|
Hapticity
In coordination chemistry, hapticity is the coordination complex, coordination of a ligand to a metal center via an uninterrupted and contiguous series of atoms. The hapticity of a ligand is described with the Greek letter eta (letter), η ('eta'). For example, η2 describes a ligand that coordinates through 2 contiguous atoms. In general the η-notation only applies when multiple atoms are coordinated (otherwise the denticity, κ-notation is used). In addition, if the ligand coordinates through multiple atoms that are contiguous then this is considered denticity (not hapticity), and the κ-notation is used once again. When naming complexes care should be taken not to confuse η with mu (letter), μ ('mu'), which relates to bridging ligands. History The need for additional nomenclature for organometallic compounds became apparent in the mid-1950s when Dunitz, Leslie Orgel, Orgel, and Rich described the structure of the "sandwich compound, sandwich complex" ferrocene by X-ray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis acids and bases, Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent bond, covalent to ionic bond, ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acids and bases, Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity (chemistry), reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
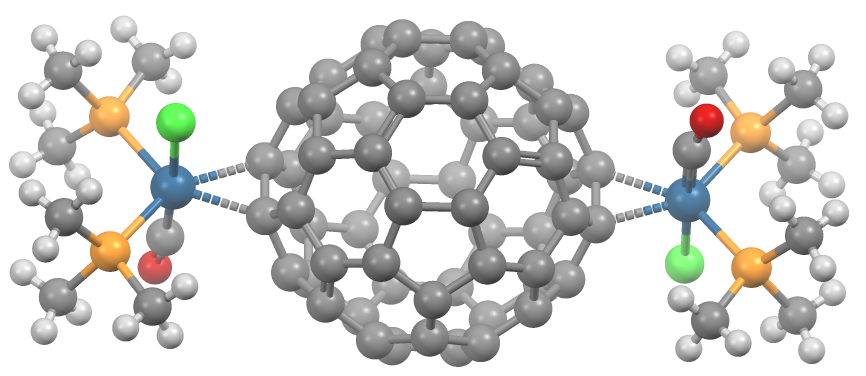
Fullerene Ligand
A transition metal fullerene complex is a coordination complex wherein fullerene serves as a ligand. Fullerenes are typically spheroidal carbon compounds, the most prevalent being buckminsterfullerene, C60. One year after it was prepared in milligram quantities in 1990, C60 was shown to function as a ligand in the complex h3Psub>2Pt(η2-C60). Since this report, a variety of transition metals and binding modes were demonstrated. Most transition metal fullerene complex are derived from C60, although other fullerenes also coordinate to metals as seen with C70Rh(H)(CO)(PPh3)2. Binding modes As ligands, fullerenes behave similarly to electron-deficient alkenes such as tetracyanoethylene. Thus, their complexes are a subset of metal-alkene complexes. They almost always coordinate in a dihapto fashion and prefer electron-rich metal centers.Spessard, p. 162 This binding occurs on the junction of two 6-membered rings. Hexahapto and pentahapto bonding is rarely observed.Spessard, p. 165 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrocene
Ferrocene is an organometallic chemistry, organometallic compound with the formula . The molecule is a Cyclopentadienyl complex, complex consisting of two Cyclopentadienyl anion, cyclopentadienyl rings sandwiching a central iron atom. It is an orange solid with a camphor-like odor that Sublimation (phase transition), sublimes above room temperature, and is soluble in most organic solvents. It is remarkable for its stability: it is unaffected by air, water, strong bases, and can be heated to 400 °C without decomposition. In oxidizing conditions it can reversibly react with strong acids to form the ferrocenium cation . Ferrocene and the ferrocenium cation are sometimes abbreviated as Fc and respectively. The first reported synthesis of ferrocene was in 1951. Its unusual stability puzzled chemists, and required the development of new theory to explain its formation and bonding. The discovery of ferrocene and its many Structural analog, analogues, known as metallocenes, sparke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranocene
Uranocene, U(C8H8)2, is an organouranium compound composed of a uranium atom sandwiched between two cyclooctatetraene, cyclooctatetraenide rings. It was one of the first Organoactinide chemistry, organoactinide compounds to be synthesized. It is a green air-sensitive solid that dissolves in organic solvents. Uranocene, a member of the "actinocenes," a group of metallocenes incorporating Chemical element, elements from the actinide series. It is the most studied bisCyclooctatetraene, [8]annulene-metal system, although it has no known practical applications. Synthesis, structure and bonding Uranocene was first described in 1968 by the group of Andrew Streitwieser, when it was prepared by the reaction of dipotassium cyclooctatetraenide and uranium tetrachloride in THF at 0°C: : Uranocene is highly reactive toward oxygen, being pyrophoricity, pyrophoric in air but stable to hydrolysis. The x-ray crystal structure of uranocene was first elucidated by the group of Ken Raymond. Conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarium
Samarium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sm and atomic number 62. It is a moderately hard silvery metal that slowly oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually has the oxidation state +3. Compounds of samarium(II) are also known, most notably the monoxide SmO, monochalcogenides SmS, SmSe and SmTe, as well as samarium(II) iodide. Discovered in 1879 by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran, samarium was named after the mineral samarskite from which it was isolated. The mineral itself was named after a Russian mine official, Colonel Vassili Samarsky-Bykhovets, who thus became the first person to have a chemical element named after him, though the name was indirect. Samarium occurs in concentration up to 2.8% in several minerals including cerite, gadolinite, samarskite, monazite and bastnäsite, the last two being the most common commercial sources of the element. These minerals are mostly found in China, the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylene
Acetylene (Chemical nomenclature, systematic name: ethyne) is a chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution. Pure acetylene is odorless, but commercial grades usually have a marked odor due to impurities such as divinyl sulfide and phosphine.Compressed Gas Association (1995Material Safety and Data Sheet – Acetylene As an alkyne, acetylene is Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated because its two carbon atoms are Chemical bond, bonded together in a triple bond. The carbon–carbon triple bond places all four atoms in the same straight line, with CCH bond angles of 180°. The triple bond in acetylene results in a high energy content that is released when acetylene is burned. Discovery Acetylene was discovered in 1836 by Edmund Davy, who identified it as a "new carburet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Of Crystallization
In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a chemical substance, substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the Crystal structure, crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt (chemistry), salt, which is not directly chemical bond, bonded to the metal cation. Upon crystallization from water, or water-containing solvents, many chemical compound, compounds incorporate water molecules in their crystalline frameworks. Water of crystallization can generally be removed by heating a sample but the crystalline properties are often lost. Compared to Inorganic compound, inorganic salts, proteins crystallize with large amounts of water i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeise's Salt
Zeise's salt, potassium trichloro(ethylene)platinate(II) hydrate, is the chemical compound with the formula K platinum.html" ;"title="/nowiki>platinum">PtCl3(C2H4)�H2O. The anion of this air-stable, yellow, coordination complex contains an hapticity">''η''2-ethylene ligand">ethylene.html" ;"title="hapticity">''η''2-ethylene">hapticity">''η''2-ethylene ligand. The anion features a platinum atom with a square planar geometry. The salt is of historical importance in the area of organometallic chemistry as one of the first examples of a transition metal alkene complex and is named for its discoverer, William Christopher Zeise. Preparation This compound is commercially available as a hydrate. The hydrate is commonly prepared from K2SnCl2. The water of hydration can be removed ''in vacuo''. Structure The alkene C=C bond is approximately perpendicular to the PtCl3 plane. In Zeise's salt and related compounds, the alkene rotates about the metal-alkene bond with a modest activatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon–carbon bond, carbon–carbon double bonds). Ethylene is widely used in the chemical industry, and its worldwide production (over 150 million tonnes in 2016) exceeds that of any other organic compound. Much of this production goes toward creating polyethylene, which is a widely used plastic containing polymer chains of ethylene units in various chain lengths. Production greenhouse gas emissions, emits greenhouse gases, including methane from feedstock production and carbon dioxide from any non-sustainable energy used. Ethylene is also an important natural plant hormone and is used in agriculture to induce ripening of fruits. The hydrate of ethylene is ethanol. Structure and properties This hydrocarbon has four hydrogen atoms bound to a pair of carbon atoms that are con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second-largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accounts Of Chemical Research
Account (abbreviated a/c) may refer to: * Account (bookkeeping) * A report * A bank account ** Deposit account ** Personal account ** Sweep account ** Transaction account * User account, the means by which a user can access a computer system * Customer In sales, commerce, and economics, a customer (sometimes known as a Client (business), client, buyer, or purchaser) is the recipient of a Good (economics), good, service (economics), service, product (business), product, or an Intellectual prop ... of a company, used in B2B business ** account manager ** account executive {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |