|
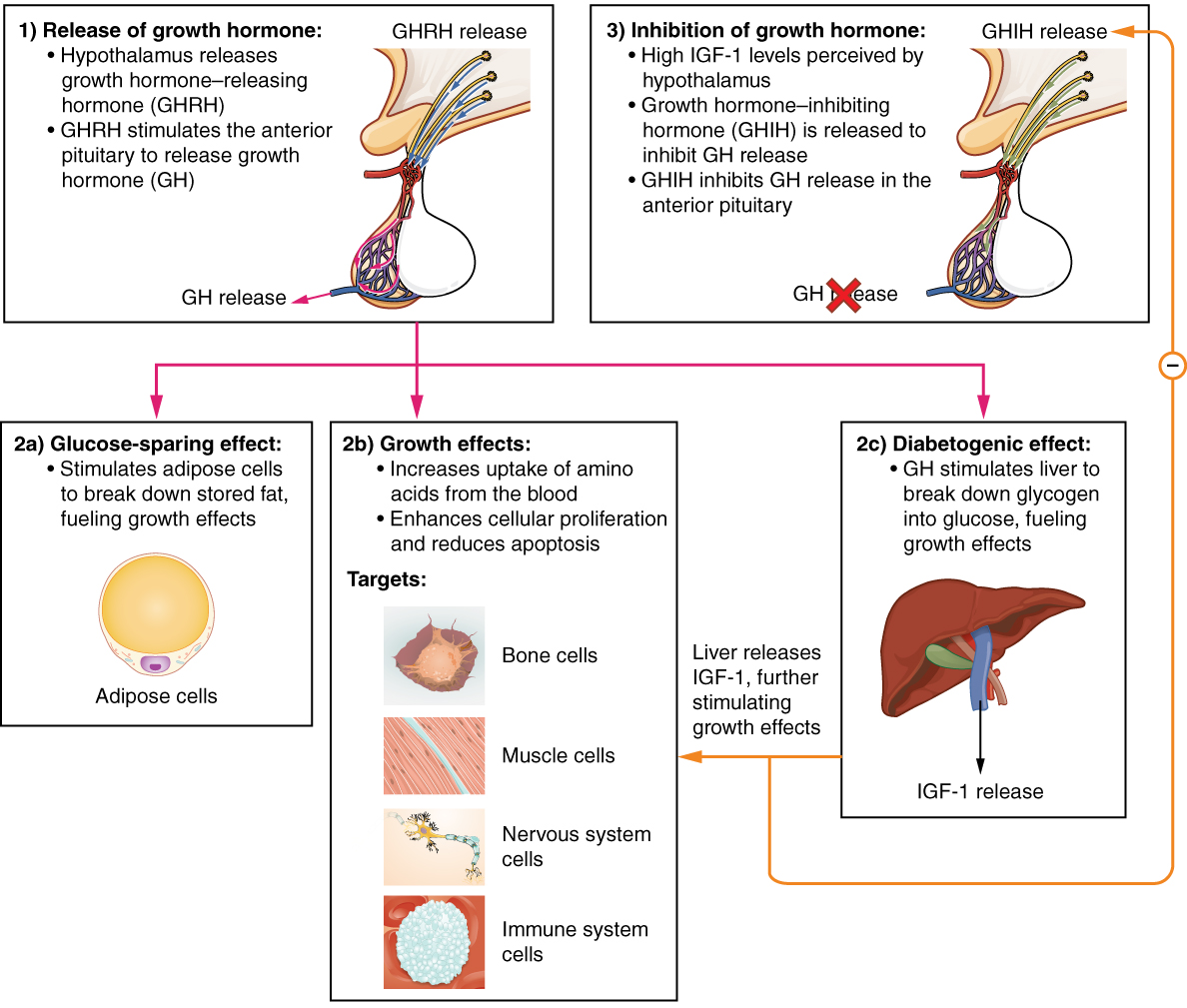
Hypothalamic–pituitary–somatotropic Axis
The hypothalamic–pituitary–somatotropic axis (HPS axis), or hypothalamic–pituitary–somatic axis, also known as the hypothalamic–pituitary–growth axis, is a hypothalamic–pituitary axis which includes the secretion of growth hormone (GH; somatotropin) from the somatotropes of the pituitary gland into the circulatory system, circulation and the subsequent stimulation of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1; somatomedin-1) biosynthesis, production by GH in tissue (biology), tissues such as, namely, the liver. Other hypothalamic–pituitary hormones such as growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH; somatocrinin), growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH; somatostatin), and ghrelin () are involved in the control of GH secretion from the pituitary gland. The HPS axis is involved in postnatal human development (biology), human growth. Individuals with growth hormone deficiency or Laron syndrome ( insensitivity) show symptoms like short stature, dwarfism and obesity, but are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrine Growth Regulation
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant Organ (biology), organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems. In humans, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid gland, thyroid, parathyroid gland, parathyroid, pituitary gland, pituitary, pineal gland, pineal, and adrenal glands, and the (male) testis and (female) ovaries. The hypothalamus, pancreas, and thymus also function as endocrine glands, among other functions. (The hypothalamus and pituitary glands are organs of the Neuroendocrinology#Neuroendocrine system, neuroendocrine system. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamusit is located in the brain adjacent to the pituitary glandis to link the endocrine system to the nervous system via the pituitary gland.) Other organs, such as the kidneys, also have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone Deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD), or hyposomatotropism, is a medical condition resulting from not enough growth hormone (GH). Generally the most noticeable symptom is that an individual attains a short height. Newborns may also present low blood sugar or a small penis size. In adults there may be decreased muscle mass, high cholesterol levels, or poor bone density. GHD can be present at birth or develop later in life. Causes may include genetics, trauma, infections, tumors, or radiation therapy. Genes that may be involved include '' GH1'', '' GHRHR'', or '' BTK''. In a third of cases no cause is apparent. The underlying mechanism generally involves problems with the pituitary gland. Some cases are associated with a lack of other pituitary hormones, in which case it is known as combined pituitary hormone deficiency. Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure growth hormone levels. Treatment is by growth hormone replacement using synthetic human growth hormone. The frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormones
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in human development. GH also stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and increases the concentration of glucose and free fatty acids. It is a type of mitogen which is specific only to the receptors on certain types of cells. GH is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland. A recombinant form of HGH called somatropin ( INN) is used as a prescription drug to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies by prescription from a licensed health care provider. In recent years in the United States, some health care ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatopause
Somatopause is the progressive decline in the levels of growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), hormones of the hypothalamic–pituitary–somatotropic axis (HPS axis), with age. Secretion of GH may only be 60% of that of a young adult by age 70 years. Somatopause results in changes in the body, such as body composition changes like a decrease in lean body mass. Estrogens and progesterone Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the ma ... may oppose somatopause by increasing GH and IGF-1 levels. References Developmental stages Endocrine system {{Biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tall Stature
Human height or stature is the distance from the bottom of the feet to the top of the head in a human body, standing erect. It is measured using a stadiometer, in centimetres when using the metric system or SI system, or feet and inches when using United States customary units or the imperial system. In the early phase of anthropometric research history, questions about height measuring techniques for measuring nutritional status often concerned genetic differences. Height is also important because it is closely correlated with other health components, such as life expectancy. Studies show that there is a correlation between small stature and a longer life expectancy. Individuals of small stature are also more likely to have lower blood pressure and are less likely to acquire cancer. The University of Hawaii has found that the "longevity gene" FOXO3 that reduces the effects of aging is more commonly found in individuals of small body size. Short stature decreases the risk of Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overgrowth Syndrome
Overgrowth syndromes in children constitute a group of rare disorders that are characterised by tissue hypertrophy. Individual overgrowth syndromes have been shown to overlap with regard to clinical and radiologic features. The details of the genetic bases of these syndromes are unfolding. Any of the three embryonic tissue layers may be involved. The syndromes may manifest in localized or generalized tissue overgrowth. Latitudinal and longitudinal growth may be affected.Ko JM (2013)"Genetic syndromes associated with overgrowth in childhood" ''Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab''. 18(3):101-5. . Lacerda L da S, Alves ÚD, Zanier JFC, Machado DC, Camilo GB, Lopes AJ (2014)"Differential diagnoses of overgrowth syndromes: The most important clinical and radiological disease manifestations" ''Radiol Res Pract''. 2014:947451. . . Nevertheless, the musculoskeletal features are central to the diagnosis of some syndromes such as Proteus syndrome.EL-Sobky TA, Elsayed SM, EL Mikkawy DME (2015)"Orth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary Tumor
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.Pituitary Tumors Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version NIH National Cancer Institute Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial , with an estimated prevalence rate in the general population of approximately 17%. Non-invasive and non-secreting pituitary adenomas are considered to be |
Gigantism
Gigantism (, ''gígas'', "wiktionary:giant, giant", plural γίγαντες, ''gígantes''), also known as giantism, is a condition characterized by excessive growth and height significantly above average height, average. In humans, this condition is caused by over-production of growth hormone in childhood. It is a rare disorder resulting from increased levels of growth hormone before the fusion of the Epiphyseal plate, growth plate which usually occurs at some point soon after puberty. This increase is most often due to abnormal tumor growths on the pituitary gland. Gigantism should not be confused with acromegaly, the adult form of the disorder, characterized by Somatic (biology), somatic enlargement specifically in the extremities and face. Cause Gigantism is characterized by an excess of growth hormone (GH). The excess of growth hormone that brings about gigantism is virtually always caused by pituitary growths (adenomas). These adenomas are on the Anterior pituitary, anteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a disorder that results in excess growth of certain parts of the human body. It is caused by excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed. The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There may also be an enlargement of the forehead, jaw, and nose. Other symptoms may include joint pain, thicker skin, deepening of the voice, headaches, and Visual impairment, problems with vision. Complications of the disease may include type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure. Signs and symptoms Features that may result from a high level of GH or expanding tumor include: * Headaches * Enlargement of the hands, feet, nose, lips, and ears, and a general thickening of the skin * Soft tissue swelling of internal organs, notably the heart with the attendant weakening of its muscularity, and the kidneys, also the vocal cords resulting in a characteristic thick, deep voice and slowing of speech * Generalized expansion of the skull at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible Signs and symptoms of cancer, signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in defecation, bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. List of cancer types, Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor Diet (nutrition), diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity or Alcohol abuse, excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. infectious causes of cancer, Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over ; the range is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is Obesity-associated morbidity, correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis. Obesity has individual, socioeconomic, and environmental causes. Some known causes are Western pattern diet, diet, low physical activity, automation, urbanization, quantitative trait locus, genetic susceptibility, medications, mental disorders, Economic policy, economic pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarfism
Dwarfism is a condition of people and animals marked by unusually small size or short stature. In humans, it is sometimes defined as an adult height of less than , regardless of sex; the average adult height among people with dwarfism is . ''Disproportionate dwarfism'' is characterized by either Rhizomelia, short limbs or a short torso. In cases of ''proportionate dwarfism'', both the limbs and torso are unusually small. Intelligence is usually normal, and most people with it have a nearly normal life expectancy. People with dwarfism can usually bear children, although there are additional Pregnancy risks, risks to the mother and child depending upon the underlying condition. The most common and recognizable form of dwarfism in humans (comprising 70% of cases) is achondroplasia, a genetic disorder whereby the limbs are diminutive. Growth hormone deficiency is responsible for most other cases. There are many other less common causes. Treatment of the condition depends on the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |