|
Genome Project
Genome projects are scientific endeavours that ultimately aim to determine the complete genome sequence of an organism (be it an animal, a plant, a fungus, a bacterium, an archaean, a protist or a virus) and to annotate protein-coding genes and other important genome-encoded features. The genome sequence of an organism includes the collective DNA sequences of each chromosome in the organism. For a bacterium containing a single chromosome, a genome project will aim to map the sequence of that chromosome. For the human species, whose genome includes 22 pairs of autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes, a complete genome sequence will involve 46 separate chromosome sequences. The Human Genome Project is a well known example of a genome project. Genome assembly Genome assembly refers to the process of taking a large number of short DNA sequences and reassembling them to create a representation of the original chromosomes from which the DNA originated. In a shotgun sequencing proje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Trait inheritance and molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the cell, the organism (e.g. dominance), and within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project (HGP) was an international scientific research project with the goal of determining the base pairs that make up human DNA, and of identifying, mapping and sequencing all of the genes of the human genome from both a physical and a functional standpoint. It started in 1990 and was completed in 2003. It remains the world's largest collaborative biological project. Planning started after the idea was picked up in 1984 by the US government, the project formally launched in 1990, and was declared essentially complete on April 14, 2003, but included only about 85% of the genome. Level "complete genome" was achieved in May 2021, with a remaining only 0.3% bases covered by potential issues. The final gapless assembly was finished in January 2022. Funding came from the United States government through the National Institutes of Health (NIH) as well as numerous other groups from around the world. A parallel project was conducted outside the government by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequence
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with modern D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Annotation
DNA annotation or genome annotation is the process of identifying the locations of genes and all of the coding regions in a genome and determining what those genes do. An annotation (irrespective of the context) is a note added by way of explanation or commentary. Once a genome is sequenced, it needs to be annotated to make sense of it. Genes in a eukaryotic genome can be annotated using various annotation tools such as FINDER. A modern annotation pipeline can support a user-friendly web interface and software containerization such as MOSGA. For DNA annotation, a previously unknown sequence representation of genetic material is enriched with information relating genomic position to intron-exon boundaries, regulatory sequences, repeats, gene names and protein products. This annotation is stored in genomic databases such as Mouse Genome Informatics, FlyBase, and WormBase. Educational materials on some aspects of biological annotation from the 2006 Gene Ontology annotation camp a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for '' in silico'' analyses of biological queries using computational and statistical techniques. Bioinformatics includes biological studies that use computer programming as part of their methodology, as well as specific analysis "pipelines" that are repeatedly used, particularly in the field of genomics. Common uses of bioinformatics include the identification of candidates genes and single nucleotide polymorphisms ( SNPs). Often, such identification is made with the aim to better understand the genetic basis of disease, unique adaptations, desirable properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physical structure of biological macromolecules is known as molecular biology. Molecular biology was first described as an approach focused on the underpinnings of biological phenomena - uncovering the structures of biological molecules as well as their interactions, and how these interactions explain observations of classical biology. In 1945 the term molecular biology was used by physicist William Astbury. In 1953 Francis Crick, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and colleagues, working at Medical Research Council unit, Cavendish laboratory, Cambridge (now the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology), made a double helix model of DNA which changed the entire research scenario. They proposed the DNA structure based on previous research done by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, at a specific base position in the human genome, the G nucleotide may appear in most individuals, but in a minority of individuals, the position is occupied by an A. This means that there is a SNP at this specific position, and the two possible nucleotide variations – G or A – are said to be the alleles for this specific position. SNPs pinpoint differences in our susceptibility to a wide range of diseases, for example age-related macular degeneration (a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of the disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (a SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is associated wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing Genomics Institute
BGI Group, formerly Beijing Genomics Institute, is a Chinese genomics company with headquarters in Yantian District, Shenzhen. The company was originally formed in 1999 as a genetics research center to participate in the Human Genome Project. It also sequences the genomes of other animals, plants and microorganisms. BGI has transformed from a small research institute, notable for decoding the DNA of pandas and rice plants, into a diversified company active in animal cloning, health testing, and contract research. BGI's earlier research was continued by the Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. BGI Research, the group's nonprofit division, works with the Institute of Genomics and operates the China National GeneBank under a contract with the Chinese government. BGI Genomics, a subsidiary, was listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange in 2017. In 2021, details came to light about multiple controversies involving the BGI Group. These controversies include alleged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Assembly
In bioinformatics, sequence assembly refers to aligning and merging fragments from a longer DNA sequence in order to reconstruct the original sequence. This is needed as DNA sequencing technology might not be able to 'read' whole genomes in one go, but rather reads small pieces of between 20 and 30,000 bases, depending on the technology used. Typically, the short fragments (reads) result from shotgun sequencing genomic DNA, or gene transcript ( ESTs). The problem of sequence assembly can be compared to taking many copies of a book, passing each of them through a shredder with a different cutter, and piecing the text of the book back together just by looking at the shredded pieces. Besides the obvious difficulty of this task, there are some extra practical issues: the original may have many repeated paragraphs, and some shreds may be modified during shredding to have typos. Excerpts from another book may also be added in, and some shreds may be completely unrecognizable. Genome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Mapping
Gene mapping describes the methods used to identify the locus of a gene and the distances between genes. Gene mapping can also describe the distances between different sites within a gene. The essence of all genome mapping is to place a collection of molecular markers onto their respective positions on the genome. Molecular markers come in all forms. Genes can be viewed as one special type of genetic markers in the construction of genome maps, and mapped the same way as any other markers. In some areas of study, gene mapping contributes to the creation of new recombinants within an organism. Genetic vs physical There are two distinctive types of "maps" used in the field of genome mapping: genetic maps and physical maps. While both maps are a collection of genetic markers and gene loci, genetic maps' distances are based on the genetic linkage information, while physical maps use actual physical distances usually measured in number of base pairs. While the physical map ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
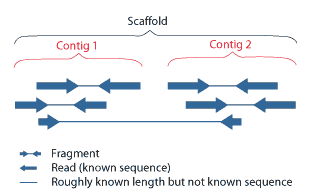
Contig
A contig (from ''contiguous'') is a set of overlapping DNA segments that together represent a consensus region of DNA.Gregory, S. ''Contig Assembly''. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, 2005. In bottom-up sequencing projects, a contig refers to overlapping sequence data ( reads); in top-down sequencing projects, contig refers to the overlapping clones that form a physical map of the genome that is used to guide sequencing and assembly.Dear, P. H. ''Genome Mapping''. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, 2005. . Contigs can thus refer both to overlapping DNA sequences and to overlapping physical segments (fragments) contained in clones depending on the context. Original definition of contig In 1980, Staden wrote: ''In order to make it easier to talk about our data gained by the shotgun method of sequencing we have invented the word "contig". A contig is a set of gel readings that are related to one another by overlap of their sequences. All gel readings belong to one and only one con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repeated Sequence (DNA)
Repeated sequences (also known as repetitive elements, repeating units or repeats) are short or long patterns of nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) that occur in multiple copies throughout the genome. In many organisms, a significant fraction of the genomic DNA is repetitive, with over two-thirds of the sequence consisting of repetitive elements in humans. Some of these repeated sequences are necessary for maintaining important genome structures such as telomeres or centromeres. Repeated sequences are categorized into different classes depending on features such as structure, length, location, origin, and mode of multiplication. The disposition of repetitive elements throughout the genome can consist either in directly-adjacent arrays called tandem repeats or in repeats dispersed throughout the genome called interspersed repeats. Tandem repeats and interspersed repeats are further categorized into subclasses based on the length of the repeated sequence and/or the mode of multiplication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |