|
Haptonema
The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta (named for '' Prymnesium''), are a clade of algae. The names Haptophyceae or Prymnesiophyceae are sometimes used instead. This ending implies classification at the class rank rather than as a division. Although the phylogenetics of this group has become much better understood in recent years, there remains some dispute over which rank is most appropriate. Characteristics The chloroplasts are pigmented similarly to those of the heterokonts, but the structure of the rest of the cell is different, so it may be that they are a separate line whose chloroplasts are derived from similar red algal endosymbionts. The cells typically have two slightly unequal flagella, both of which are smooth, and a unique organelle called a '' haptonema'', which is superficially similar to a flagellum but differs in the arrangement of microtubules and in its use. The name comes from the Greek ''hapsis'', touch, and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haptonema
The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta (named for '' Prymnesium''), are a clade of algae. The names Haptophyceae or Prymnesiophyceae are sometimes used instead. This ending implies classification at the class rank rather than as a division. Although the phylogenetics of this group has become much better understood in recent years, there remains some dispute over which rank is most appropriate. Characteristics The chloroplasts are pigmented similarly to those of the heterokonts, but the structure of the rest of the cell is different, so it may be that they are a separate line whose chloroplasts are derived from similar red algal endosymbionts. The cells typically have two slightly unequal flagella, both of which are smooth, and a unique organelle called a '' haptonema'', which is superficially similar to a flagellum but differs in the arrangement of microtubules and in its use. The name comes from the Greek ''hapsis'', touch, and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haptophyta Cell Scheme
The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta (named for '' Prymnesium''), are a clade of algae. The names Haptophyceae or Prymnesiophyceae are sometimes used instead. This ending implies classification at the class rank rather than as a division. Although the phylogenetics of this group has become much better understood in recent years, there remains some dispute over which rank is most appropriate. Characteristics The chloroplasts are pigmented similarly to those of the heterokonts, but the structure of the rest of the cell is different, so it may be that they are a separate line whose chloroplasts are derived from similar red algal endosymbionts. The cells typically have two slightly unequal flagella, both of which are smooth, and a unique organelle called a ''haptonema'', which is superficially similar to a flagellum but differs in the arrangement of microtubules and in its use. The name comes from the Greek ''hapsis'', touch, and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
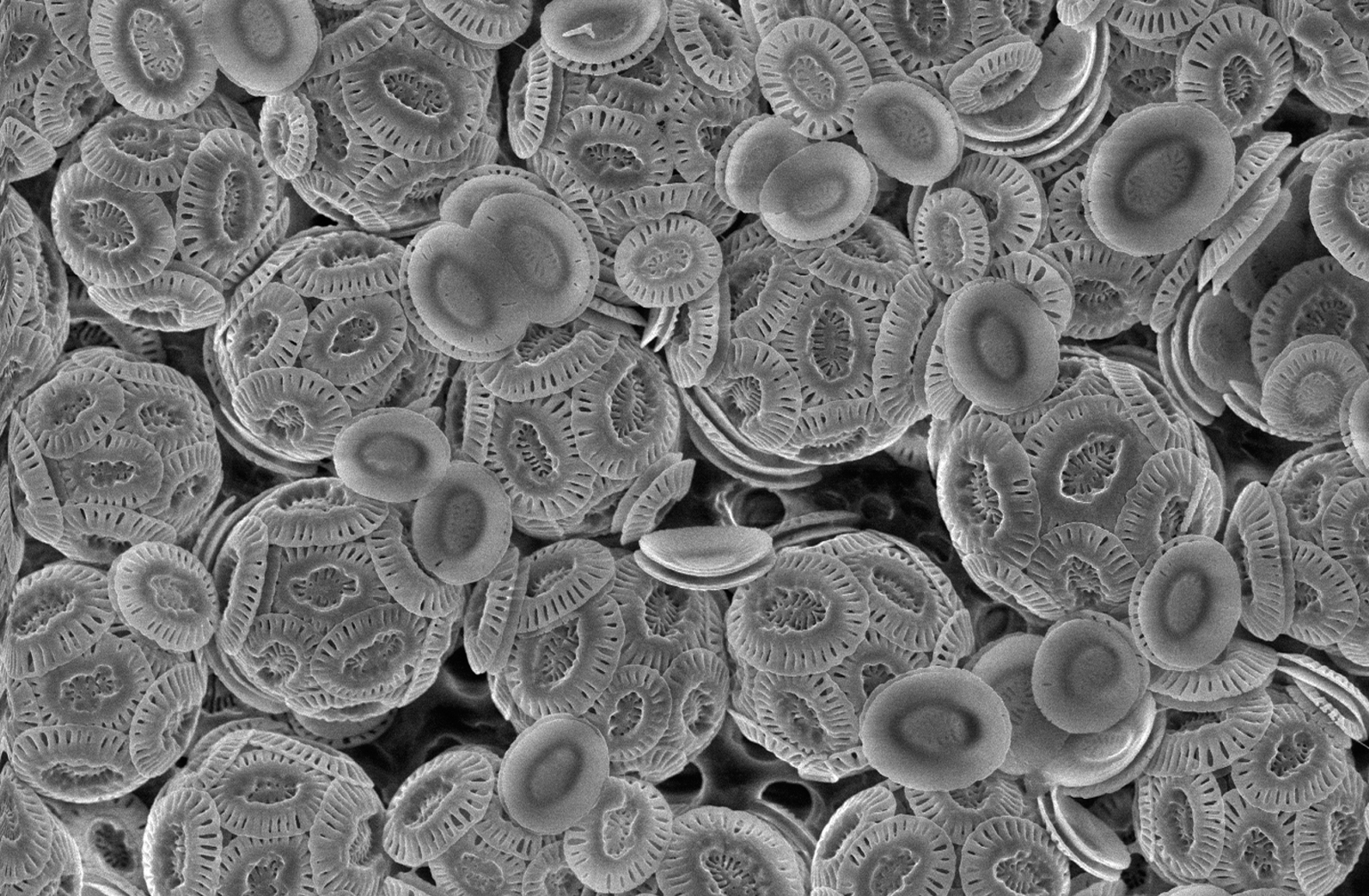
Coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker's Five kingdom classification, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae (or Coccolithophyceae). Coccolithophores are almost exclusively marine, are photosynthetic, and exist in large numbers throughout the sunlight zone of the ocean. Coccolithophores are the most productive calcifying organisms on the planet, covering themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a ''coccosphere''. However, the reasons they calcify remains elusive. One key function may be that the coccosphere offers protection against microzooplankton predation, which is one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prymnesium
''Prymnesium'' is a genus of haptophytes, including the species '' Prymnesium parvum''. The genus is a unicellular motile alga. It is ellipsoidal in shape one flagellum is straight and there are two longer ones which enable movement. The name Latinizes the Greek ' ‘cable (for mooring A mooring is any permanent structure to which a vessel may be secured. Examples include quays, wharfs, jetties, piers, anchor buoys, and mooring buoys. A ship is secured to a mooring to forestall free movement of the ship on the water. An ''an ...)’, from ' ‘stern’, from ' ‘hindmost’. Morphology References Haptophyte genera {{Haptophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium '' Helicobacter pylori'' for example uses its multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium, where it may cause a gastric ulcer to develop. In some bacteria the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its lash-like swimming motion. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Euk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority of species (6,793) are found in the Florideophyceae (class), and mostly consist of multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats but relatively rare in freshwaters. Approximately 5% of red algae species occur in freshwater environments, with greater concentrations found in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, there are no terrestrial species, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck in which the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity. The red algae form a distinct group characterized by having eukaryotic cells without flagella and centrioles, chloroplasts tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterokont
Heterokonts are a group of protists (formally referred to as Heterokonta, Heterokontae or Heterokontophyta). The group is a major line of eukaryotes. Most are algae, ranging from the giant multicellular kelp to the unicellular diatoms, which are a primary component of plankton. Other notable members of the Stramenopiles include the (generally) parasitic oomycetes, including '' Phytophthora'', which caused the Great Famine of Ireland, and '' Pythium'', which causes seed rot and damping off. The name "heterokont" refers to the type of motile life cycle stage, in which the flagellated cells possess two differently arranged flagella (see zoospore). History In 1899, Alexander Luther created the term "Heterokontae" for some algae with unequal flagella, today called Xanthophyceae. Later, some authors (e.g., Copeland, 1956) included other groups in Heterokonta, expanding the name's sense. The term continues to be applied in different ways, leading to Heterokontophyta being appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like '' Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they cir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomic Rank
In biological classification, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms (a taxon) in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain. While older approaches to taxonomic classification were phenomenological, forming groups on the basis of similarities in appearance, organic structure and behaviour, methods based on genetic analysis have opened the road to cladistics. A given rank subsumes under it less general categories, that is, more specific descriptions of life forms. Above it, each rank is classified within more general categories of organisms and groups of organisms related to each other through inheritance of traits or features from common ancestors. The rank of any ''species'' and the description of its ''genus'' is ''basic''; which means that to identify a particular organism, it is usually not necessary to specify ranks other than these first two. Consider a parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (biology)
In biological classification, class ( la, classis) is a taxonomic rank, as well as a taxonomic unit, a taxon, in that rank. It is a group of related taxonomic orders. Other well-known ranks in descending order of size are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class fitting between phylum and order. History The class as a distinct rank of biological classification having its own distinctive name (and not just called a ''top-level genus'' ''(genus summum)'') was first introduced by the French botanist Joseph Pitton de Tournefort in his classification of plants that appeared in his ''Eléments de botanique'', 1694. Insofar as a general definition of a class is available, it has historically been conceived as embracing taxa that combine a distinct ''grade'' of organization—i.e. a 'level of complexity', measured in terms of how differentiated their organ systems are into distinct regions or sub-organs—with a distinct ''type'' of construction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |