|
Helix (ear)
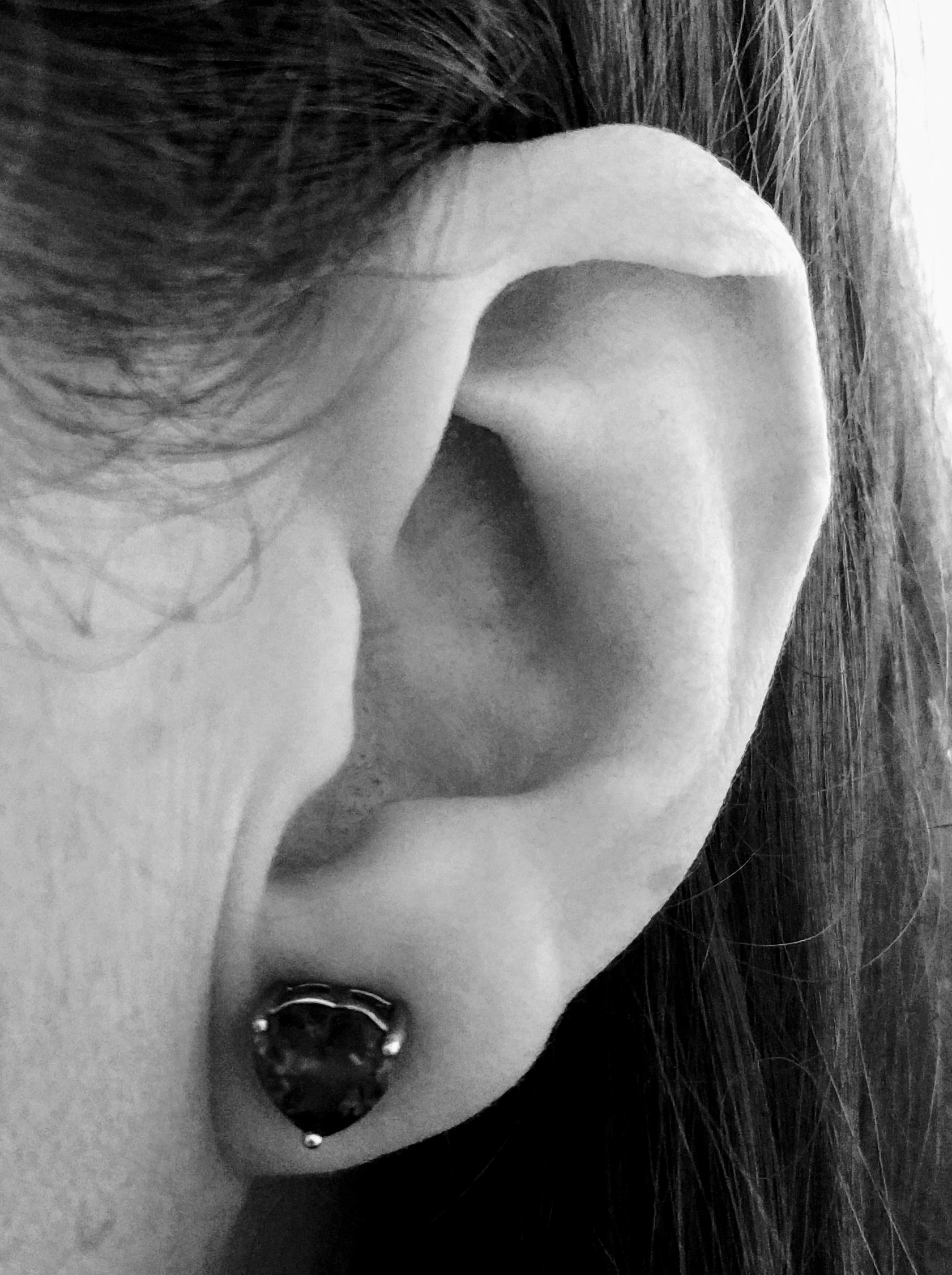
The helix is the prominent rim of the auricle. Where the helix turns downwards posteriorly, a small tubercle is sometimes seen, namely the '' auricular tubercle of Darwin''. Additional images File:Gray906.png, The muscles of the auricula. File:Darwin-s-tubercle.jpg, Left: Darwin's tubercle. Right: the homologous point in a macaque. File:Slide2COR.JPG, External ear. Right auricle. Lateral view. File:Slide3COR.JPG, External ear. Right auricle. Lateral view. File:Slide4COR.JPG, External ear. Right auricle. Lateral view. References Ear {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auricle (anatomy)
The auricle or auricula is the visible part of the ear that is outside the head. It is also called the pinna (Latin for 'wing' or ' fin', : pinnae), a term that is used more in zoology. Structure The diagram shows the shape and location of most of these components: * ''antihelix'' forms a 'Y' shape where the upper parts are: ** ''Superior crus'' (to the left of the ''fossa triangularis'' in the diagram) ** ''Inferior crus'' (to the right of the ''fossa triangularis'' in the diagram) * ''Antitragus'' is below the ''tragus'' * ''Aperture'' is the entrance to the ear canal * ''Auricular sulcus'' is the depression behind the ear next to the head * ''Concha'' is the hollow next to the ear canal * Conchal angle is the angle that the back of the ''concha'' makes with the side of the head * ''Crus'' of the helix is just above the ''tragus'' * ''Cymba conchae'' is the narrowest end of the ''concha'' * External auditory meatus is the ear canal * ''Fossa triangularis'' is the depression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes, axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubercle
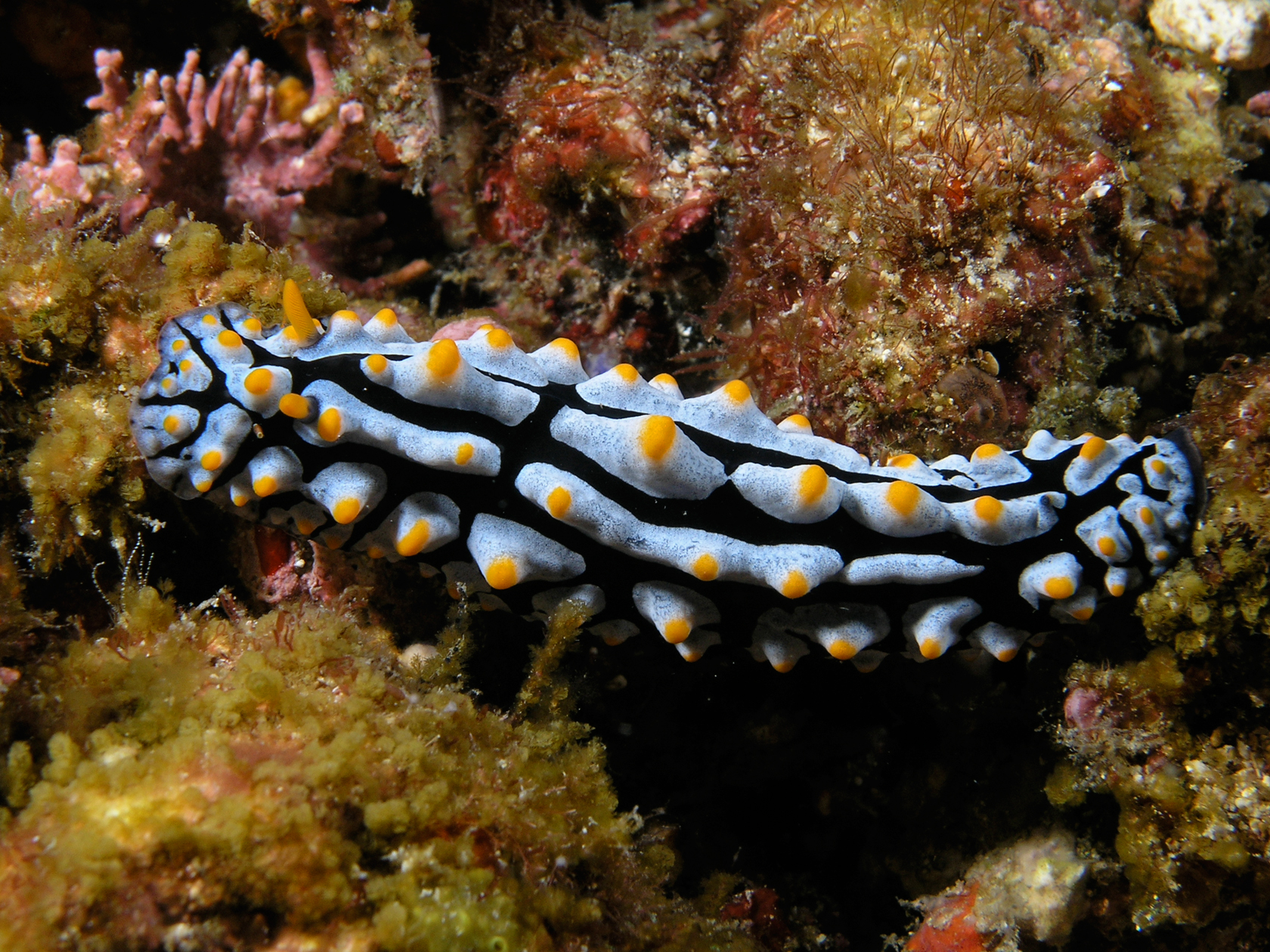
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal. In plants A tubercle is generally a wart-like projection, but it has slightly different meaning depending on which family of plants or animals it is used to refer to. In the case of certain orchids and cacti, it denotes a round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on the lip. They are also known as podaria (singular ''podarium''). When referring to some members of the pea family, it is used to refer to the wart-like excrescences that are found on the roots. In fungi In mycology, a tubercle is used to refer to a mass of hyphae from which a mushroom is made. In animals When it is used in relation to certain dorid nudibranchs such as '' Peltodoris nobilis'', it means the nodules on the dorsum of the animal. The tubercles in nudibranchs can present themselves in different way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darwin's Tubercle
Darwin's tubercle (or auricular tubercle) is a congenital ear condition which often presents as a thickening on the helix at the junction of the upper and middle thirds. History This atavistic feature is so called because its description was first published by Charles Darwin in the opening pages of ''The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex'', as evidence of a vestigial feature indicating common ancestry among primates which have pointy ears. However, Darwin himself named it the Woolnerian tip, after Thomas Woolner, a British sculptor who had depicted it in one of his sculptures and had first theorised that it was an atavistic feature. Prevalence The feature is present in approximately 10.4% of the Spanish adult population, 40% of adults in India, and 58% of Swedish school children. This acuminate nodule represents the point of the mammalian ear. The trait can potentially be bilateral, meaning present on both ears, or unilateral, where it is present on only on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity in anatomical structures or genes between organisms of different taxa due to shared ancestry, ''regardless'' of current functional differences. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures as retained heredity from a common descent, common ancestor after having been subjected to adaptation (biology), adaptive modifications for different purposes as the result of natural selection. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this from Aristotle's biology onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the bat wing development, wings of bats and origin of avian flight, birds, the arms of primates, the front flipper (anatomy), flippers of whales, and the forelegs of quadrupedalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macaque
The macaques () constitute a genus (''Macaca'') of gregarious Old World monkeys of the subfamily Cercopithecinae. The 23 species of macaques inhabit ranges throughout Asia, North Africa, and Europe (in Gibraltar). Macaques are principally frugivorous (preferring fruit), although their diet also includes seeds, leaves, flowers, and tree bark. Some species such as the long-tailed macaque (''M. fascicularis''; also called the crab-eating macaque) will supplement their diets with small amounts of meat from shellfish, insects, and small mammals. On average, a southern pig-tailed macaque (''M. nemestrina'') in Malaysia eats about 70 large rats each year. All macaque social groups are arranged around dominant matriarchs. Macaques are found in a variety of habitats throughout the Asian continent and are highly adaptable. Certain species are synanthropic, having learned to live alongside humans, but they have become problematic in urban areas in Southeast Asia and are not suitabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |