|
Homology Model
Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "''target''" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the "''template''"). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of a sequence alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been seen that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure. Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure. It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DHRS7B Homology Model
Dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 7B is an enzyme encoded by the DHRS7B gene in humans, found on chromosome 17p11.2. DHRS7B encodes a protein that is predicted to function in steroid hormone regulation. A deletion in the chromosomal region 17p11.2 has been associated with Smith-Magenis Syndrome, a genetic developmental disorder. Gene Overview The DHRS7B gene is located on the positive strand of chromosome 17, beginning at position 21030258 and ending at position 21094836 (64579 bp). DHRS7B contains seven exons with no predicted alternate splice forms, resulting in an 1841 bp mRNA product. Upstream of DHRS7B on the negative strand of chromosome 17p11.2 are the genes ''Coiled-coil domain containing 144 family, N-terminal-like'' (CCDC144NL) and ''Ubiquitin specific peptidase 22'' (USP22). Downstream of DHSRS7B on the negative strand of chromosome 17p11.2 is the gene ''Transmembrane protein 11'' (TMEM11), and on the positive strand is the gene ''Mitogen-activated prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein NMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (usually abbreviated protein NMR) is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins, and also nucleic acids, and their complexes. The field was pioneered by Richard R. Ernst and Kurt Wüthrich at the ETH, and by Ad Bax, Marius Clore, Angela Gronenborn at the National Institutes of Health, NIH, and Gerhard Wagner (physicist), Gerhard Wagner at Harvard University, among others. Structure determination by NMR spectroscopy usually consists of several phases, each using a separate set of highly specialized techniques. The sample is prepared, measurements are made, interpretive approaches are applied, and a structure is calculated and validated. NMR involves the quantum-mechanical properties of the central core ("Atomic nucleus, nucleus") of the atom. These properties depend on the local molecular environment, and their measurement provides a map of how t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartesian Coordinates
In geometry, a Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of real numbers called ''coordinates'', which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, called '' coordinate lines'', ''coordinate axes'' or just ''axes'' (plural of ''axis'') of the system. The point where the axes meet is called the '' origin'' and has as coordinates. The axes directions represent an orthogonal basis. The combination of origin and basis forms a coordinate frame called the Cartesian frame. Similarly, the position of any point in three-dimensional space can be specified by three ''Cartesian coordinates'', which are the signed distances from the point to three mutually perpendicular planes. More generally, Cartesian coordinates specify the point in an -dimensional Euclidean space for any dimension . These coordinates are the signed distances from the point to mutually perpendicular fixed h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift, also known as random genetic drift, allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the Allele frequency, frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation. It can also cause initially rare alleles to become much more frequent and even fixed. When few copies of an allele exist, the effect of genetic drift is more notable, and when many copies exist, the effect is less notable (due to the law of large numbers). In the middle of the 20th century, vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian inheritance, Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, population geneticist Mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic
Stochastic (; ) is the property of being well-described by a random probability distribution. ''Stochasticity'' and ''randomness'' are technically distinct concepts: the former refers to a modeling approach, while the latter describes phenomena; in everyday conversation, however, these terms are often used interchangeably. In probability theory, the formal concept of a '' stochastic process'' is also referred to as a ''random process''. Stochasticity is used in many different fields, including image processing, signal processing, computer science, information theory, telecommunications, chemistry, ecology, neuroscience, physics, and cryptography. It is also used in finance (e.g., stochastic oscillator), due to seemingly random changes in the different markets within the financial sector and in medicine, linguistics, music, media, colour theory, botany, manufacturing and geomorphology. Etymology The word ''stochastic'' in English was originally used as an adjective with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein protein folding, folds into its three dimensional protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the Amine, amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone chain, backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone Dihedral angle#Dihedral angles of proteins, dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operon
In genetics, an operon is a functioning unit of DNA containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter. The genes are transcribed together into an mRNA strand and either translated together in the cytoplasm, or undergo splicing to create monocistronic mRNAs that are translated separately, i.e. several strands of mRNA that each encode a single gene product. The result of this is that the genes contained in the operon are either expressed together or not at all. Several genes must be ''co-transcribed'' to define an operon. Originally, operons were thought to exist solely in prokaryotes (which includes organelles like plastids that are derived from bacteria), but their discovery in eukaryotes was shown in the early 1990s, and are considered to be rare. In general, expression of prokaryotic operons leads to the generation of polycistronic mRNAs, while eukaryotic operons lead to monocistronic mRNAs. Operons are also found in viruses such as bacteriophages. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RaptorX
RaptorX is a software and web server for protein structure and function prediction that is free for non-commercial use. RaptorX is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction. Like other remote homology recognition and protein threading techniques, RaptorX is able to regularly generate reliable protein models when the widely used PSI-BLAST cannot. However, RaptorX is also significantly different from profile-based methods (e.g., HHPred and Phyre2) in that RaptorX excels at modeling of protein sequences without a large number of sequence homologs by exploiting structure information. RaptorX Server has been designed to ensure a user-friendly interface for users inexpert in protein structure prediction methods. Description The RaptorX project was started in 2008 and RaptorX Server was released to the public in 2011. Standard usage After pasting a protein sequence into the RaptorX submission form, a user will typically wait a couple of hours (depending on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Threading
In molecular biology, protein threading, also known as fold recognition, is a method of protein modeling which is used to model those proteins which have the same fold as proteins of known structures, but do not have homologous proteins with known structure. It differs from the homology modeling method of structure prediction as it (protein threading) is used for proteins which do not have their homologous protein structures deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), whereas homology modeling is used for those proteins which do. Threading works by using statistical knowledge of the relationship between the structures deposited in the PDB and the sequence of the protein which one wishes to model. The prediction is made by "threading" (i.e. placing, aligning) each amino acid in the target sequence to a position in the template structure, and evaluating how well the target fits the template. After the best-fit template is selected, the structural model of the sequence is built base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Position-specific Scoring Matrix
A position weight matrix (PWM), also known as a position-specific weight matrix (PSWM) or position-specific scoring matrix (PSSM), is a commonly used representation of motifs (patterns) in biological sequences. PWMs are often derived from a set of aligned sequences that are thought to be functionally related and have become an important part of many software tools for computational motif discovery. Background Creation Conversion of sequence to position probability matrix A PWM has one row for each symbol of the alphabet (4 rows for nucleotides in DNA sequences or 20 rows for amino acids in protein sequences) and one column for each position in the pattern. In the first step in constructing a PWM, a basic position frequency matrix (PFM) is created by counting the occurrences of each nucleotide at each position. From the PFM, a position probability matrix (PPM) can now be created by dividing that former nucleotide count at each position by the number of sequences, thereb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
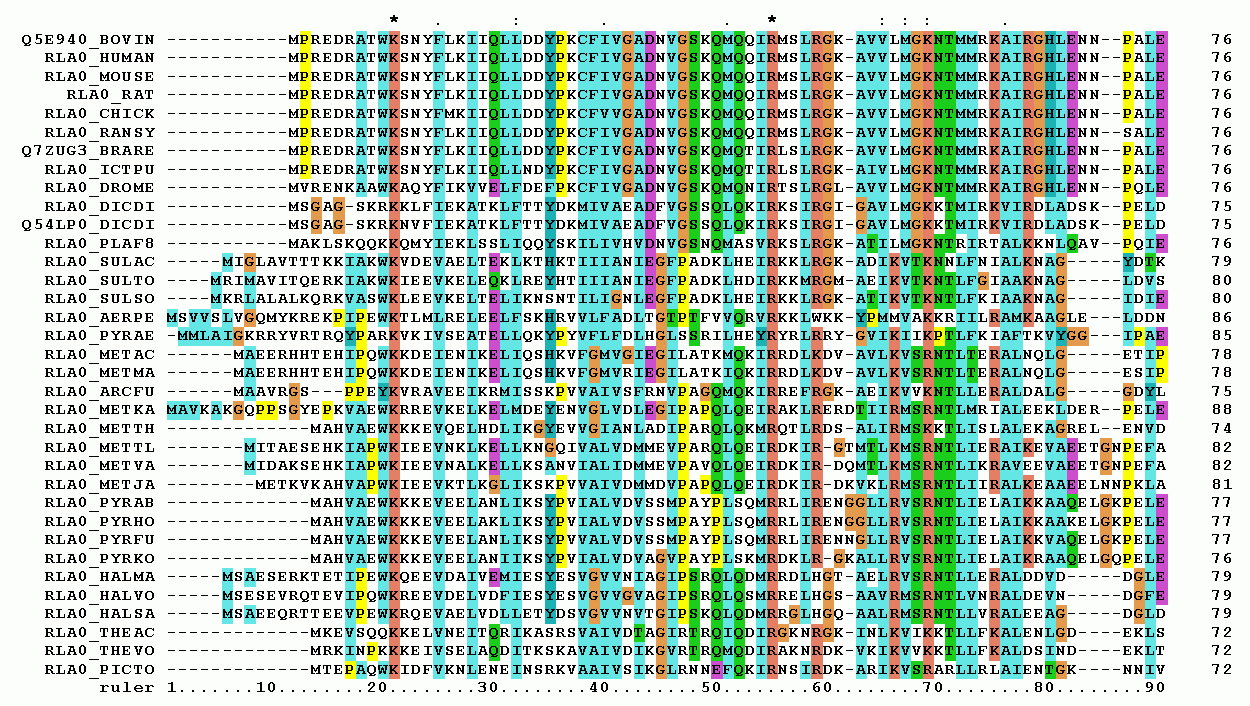
Multiple Sequence Alignment
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. These alignments are used to infer evolutionary relationships via phylogenetic analysis and can highlight homologous features between sequences. Alignments highlight mutation events such as point mutations (single amino acid or nucleotide changes), insertion mutations and deletion mutations, and alignments are used to assess sequence conservation and infer the presence and activity of protein domains, tertiary structures, secondary structures, and individual amino acids or nucleotides. Multiple sequence alignments require more sophisticated methodologies than pairwise alignments, as they are more computationally complex. Most multiple sequence alignment programs use heuristic methods rather than global optimization because identifying the optimal alignment between more than a few sequences of moderate length is prohibiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BLAST (biotechnology)
In bioinformatics, BLAST (basic local alignment search tool) is an algorithm and program for comparing Primary structure, primary biological sequence information, such as the amino acid, amino-acid sequences of proteins or the nucleotides of DNA sequence, DNA and/or RNA sequences. A BLAST search enables a researcher to compare a subject protein or nucleotide sequence (called a query) with a library or database of sequences, and identify database sequences that resemble the query sequence above a certain threshold. For example, following the discovery of a previously unknown gene in the Mus musculus, mouse, a scientist will typically perform a BLAST search of the human genome to see if humans carry a similar gene; BLAST will identify sequences in the human genome that resemble the mouse gene based on similarity of sequence. Background BLAST is one of the most widely used bioinformatics programs for sequence searching. It addresses a fundamental problem in bioinformatics research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |