|
Galaxolide
Galaxolide (trade name; also known as Abbalide, Pearlide, Astrolide, Musk 50, Polarlide; chemical name 1,3,4,6,7,8-hexahydro-4,6,6,7,8,8,-hexamethyl-cyclopenta 'g''enzopyran or HHCB, hexamethylindanopyran) is a synthetic musk with a clean sweet musky floral woody odor used in fragrances. It is one of the musk components that perfume and cologne manufacturers use to add a musk odor to their products. Galaxolide was first synthesized in 1965, and used in the late 1960s in some fabric softeners and detergents. High concentrations were also incorporated in fine fragrances. Chemistry Galaxolide is the trade name from International Flavors & Fragrances Inc. (IFF) for the fragrance material with CAS Registry Number 1222-05-5 and CAS chemical name cyclopenta(g)-2-benzopyran, 1,3,4,6,7,8-hexahydro-4,6,6,7,8,8-hexamethyl-. Galaxolide is also known by its IUPAC name 4,6,6,7,8,8-hexamethyl-1,3,4,6,7,8-hexahydro-cyclopenta 'g''isochromene and the more commonly used acronym of the chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Musk
Synthetic musks are a class of synthetic aroma compounds to emulate the scent of deer musk and other animal musks (castoreum and civet). Synthetic musks have a clean, smooth and sweet scent lacking the fecal notes of animal musks. They are used as flavorings and fixatives in cosmetics, detergents, perfumes and foods, supplying the base note of many perfume formulas. Most musk fragrance used in perfumery today is synthetic. Synthetic musks in a narrower sense are chemicals modeled after the main odorants in animal musk: muscone in deer musk, and civetone in civet. Muscone and civetone are macrocyclic ketones. Other structurally different but functionally similar compounds also came to be known as musks. Nitro musks An artificial musk was obtained by Albert Baur in 1888 by condensing toluene with isobutyl bromide in the presence of aluminium chloride, and nitrating the product. It was discovered accidentally as a result of Baur's attempts at producing a more effective form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
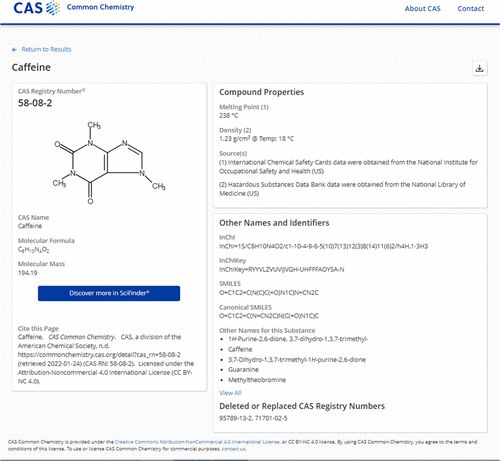
CAS Registry Number
A CAS Registry Number (also referred to as CAS RN or informally CAS Number) is a unique identification number assigned by the Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS), US to every chemical substance described in the open scientific literature. It includes all substances described from 1957 through the present, plus some substances from as far back as the early 1800s. It is a chemical database that includes organic and inorganic compounds, minerals, isotopes, alloys, mixtures, and nonstructurable materials (UVCBs, substances of unknown or variable composition, complex reaction products, or biological origin). CAS RNs are generally serial numbers (with a check digit), so they do not contain any information about the structures themselves the way SMILES and InChI strings do. The registry maintained by CAS is an authoritative collection of disclosed chemical substance information. It identifies more than 182 million unique organic and inorganic substances and 68 million protein and DNA seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Nomenclature Of Cosmetic Ingredients
The International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients, abbreviated INCI, are the unique identifiers for cosmetic ingredients such as waxes, oils, pigments, and other chemicals that are assigned in accordance with rules established by the Personal Care Products Council (PCPC), previously the Cosmetic, Toiletry, and Fragrance Association (CTFA). INCI names often differ greatly from systematic chemical nomenclature or from more common trivial names and is a mixture of conventional scientific names, Latin and English words. INCI nomenclature conventions "are continually reviewed and modified when necessary to reflect changes in the industry, technology, and new ingredient developments". INCI and CAS The relationship between a CAS Registry Number and an INCI name is not always one-to-one. In some cases, more than one INCI name may have the same CAS number, or more than one CAS number may apply to an INCI name. For example, the CAS number 1245638-61-2 has the CA Index Name of 2-Propeno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers. Isomers do not necessarily share similar chemical or physical properties. Two main forms of isomerism are structural or constitutional isomerism, in which ''bonds'' between the atoms differ; and stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism, in which the bonds are the same but the ''relative positions'' of the atoms differ. Isomeric relationships form a hierarchy. Two chemicals might be the same constitutional isomer, but upon deeper analysis be stereoisomers of each other. Two molecules that are the same stereoisomer as each other might be in different conformational forms or be different isotopologues. The depth of analysis depends on the field of study or the chemical and physical properties of interest. The English word "isomer" () is a back-for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiral Center
In stereochemistry, a stereocenter of a molecule is an atom (center), axis or plane that is the focus of stereoisomerism; that is, when having at least three different groups bound to the stereocenter, interchanging any two different groups creates a new stereoisomer. Stereocenters are also referred to as stereogenic centers. A stereocenter is geometrically defined as a point (location) in a molecule; a stereocenter is usually but not always a specific atom, often carbon. Stereocenters can exist on chiral or achiral molecules; stereocenters can contain single bonds or double bonds. The number of hypothetical stereoisomers can be predicted by using 2''n'', with ''n'' being the number of tetrahedral stereocenters; however, exceptions such as meso compounds can reduce the prediction to below the expected 2''n''. Chirality centers are a type of stereocenter with four different substituent groups; chirality centers are a specific subset of stereocenters because they can only hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Musk
Synthetic musks are a class of synthetic aroma compounds to emulate the scent of deer musk and other animal musks (castoreum and civet). Synthetic musks have a clean, smooth and sweet scent lacking the fecal notes of animal musks. They are used as flavorings and fixatives in cosmetics, detergents, perfumes and foods, supplying the base note of many perfume formulas. Most musk fragrance used in perfumery today is synthetic. Synthetic musks in a narrower sense are chemicals modeled after the main odorants in animal musk: muscone in deer musk, and civetone in civet. Muscone and civetone are macrocyclic ketones. Other structurally different but functionally similar compounds also came to be known as musks. Nitro musks An artificial musk was obtained by Albert Baur in 1888 by condensing toluene with isobutyl bromide in the presence of aluminium chloride, and nitrating the product. It was discovered accidentally as a result of Baur's attempts at producing a more effective form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octanol-water Partition Coefficient
The ''n''-octanol-water partition coefficient, ''K''ow is a partition coefficient for the two-phase system consisting of ''n''-octanol and water. ''K''ow is also frequently referred to by the symbol P, especially in the English literature. It is also called ''n''-octanol-water partition ratio. ''K''ow serves as a measure of the relationship between lipophilicity (fat solubility) and hydrophilicity (water solubility) of a substance. The value is greater than one if a substance is more soluble in fat-like solvents such as n-octanol, and less than one if it is more soluble in water. If a substance is present as several chemical species in the octanol-water system due to association or dissociation, each species is assigned its own ''K''ow value. A related value, D, does not distinguish between different species, only indicating the concentration ratio of the substance between the two phases. History In 1899, Charles Ernest Overton and Hans Horst Meyer independently proposed that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistent, Bioaccumulative And Toxic Substances
Persistent, bioaccumulative and toxic substances (PBTs) are a class of compounds that have high resistance to degradation from abiotic and biotic factors, high mobility in the environment and high toxicity. Because of these factors PBTs have been observed to have a high order of bioaccumulation and biomagnification, very long retention times in various media, and widespread distribution across the globe. Most PBTs in the environment are either created through industry or are unintentional byproducts.Blais J. 2005. Biogeochemistry of persistent bioaccumulative toxicants: processes affecting the transport of contaminants to remote areas. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 62: 236-243. History Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) were the focal point of the Stockholm Convention 2001 due to their persistence, ability to biomagnify and the threat posed to both human health and the environment. The goal of the Stockholm Convention was to determine the classification of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozonation
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to (dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the latter, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ozone's odour is reminiscent of chlorine, and detectable by many people at concentrations of as little as in air. Ozone's O3 structure was determined in 1865. The molecule was later proven to have a bent structure and to be weakly diamagnetic. In standard conditions, ozone is a pale blue gas that condenses at cryogenic temperatures to a dark blue liquid and finally a violet-black solid. Ozo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wastewater
Wastewater is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industrial, commercial or agricultural activities, surface runoff / storm water, and any sewer inflow or sewer infiltration". In everyday usage, wastewater is commonly a synonym for sewage (also called sewerage, domestic wastewater, or municipal wastewater), which is wastewater that is produced by a community of people. As a generic term wastewater may also be used to describe water containing contaminants accumulated in other settings, such as: * Industrial wastewater: waterborne waste generated from a variety of industrial processes, such as manufacturing operations, mineral extraction, power generation, or water and wastewater treatment. ** Cooling water, released with potential thermal pollution after use to condense steam or reduce machi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfume Ingredients
Perfume (, ; french: parfum) is a mixture of fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent. The 1939 Nobel Laureate for Chemistry, Leopold Ružička stated in 1945 that "right from the earliest days of scientific chemistry up to the present time, perfumes have substantially contributed to the development of organic chemistry as regards methods, systematic classification, and theory." Ancient texts and archaeological excavations show the use of perfumes in some of the earliest human civilizations. Modern perfumery began in the late 19th century with the commercial synthesis of aroma compounds such as vanillin or coumarin, which allowed for the composition of perfumes with smells previously unattainable solely from natural aromatics. History The word ''perfume'' derives from the Latin ''perfumare'', meaning "to smoke through" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |