|
History Of Chinese Dance
Dance in China has a long recorded history. Depictions of dancing in China appeared over 4,000 years ago. The early dances may be folk dances or ritual dances, some of which developed into court dances. The most important of the early dances served important ritual and ceremonial roles and are known as ''yayue'' which continued to be performed at the imperial court until the Qing dynasty. A profusion of dances in popular and court entertainment as well as folk dances have been recorded in ancient texts. The art of dance in China reached a peak during the Tang dynasty (618–907 CE) when numerous dances were recorded. Dancing as an individual art form declined in the later eras when dances become incorporated into operas and female dancing also declined when footbinding became more prevalent. In more recent times dance has enjoyed a resurgence, and it is widely performed by the public and professionals alike. There are continuous written records of Chinese dances for over two thou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danseuses Chine Guimet 291002
Danseuse is a French female term in the ballet and may refer to: * Ballerina, sometimes taken as synonymous to a principal dancer * Soloist, a more general term in ballet * Corps de ballet In ballet, the ''corps de ballet'' (; French for "body of the ballet") is the group of dancers who are not principal dancers or soloists. They are a permanent part of the ballet company and often work as a backdrop for the principal dancers. ..., the group of dancers who are not soloists Danseuse(s) may also refer to: * ''Danseuse'' (Csaky) (1912), sculpture created by Joseph Csaky * " Danseuses de Delphes" (1910), one of 24 piano pieces in ''Préludes'' by Claude Debussy {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confucius
Confucius ( ; zh, s=, p=Kǒng Fūzǐ, "Master Kǒng"; or commonly zh, s=, p=Kǒngzǐ, labels=no; – ) was a Chinese philosopher and politician of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Confucius's teachings and philosophy underpin East Asian culture and society, remaining influential across China and East Asia to this day. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, correctness of social relationships, justice, kindness, and sincerity. His followers competed with many other schools during the Hundred Schools of Thought era, only to be suppressed in favor of the Legalists during the Qin dynasty. After the collapse of Qin and the victory of Han over Chu, Confucius's thoughts received official sanction in the new government. During the Tan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
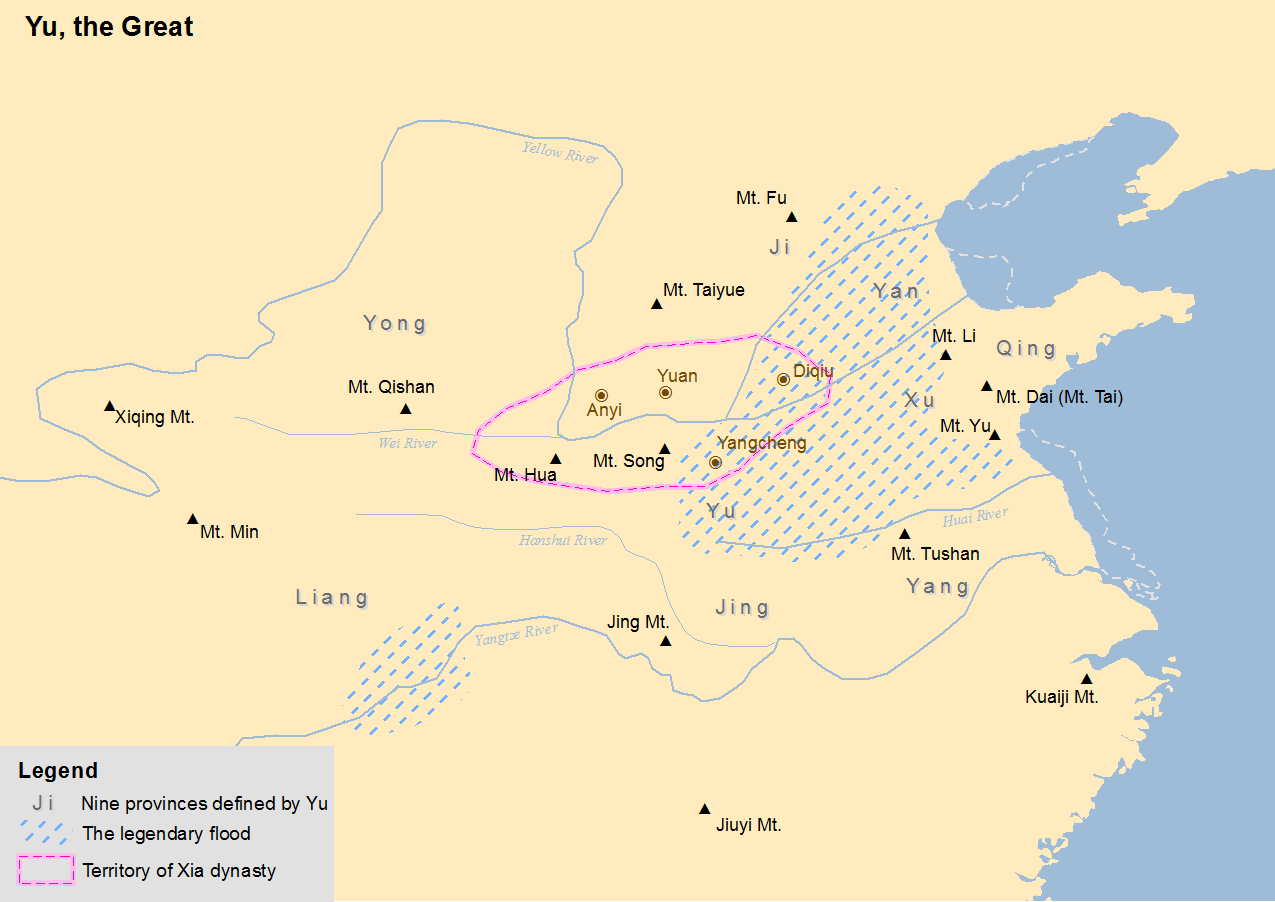
Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was later succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, who are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, since the earliest oracle bone inscriptions date from the late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the '' Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. The succession of dynasties was incorpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Of Shang
Cheng Tang (), personal name Zi Lü (), recorded on oracle bones as Da Yi (大乙), was the first king of the Shang dynasty in Chinese history. Traditionally considered a virtuous ruler, he overthrew Jie, the last ruler of the Xia dynasty. Rise of Shang Tang ruled Shang, one of the many kingdoms under the suzerainty of the Xia dynasty, for 17 years. During Jie's reign, Shang grew in power, initially at the expense of Xia's other vassals. He was able to win many supporters from as many as 40 smaller kingdoms.王恆偉. (2005) (2006) 中國歷史講堂 #1 遠古至春秋. 中華書局. . p 30. Tang recognized that Jie mistreated his people and used this to convince others. In one speech, Tang said that creating chaos was not something he wanted, but given the terror of Jie, he had to follow the Mandate of Heaven and use this opportunity to overthrow Xia. As an advantage he pointed out that even Jie's own military generals would not obey his orders. In the 15th year of Jie's rei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yu The Great
Yu the Great (大禹) was a legendary king in ancient China who was famed for his introduction of flood control, his establishment of the Xia dynasty which inaugurated dynastic rule in China, and his upright moral character. He figures prominently in the Chinese legend of "Great Yu Who Controlled the Waters" (). The dates which have been proposed for Yu's reign predate the oldest-known written records in China, the oracle bones of the late Shang dynasty, by nearly a millennium. Yu's name was not inscribed on any artifacts which were produced during the proposed era in which he lived, nor was it inscribed on the later oracle bones; his name was first inscribed on vessels which date back to the Western Zhou period (c. 1045–771 BC). The lack of substantial contemporary documentary evidence has caused some controversy over Yu's historicity. Thus, proponents of his existence theorize that stories about his life and reign were orally transmitted in various areas of China until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Shun
Emperor Shun () was a legendary leader of ancient China, regarded by some sources as one of the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors being the last of the Five Emperors. Tradition holds that he lived sometime between 2294 and 2184 BC. Tradition also holds that those with surname Chen (陳) are descendants of Emperor Shun. The Duke Hu of Chen, a descendant of Shun, became the founder of the State of Chen. Later Chen dynasty emperors such as Chen Baxian would also claim descent from Shun. Names Shun's clan name () is Yao (), his lineage name () is Youyu (). His given name was Chonghua (). Shun is sometimes referred to as the Great Shun () or as Yu Shun or Shun of Yu (), "Yu" being the name of his fief, which he received from Yao. Life of Shun According to traditional sources, Shun received the mantle of leadership from Emperor Yao at the age of 53, and then died at the age of 100 years. Before his death Shun is recorded as relinquishing his seat of power to Yu (), the founde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Yao
Emperor Yao (; traditionally c. 2356 – 2255 BCE) was a legendary Chinese ruler, according to various sources, one of the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors. Ancestry and early life Yao's ancestral name is Yi Qi () or Qi (), clan name is Taotang (), given name is Fangxun (), as the second son to Emperor Ku and Qingdu (). He is also known as Tang Yao (). Yao's mother has been worshipped as the goddess Yao-mu. Legends According to the legend, Yao became the ruler at 20 and died at 99 when he passed his throne to Shun the Great, to whom he had given his two daughters in marriage. According to the ''Bamboo Annals'', Yao abdicated his throne to Shun in his 73rd year of reign, and continued to live during Shun's reign for another 28 years. It was during the reign of Emperor Yao that the Great Flood began, a flood so vast that no part of Yao's territory was spared, and both the Yellow River and the Yangtze valleys flooded. The alleged nature of the flood is shown in the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Emperor
The Yellow Emperor, also known as the Yellow Thearch or by his Chinese name Huangdi (), is a deity ('' shen'') in Chinese religion, one of the legendary Chinese sovereigns and culture heroes included among the mytho-historical Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors and cosmological Five Regions' Highest Deities (). Calculated by Jesuit missionaries on the basis of Chinese chronicles and later accepted by the twentieth-century promoters of a universal calendar starting with the Yellow Emperor, Huangdi's traditional reign dates are 2697–2597 or 2698–2598 BC. Huangdi's cult became prominent in the late Warring States and early Han dynasty, when he was portrayed as the originator of the centralized state, as a cosmic ruler, and as a patron of esoteric arts. A large number of texts – such as the '' Huangdi Neijing'', a medical classic, and the '' Huangdi Sijing'', a group of political treatises – were thus attributed to him. Having waned in influence during most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |