent to acquire the company for $6.9 billion. The deal closed on April 27, 2020, with approval from the EU, U.S. and Chinese antitrust authorities. The company was integrated into Nvidia's networking division in 2020 and Nvidia stopped using the brand name "Mellanox" for its new networking products. History 1999–2009 Mellanox was founded in May 1999 by former Israeli executives of Intel Corporation and Galileo Technology (which was acquired by Marvell Technology Group in October 2000 for $2.8 billion) Eyal Waldman, Shai Cohen, Roni Ashuri, Michael Kagan, Evelyn Landman, Eitan Zahavi, Shimon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI, PCI-X and Accelerated Graphics Port, AGP. Developed and maintained by the PCI-SIG (PCI Special Interest Group), PCIe is commonly used to connect graphics cards, sound cards, Wi-Fi and Ethernet adapters, and storage devices such as solid-state drives and hard disk drives. Compared to earlier standards, PCIe supports faster data transfer, uses fewer pins, takes up less space, and allows devices to be added or removed while the computer is running (hot swapping). It also includes better error detection and supports newer features like I/O virtualization for advanced computing needs. PCIe connections are made through "lanes," which are pairs of wires that send and receive data. Devices can use one or more lanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omni-Path
Omni-Path Architecture (OPA) is a high-performance communication architecture developed by Intel. It aims for low communication latency, low power consumption and a high throughput. It directly competes with InfiniBand. Intel planned to develop technology based on this architecture for exascale computing. The current owner of Omni-Path is Cornelis Networks. History Production of Omni-Path products started in 2015 and delivery of these products started in the first quarter of 2016. In November 2015, adapters based on the 2-port "Wolf River" ASIC were announced, using QSFP28 connectors with channel speeds up to 100 Gbit/s. Simultaneously, switches based on the 48-port "Prairie River" ASIC were announced. First models of that series were available starting in 2015. In April 2016, implementation of the InfiniBand "verbs" interface for the Omni-Path fabric was discussed. In October 2016, IBM, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Dell, Lenovo, Samsung, Seagate Technology, Micron Techno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET. The original 10BASE5 Ethernet uses a thick coaxial cable as a shared medium. This was largely superseded by 10BASE2, which used a thinner and more flexible cable that was both less expensive and easier to use. More modern Ethernet variants use Ethernet over twisted pair, twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with Network switch, switches. Over the course of its history, Ethernet data transfer rates have been increased from the original to the lates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host Bus Adapter
In computer hardware a host controller, host adapter or host bus adapter (HBA) connects a computer system bus which acts as the host system to other network and storage devices. The terms are primarily used to refer to devices for connecting SCSI, SAS, NVMe, Fibre Channel and SATA devices. Devices for connecting to FireWire, USB and other devices may also be called host controllers or host adapters. Host adapters can be integrated in the motherboard or be on a separate expansion card. The term network interface controller (NIC) is more often used for devices connecting to computer networks, while the term converged network adapter can be applied when protocols such as iSCSI or Fibre Channel over Ethernet allow storage and network functionality over the same physical connection. SCSI A connects a host system and a peripheral SCSI device or storage system. These adapters manage service and task communication between the host and target. Typically a device driver, linked to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TOP500
The TOP500 project ranks and details the 500 most powerful non-distributed computing, distributed computer systems in the world. The project was started in 1993 and publishes an updated list of the supercomputers twice a year. The first of these updates always coincides with the International Supercomputing Conference in June, and the second is presented at the ACM/IEEE Supercomputing Conference in November. The project aims to provide a reliable basis for tracking and detecting trends in high-performance computing and bases rankings on HPL (benchmark), HPL benchmarks, a portable implementation of the high-performance LINPACK benchmarks, LINPACK benchmark written in Fortran for Distributed memory, distributed-memory computers. The most recent edition of TOP500 was published in June 2025 as the 65th edition of TOP500, while the next edition of TOP500 will be published in November 2025 as the 66th edition of TOP500. As of June 2025, the United States' El Capitan (supercomputer), El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work. One definition for software systems specifies that this may be done by adding resources to the system. In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that a company can increase sales given increased resources. For example, a package delivery system is scalable because more packages can be delivered by adding more delivery vehicles. However, if all packages had to first pass through a single warehouse for sorting, the system would not be as scalable, because one warehouse can handle only a limited number of packages. In computing, scalability is a characteristic of computers, networks, algorithms, networking protocols, programs and applications. An example is a search engine, which must support increasing numbers of users, and the number of topics it indexes. Webscale is a computer architectural approach that brings the capabilities of large-scale cloud computing companies into enterprise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switched Fabric
Switched fabric or switching fabric is a network topology in which network nodes interconnect via one or more network switches (particularly crossbar switches). Because a switched fabric network spreads network traffic across multiple physical links, it yields higher total throughput than broadcast networks, such as the early 10BASE5 version of Ethernet and most wireless networks such as Wi-Fi. The generation of high-speed serial data interconnects that appeared in 2001–2004 which provided point-to-point connectivity between processor and peripheral devices are sometimes referred to as fabrics; however, they lack features such as a message-passing protocol. For example, HyperTransport, the computer processor interconnect technology, continues to maintain a processor bus focus even after adopting a higher speed physical layer. Similarly, PCI Express is just a serial version of PCI; it adheres to PCI's host/peripheral load/store direct memory access (DMA)-based architectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabric Computing
Fabric computing or unified computing involves constructing a computing fabric consisting of interconnected nodes that look like a ''weave'' or a ''fabric'' when seen collectively from a distance. Usually the phrase refers to a consolidated high-performance computing system consisting of loosely coupled storage, networking and parallel processing functions linked by high bandwidth interconnects (such as 10 Gigabit Ethernet and InfiniBand) but the term has also been used to describe platforms such as the Azure Services Platform and grid computing in general (where the common theme is interconnected nodes that appear as a single logical unit). The fundamental components of fabrics are "nodes" (processor(s), memory, and/or peripherals) and "links" (functional connections between nodes). While the term "fabric" has also been used in association with storage area networks and with switched fabric networking, the introduction of compute resources provides a complete "unified" comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Switch
A network switch (also called switching hub, bridging hub, Ethernet switch, and, by the IEEE, MAC bridge) is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device. A network switch is a multiport network bridge that uses MAC addresses to forward data at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model. Some switches can also forward data at the network layer (layer 3) by additionally incorporating routing functionality. Such switches are commonly known as layer-3 switches or multilayer switches. Switches for Ethernet are the most common form of network switch. The first MAC Bridge was invented in 1983 by Mark Kempf, an engineer in the Networking Advanced Development group of Digital Equipment Corporation. The first 2 port Bridge product (LANBridge 100) was introduced by that company shortly after. The company subsequently produced multi-port switches for both Ethernet and FDDI such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interconnect Bottleneck
The interconnect bottleneck comprises limits on integrated circuit (IC) performance due to limits on the speed of connections between components, versus the internal speed of components. In 2006 it was predicted to be a "looming crisis" by 2010. Improved performance of computer systems has been achieved, in large part, by downscaling the IC minimum feature size. This allows the basic IC building block, the transistor, to operate at a higher frequency, performing more computations per second. However, downscaling of the minimum feature size also results in tighter packing of the wires on a microprocessor, which increases parasitic capacitance and signal propagation delay. Consequently, the delay due to the communication between the parts of a chip becomes comparable to the computation delay itself. This phenomenon, known as an "interconnect bottleneck", is becoming a major problem in high-performance computer systems. This interconnect bottleneck can be solved by using optical inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Apparatus Room
In broadcast facilities and television studios, a central apparatus room (CAR, pronounced "C-A-R"), central machine room, or central equipment room (CER), or central technical area (CTA), or rack room is where shared equipment common to all technical areas is located. Some broadcast facilities have several of these rooms. It should be air-conditioned, however low-noise specifications such as acoustical treatments are optional. Equipment is connected either directly with an attached foldout monitor, keyboard and mouse or remotely via KVM switch, SSH, VNC, RS-232 or remote desktop. Equipment These rooms contain broadcast and broadcast IT mission critical gear necessary to broadcast and television operations. CARs usually house audio routers, video routers, video servers, compressors and multiplexers that utilize broadcast automation systems with broadcast programming applications to playout television programs. They contain broadcast and monitoring equipment, throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |