|
Hydrosalpinx
A hydrosalpinx is a condition that occurs when a fallopian tube is blocked and fills with serous or clear fluid near the ovary (distal to the uterus). The blocked tube may become substantially distended giving the tube a characteristic sausage-like or retort-like shape. The condition is often bilateral and the affected tubes may reach several centimeters in diameter. The blocked tubes cause infertility. A fallopian tube filled with blood is a hematosalpinx, and with pus a pyosalpinx. Hydrosalpinx is a Compound (linguistics), composite of the Greek words ὕδωρ (hydōr – "water"Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.) and σάλπιγξ (sálpinx – "trumpet"); its plural is ''hydrosalpinges''. Signs and symptoms Symptoms can vary. Some patients have lower often recurring abdominal pain or pelvic pain, while others may be asy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynecologic Ultrasonography
Gynecologic ultrasonography or gynecologic sonography refers to the application of medical ultrasonography to the female pelvic organs (specifically the uterus, the ovaries, and the fallopian tubes) as well as the bladder, the adnexa, and the recto-uterine pouch. The procedure may lead to other medically relevant findings in the pelvis.This technique is useful to detect myomas or mullerian malformations. Routes The examination can be performed by transabdominal ultrasonography, generally with a full bladder which acts as an acoustic window to achieve better visualization of pelvis organs, or by transvaginal ultrasonography with a specifically designed vaginal transducer. Transvaginal imaging utilizes a higher frequency imaging, which gives better resolution of the ovaries, uterus and endometrium (the fallopian tubes are generally not seen unless distended), but is limited to depth of image penetration, whereas larger lesions reaching into the abdomen are better seen tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regnier De Graaf
Regnier de Graaf (English spelling), original Dutch spelling Reinier de Graaf, or Latinized Reijnerus de Graeff (30 July 164117 August 1673), was a Dutch physician, physiologist and anatomy, anatomist who made key discoveries in reproductive biology. He specialized in iatrochemistry and iatrogenesis, and was the first to develop a syringe to inject dye into human reproductive organs so that he could understand their structure and function. Biography De Graaf was born in Schoonhoven in a Roman Catholic family, as the son of a carpenter/engineer (equivalent to a modern architect). He studied medicine in Leuven (1658), Utrecht and Leiden (1663). There his co-students were Jan Swammerdam, Niels Stensen, Ole Borch and Frederik Ruysch, cooperating with professor Franciscus Sylvius, Johannes van Horne and :de:Lucas Schacht, Lucas Schacht. All of them were interested in the organs of procreation and influenced by Rene Descartes' Iatrophysics, iatrophysical approach. He submitted his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salpingectomy
Salpingectomy refers to the surgical removal of a fallopian tube. This may be done to treat an ectopic pregnancy or cancer, to prevent cancer, or as a form of contraception. This procedure is now sometimes preferred over its ovarian tube-sparing counterparts due to the risk of ectopic pregnancies. For contraceptive purposes, this procedure is an irreversible form of sterilization and more effective than tubal ligation. Classification Salpingectomy is different from and predates both salpingostomy and salpingotomy. The latter two terms are often used interchangeably and refer to creating an opening into the tube (e.g. to remove an ectopic pregnancy), but the tube itself is not removed. Technically, the creation of a new tubal opening (, after the Latin word for 'mouth') by surgery would be a ''salpingostomy'', while the incision into the tube to remove an ectopic is a ''salpingotomy''. Indications Salpingectomy was performed by Lawson Tait in 1883 in women with a bleeding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these symptoms. The pain may be described as sharp, dull, or crampy. Pain may also spread to the shoulder if bleeding into the abdomen has occurred. Severe bleeding may result in a fast heart rate, fainting, or shock. With very rare exceptions, the fetus is unable to survive. Overall, ectopic pregnancies annually affect less than 2% of pregnancies worldwide. Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy include pelvic inflammatory disease, often due to chlamydia infection; tobacco smoking; endometriosis; prior tubal surgery; a history of infertility; and the use of assisted reproductive technology. Those who have previously had an ectopic pregnancy are at much higher risk of having another one. Most ectopic pregnancies (90%) occur in the fallopian tube, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres (4-cell stage) are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, (16-cell stage) takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
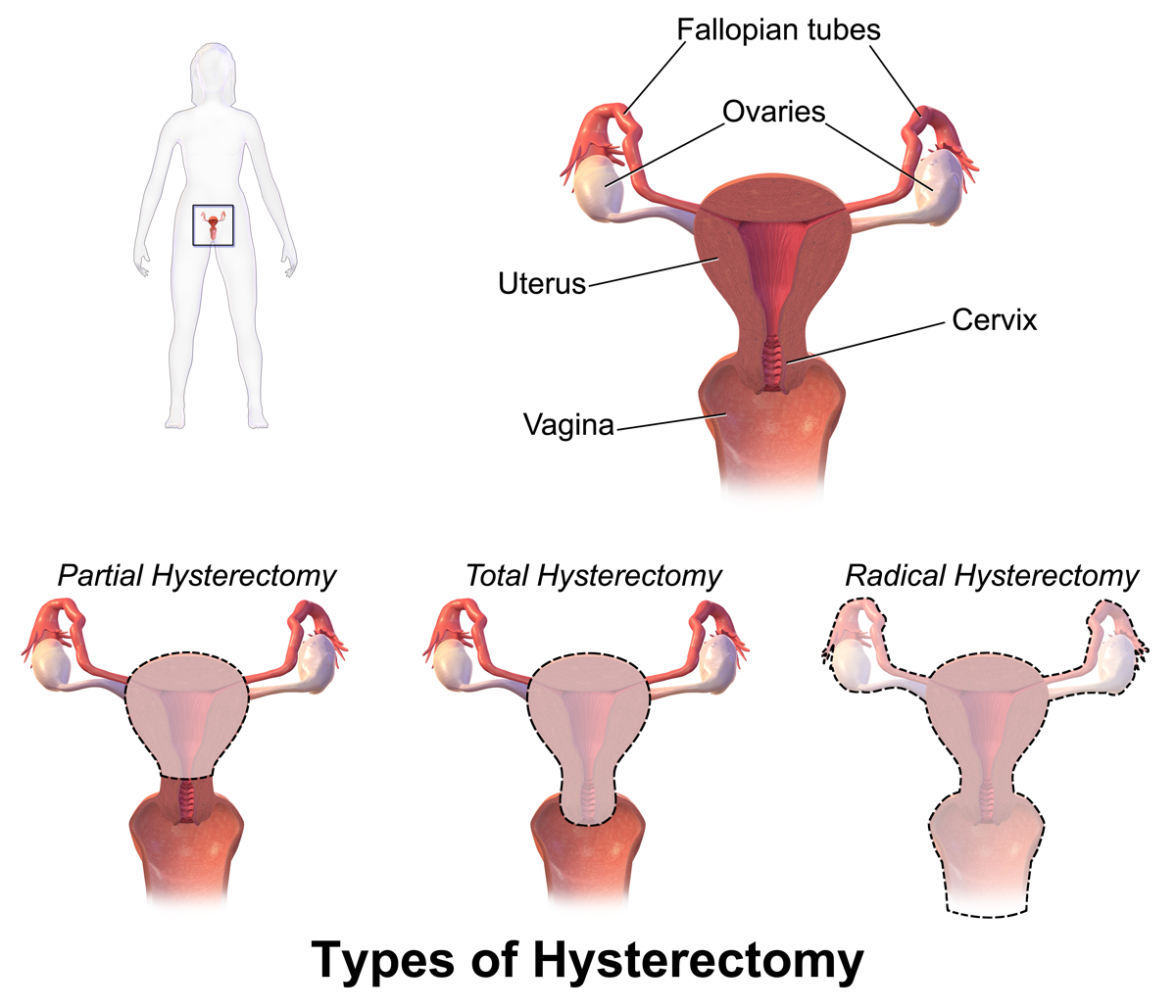
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix. Supracervical hysterectomy refers to removal of the uterus while the cervix is spared. These procedures may also involve removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy), fallopian tubes ( salpingectomy), and other surrounding structures. The term “partial” or “total” hysterectomy are lay-terms that incorrectly describe the addition or omission of oophorectomy at the time of hysterectomy. These procedures are usually performed by a gynecologist. Removal of the uterus is a form of sterilization, rendering the patient unable to bear children (as does removal of ovaries and fallopian tubes) and has surgical risks as well as long-term effects, so the surgery is normally recommended only when other treatment options are not available or have failed. It is the second most commonly performed gynecological surgical procedure, after cesarean section, in the United States. Nearly 68 percent were performed for conditions such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuboplasty
Tuboplasty refers to a number of surgical operations that attempt to restore patency and functioning of the fallopian tube(s) so that a pregnancy could be achieved. As tubal infertility is a common cause of infertility, tuboplasties were commonly performed prior to the development of effective in vitro fertilization (IVF) or repair of any type of tube-like structure, including the Eustachian tube in the head and neck. Types Different types of tuboplasty can be distinguished: * Tubal reanastomosis, involves resection of occluded tubal tissue and joining the healthy segments. * Fimbrioplasty, separating agglutinated fimbriae. * Salpingostomy, creating a new distal opening for the tube. * Salpingolysis, removing adhesions from around the tube. * Cornual implantation, resecting of an occluded transmural segment of the tube and connecting the distal patent segment of the tube to the uterus so that it links up with the endometrial cavity. Techniques Above surgical procedures are perform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexually Transmitted Infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, especially Sexual intercourse, vaginal intercourse, anal sex, oral sex, or sometimes Non-penetrative sex#Manual sex, manual sex. STIs often do not initially cause symptoms, which results in a risk of transmitting them to others. The term ''sexually transmitted infection'' is generally preferred over ''sexually transmitted disease'' or ''venereal disease'', as it includes cases with no Signs and symptoms#Symptomatic, symptomatic disease. Symptoms and signs of STIs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, genital ulcers, ulcers on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some STIs can cause infertility. Bacterial STIs include Chlamydia infection, chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Viral STIs include genital warts, genital herpes, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.MedlinePlus > Laparoscopy Update Date: 21 August 2009. Updated by: James Lee, MD // No longer valid Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive procedure, bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique. There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an exploratory laparotomy. These include reduced pain due to smaller incisions, reduced hemorrhaging, and shorter recovery time. The key element is the use of a laparoscope, a long fiber optic cable system that allows viewing of the affected area by snaking the cable from a more distant, but more easily accessible location. Laparoscopic surgery includes operations within the abdominal or pelvic cavities, whereas keyhole surgery per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |