|
Infectious Dose
The concept of a minimal infective dose (MID), also known as the infectious dose, has traditionally been used for infectious microorganisms that contaminate foods. MID was defined as the number of microorganisms ingested (the dose) from which a pathology is observed in the consumer. For example, to cause gastrointestinal disorders, the food must contain more than 100,000 ''Salmonella'' per gram or 1000 per gram for salmonellosis. however, some viruses like DHBV( duck hepatitis B virus) need as low as 9.5 x 10(9) virus per milliliters to cause liver infections.To know the dose ingested, it is also necessary to know the mass of the portion. This may be calculated using the following formula: :d\ =\ c \times m where: *d = number of bacteria i.e. dose *c = concentration of bacteria *m = mass This formulation has served as a basis for reasoning to establish the maximum concentrations permitted by the microbiological regulatory criteria intended to protect the health of consumers. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an Disease#Terminology, illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune systems. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an Innate immune system, innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an Adaptive immune system, adaptive response. Treatment for infections depends on the type of pathogen involved. Common medications include: * Antibiotics for bacterial infections. * Antivirals for viral infections. * Antifungals for fungal infections. * Antiprotozoals for protozoan infections. * Antihelminthics for infections caused by parasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an event is to occur."Kendall's Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1: Distribution Theory", Alan Stuart and Keith Ord, 6th ed., (2009), .William Feller, ''An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications'', vol. 1, 3rd ed., (1968), Wiley, . This number is often expressed as a percentage (%), ranging from 0% to 100%. A simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. Since the coin is fair, the two outcomes ("heads" and "tails") are both equally probable; the probability of "heads" equals the probability of "tails"; and since no other outcomes are possible, the probability of either "heads" or "tails" is 1/2 (which could also be written as 0.5 or 50%). These concepts have been given an axiomatic mathematical formaliza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus Quantification
Virus quantification is counting or calculating the number of virus particles (virions) in a sample to determine the virus concentration. It is used in both research and development (R&D) in academic and commercial laboratories as well as in production situations where the quantity of virus at various steps is an important variable that must be monitored. For example, the production of virus-based vaccines, recombinant proteins using viral vectors, and viral antigens all require virus quantification to continually monitor and/or modify the process in order to optimize product quality and production yields and to respond to ever changing demands and applications. Other examples of specific instances where viruses need to be quantified include clone screening, multiplicity of infection (MOI) optimization, and adaptation of methods to cell culture. There are many ways to categorize virus quantification methods. Here, the methods are grouped according to what is being measured and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
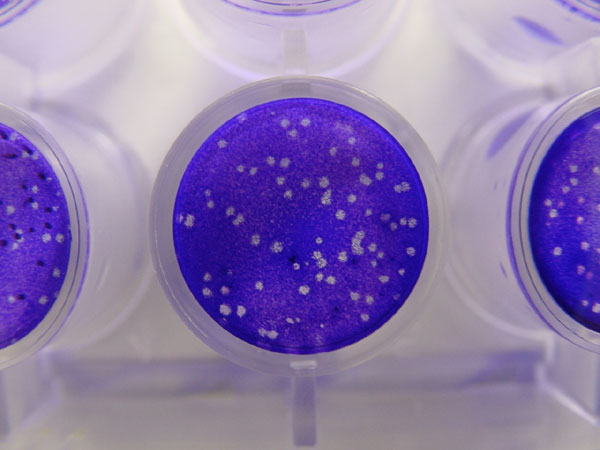
Plaque-forming Unit
A plaque-forming unit (PFU) is a measure used in virology to describe the number of virus particles capable of forming plaques per unit volume. It is a proxy measurement rather than a measurement of the absolute quantity of particles: viral particles that are defective or which fail to infect their target cell will not produce a plaque and thus will not be counted. For example, a solution of tick-borne encephalitis virus with a concentration of 1,000 PFU/μL indicates that 1 μL of the solution contains enough virus particles to produce 1000 infectious plaques in a layer of cells. However, the number of virus particles might be greater than the number of PFU if some virus particles fail to form plaques because they are defective or otherwise failed to infect cells. The concept of plaque-forming units of virus is equivalent to the concept of colony-forming units of bacteria. See also *Viral load * Minimal infective dose *Virus quantification Virus quantification is countin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Load
Viral load, also known as viral burden, is a numerical expression of the quantity of virus in a given volume of fluid, including biological and environmental specimens. It is not to be confused with viral titre or viral titer, which depends on the assay. When an assay for measuring the infective virus particle is done (Plaque assay, Focus assay), viral titre often refers to the ''concentration'' of infectious viral particles, which is different from the ''total'' viral particles. Viral load is measured using body fluids sputum and blood plasma. As an example of environmental specimens, the viral load of norovirus can be determined from run-off water on garden produce. Norovirus has not only prolonged viral shedding and has the ability to survive in the environment but a minuscule infectious dose is required to produce infection in humans: less than 100 viral particles. Viral load is often expressed as viral particles, (virions) or infectious particles per mL depending on the type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Cereus
''Bacillus cereus'' is a Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-positive Bacillus, rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in soil, food, and marine sponges. The specific name, ''cereus'', meaning "waxy" in Latin, refers to the appearance of colonies grown on blood agar. Some strains are harmful to humans and cause foodborne illness due to their spore-forming nature, while other strains can be beneficial as probiotics for animals, and even exhibit mutualism with certain plants. ''B. cereus'' bacteria may be Aerobic organism, aerobes or facultative anaerobes, and like other members of the genus ''Bacillus'', can produce protective endospores. They have a wide range of virulence factors, including phospholipase C, cereulide, Metalloproteinase, sphingomyelinase, metalloproteases, and cytotoxin K, many of which are regulated via quorum sensing. ''B. cereus'' strains exhibit Flagellum, flagellar motility. The ''Bacillus cereus'' group comprises seven closely related species: ''B. cereus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe, meaning that it can grow without oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli
Enterotoxigenic ''Escherichia coli'' (ETEC) is a type of ''Escherichia coli'' and one of the leading bacterial causes of diarrhea in the developing world, as well as the most common cause of travelers' diarrhea. Insufficient data exists, but conservative estimates suggest that each year, about 157,000 deaths occur, mostly in children, from ETEC. A number of pathogenic isolates are termed ETEC, but the main hallmarks of this type of bacterium are expression of one or more enterotoxins and presence of fimbriae used for attachment to host intestinal cells. The bacterium was identified by the Bradley Sack lab in Kolkata in 1968. Signs and symptoms Infection with ETEC can cause profuse, watery diarrhea with no blood or leukocytes and abdominal cramping. Fever, nausea with or without vomiting, chills, loss of appetite, headache, muscle aches and bloating can also occur, but are less common. Pathogenic factors Attachment ETEC use fimbrial colonization factor (CF) or coli surface (C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. They occur especially as proteins, often conjugated. The term was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919), derived from '' toxic''. Toxins can be small molecules, peptides, or proteins that are capable of causing disease on contact with or absorption by body tissues interacting with biological macromolecules such as enzymes or cellular receptors. They vary greatly in their toxicity, ranging from usually minor (such as a bee sting) to potentially fatal even at extremely low doses (such as botulinum toxin). Terminology Toxins are often distinguished from other chemical agents strictly based on their biological origin. Less strict understandings embrace naturally occurring inorganic toxins, such as arsenic. Other understandings embrace synthetic analogs of naturally occurring organic poisons as toxins, and may or may not embrace naturally oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infections, an attack rate in excess of 15 cases per 100,000 people for two consecutive weeks is considered an epidemic. Epidemics of infectious disease are generally caused by several factors including a change in the ecology of the host population (e.g., increased stress or increase in the density of a vector species), a genetic change in the pathogen reservoir or the introduction of an emerging pathogen to a host population (by movement of pathogen or host). Generally, an epidemic occurs when host immunity to either an established pathogen or newly emerging novel pathogen is suddenly reduced below that found in the endemic equilibrium and the transmission threshold is exceeded. An epidemic may be restricted to one location; however, if it sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listeriosis
Listeriosis is a bacterial infection most commonly caused by '' Listeria monocytogenes'', although '' L. ivanovii'' and '' L. grayi'' have been reported in certain cases. Listeriosis can cause severe illness, including severe sepsis, meningitis, or encephalitis, sometimes resulting in lifelong harm and even death. Those at risk of severe illness are the elderly, fetuses, newborns, and those who are immunocompromised. In pregnant women, it may cause stillbirth or spontaneous abortion, and preterm birth is common. Listeriosis may cause mild, self-limiting gastroenteritis and fever in anyone. ''Listeria'' is ubiquitous and is primarily transmitted via the oral route after ingestion of contaminated food products, after which the bacteria penetrates the intestinal tract to cause systemic infections. The diagnosis of listeriosis requires the isolation of the causative bacteria from the blood or the cerebrospinal fluid. Treatment includes prolonged administration of antibioti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |