|
Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor
The heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) is a type of bipolar junction transistor (BJT) which uses differing semiconductor materials for the emitter and base regions, creating a heterojunction. The HBT improves on the BJT in that it can handle signals of very high frequencies, up to several hundred GHz. It is commonly used in modern ultrafast circuits, mostly radio frequency (RF) systems, and in applications requiring a high power efficiency, such as RF power amplifiers in cellular phones. The idea of employing a heterojunction is as old as the conventional BJT, dating back to a patent from 1951. Detailed theory of heterojunction bipolar transistor was developed by Herbert Kroemer in 1957. Materials The principal difference between the BJT and HBT is in the use of differing semiconductor materials for the emitter-base junction and the base-collector junction, creating a heterojunction. The effect is to limit the injection of holes from the base into the emitter region, since t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Junction Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
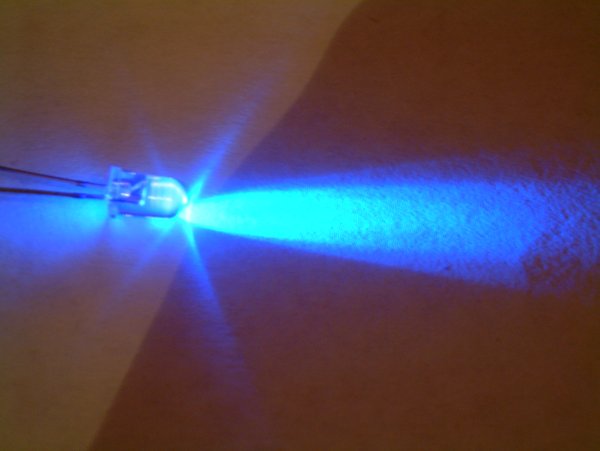
Indium Gallium Nitride
Indium gallium nitride (InGaN, ) is a semiconductor material made of a mix of gallium nitride (GaN) and indium nitride (InN). It is a ternary group III/ group V direct bandgap semiconductor. Its bandgap can be tuned by varying the amount of indium in the alloy. InxGa1−xN has a direct bandgap span from the infrared (0.69 eV) for InN to the ultraviolet (3.4 eV) of GaN. The ratio of In/Ga is usually between 0.02/0.98 and 0.3/0.7. Applications LEDs Indium gallium nitride is the light-emitting layer in modern blue and green LEDs and often grown on a GaN buffer on a transparent substrate as, e.g. sapphire or silicon carbide. It has a high heat capacity and its sensitivity to ionizing radiation is low (like other group III nitrides), making it also a potentially suitable material for solar photovoltaic devices, specifically for arrays for satellites. It is theoretically predicted that spinodal decomposition of indium nitride should occur for compositions between 15% and 85%, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave Technology
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ranges as microwaves; the above broad definition includes both UHF and EHF ( millimeter wave) bands. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz (wavelengths between 0.3 m and 3 mm). In all cases, microwaves include the entire SHF band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum. Frequencies in the microwave range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations. The prefix ' in ''microwave'' is not meant to suggest a wavelength in the micrometer range. Rather, it indicates that microwaves are "small" (having shorter wavelengths), compared to the radio waves used prior to microwave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MESFET
A MESFET (metal–semiconductor field-effect transistor) is a field-effect transistor semiconductor device similar to a JFET with a Schottky (metal–semiconductor) junction instead of a p–n junction for a gate. Construction MESFETs are constructed in compound semiconductor technologies lacking high quality surface passivation, such as gallium arsenide, indium phosphide, or silicon carbide, and are faster but more expensive than silicon-based JFETs or MOSFETs. Production MESFETs are operated up to approximately 45 GHz, and are commonly used for microwave frequency communications and radar. The first MESFETs were developed in 1966, and a year later their extremely high frequency RF microwave performance was demonstrated. radio-electronics.com. Functiona ...
|
High Electron Mobility Transistor
A high-electron-mobility transistor (HEMT), also known as heterostructure FET (HFET) or modulation-doped FET (MODFET), is a field-effect transistor incorporating a junction between two materials with different band gaps (i.e. a heterojunction) as the channel instead of a doped region (as is generally the case for a MOSFET). A commonly used material combination is GaAs with AlGaAs, though there is wide variation, dependent on the application of the device. Devices incorporating more indium generally show better high-frequency performance, while in recent years, gallium nitride HEMTs have attracted attention due to their high-power performance. Like other FETs, HEMTs are used in integrated circuits as digital on-off switches. FETs can also be used as amplifiers for large amounts of current using a small voltage as a control signal. Both of these uses are made possible by the FET’s unique current–voltage characteristics. HEMT transistors are able to operate at higher frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter '' lambda'' (λ). The term ''wavelength'' is also sometimes applied to modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or waves formed by interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency of the wave: waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths, and lower frequencies have longer wavelengths. Wavelength depends on the medium (for example, vacuum, air, or water) that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Illinois At Urbana-Champaign
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the University of Illinois system and was founded in 1867. Enrolling over 56,000 undergraduate and graduate students, the University of Illinois is one of the largest public universities by enrollment in the country. The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". In fiscal year 2019, research expenditures at Illinois totaled $652 million. The campus library system possesses the second-largest university library in the United States by holdings after Harvard University. The university also hosts the National Center for Supercomputing Applications and is home to the fastest supercomputer on a university camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
III-V
Semiconductor materials are nominally small band gap insulators. The defining property of a semiconductor material is that it can be compromised by doping it with impurities that alter its electronic properties in a controllable way. Because of their application in the computer and photovoltaic industry—in devices such as transistors, lasers, and solar cells—the search for new semiconductor materials and the improvement of existing materials is an important field of study in materials science. Most commonly used semiconductor materials are crystalline inorganic solids. These materials are classified according to the periodic table groups of their constituent atoms. Different semiconductor materials differ in their properties. Thus, in comparison with silicon, compound semiconductors have both advantages and disadvantages. For example, gallium arsenide (GaAs) has six times higher electron mobility than silicon, which allows faster operation; wider band gap, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOVPE
Metalorganic vapour-phase epitaxy (MOVPE), also known as organometallic vapour-phase epitaxy (OMVPE) or metalorganic chemical vapour deposition (MOCVD), is a chemical vapour deposition method used to produce single- or polycrystalline thin films. It is a process for growing crystalline layers to create complex semiconductor multilayer structures. In contrast to molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE), the growth of crystals is by chemical reaction and not physical deposition. This takes place not in vacuum, but from the gas phase at moderate pressures (10 to 760 Torr). As such, this technique is preferred for the formation of devices incorporating thermodynamically metastable alloys, and it has become a major process in the manufacture of optoelectronics, such as Light-emitting diodes. It was invented in 1968 at North American Aviation (later Rockwell International) Science Center by Harold M. Manasevit. Basic principles In MOCVD ultrapure precursor gases are injected into a reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Vapor Deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films. In typical CVD, the wafer (substrate) is exposed to one or more volatile precursors, which react and/or decompose on the substrate surface to produce the desired deposit. Frequently, volatile by-products are also produced, which are removed by gas flow through the reaction chamber. Microfabrication processes widely use CVD to deposit materials in various forms, including: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous, and epitaxial. These materials include: silicon (dioxide, carbide, nitride, oxynitride), carbon (fiber, nanofibers, nanotubes, diamond and graphene), fluorocarbons, filaments, tungsten, titanium nitride and various high-κ dielectrics. The term ''chemical vapour deposition'' was coined 1960 by ''John M. Blocher, Jr.'' who intended to differentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photolithography
In integrated circuit manufacturing, photolithography or optical lithography is a general term used for techniques that use light to produce minutely patterned thin films of suitable materials over a substrate, such as a silicon wafer, to protect selected areas of it during subsequent etching, deposition, or implantation operations. Typically, ultraviolet light is used to transfer a geometric design from an optical mask to a light-sensitive chemical ( photoresist) coated on the substrate. The photoresist either breaks down or hardens where it is exposed to light. The patterned film is then created by removing the softer parts of the coating with appropriate solvents. Conventional photoresists typically consists of three components: resin, sensitizer, and solvent. Photolithography processes can be classified according to the type of light used, such as ultraviolet, deep ultraviolet, extreme ultraviolet, or X-ray. The wavelength of light used determines the minimum feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohmic Contact
An ohmic contact is a non-rectifying electrical junction: a junction between two conductors that has a linear current–voltage (I–V) curve as with Ohm's law. Low-resistance ohmic contacts are used to allow charge to flow easily in both directions between the two conductors, without blocking due to rectification or excess power dissipation due to voltage thresholds. By contrast, a junction or contact that does not demonstrate a linear I–V curve is called non-ohmic. Non-ohmic contacts come in a number of forms, such as p–n junction, Schottky barrier, rectifying heterojunction, or breakdown junction. Generally the term "ohmic contact" implicitly refers to an ohmic contact of a metal to a semiconductor, where achieving ohmic contact resistance is possible but requires careful technique. Metal–metal ohmic contacts are relatively simpler to make, by ensuring direct contact between the metals without intervening layers of insulating contamination, excessive roughness or oxida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |