|
Galactitol
Galactitol (dulcitol) is a sugar alcohol, the reduction product of galactose. It has a slightly sweet taste. In people with galactokinase deficiency, a form of galactosemia, excess dulcitol forms in the lens of the eye leading to cataracts. Galactitol is produced from galactose in a reaction catalyzed by aldose reductase. The other common galactose metabolism defect is a defect in galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase, an autosomal recessive disorder An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes ..., which also causes a buildup of galactitol as a result of increased concentrations of galactose-1-phosphate and galactose. This disorder leads to cataracts caused by galactitol buildup. References External links * {{Fructose and galactose metabolic intermediates Sugar alco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactosemia
Galactosemia (British galactosaemia, from Greek γαλακτόζη + αίμα, meaning galactose + blood, accumulation of galactose in blood) is a rare genetic metabolic disorder that affects an individual's ability to metabolize the sugar galactose properly. Galactosemia follows an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance that confers a deficiency in an enzyme responsible for adequate galactose degradation. Friedrich Goppert (1870–1927), a German physician, first described the disease in 1917, with its cause as a defect in galactose metabolism being identified by a group led by Herman Kalckar in 1956. Galactosemia was the second disorder found to be detectable through newborn screening methods by Robert Guthrie. Its incidence is about 1 per 60,000 births for people of European ancestry. In other populations the incidence rate differs. Galactosaemia is about one hundred times more common (1:480 births) in the Irish Traveller population. Symptoms Adults Infants Infant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactokinase Deficiency
Galactokinase deficiency is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder marked by an accumulation of galactose and galactitol secondary to the decreased conversion of galactose to galactose-1-phosphate by galactokinase. The disorder is caused by mutations in the GALK1 gene, located on chromosome 17q24. Galactokinase catalyzes the first step of galactose phosphorylation in the Leloir pathway of intermediate metabolism. Galactokinase deficiency is one of the three inborn errors of metabolism that lead to hypergalactosemia. The disorder is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. Unlike classic galactosemia, which is caused by deficiency of galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase, galactokinase deficiency does not present with severe manifestations in early infancy. Its major clinical symptom is the development of cataracts during the first weeks or months of life, as a result of the accumulation, in the lens, of galactitol, a product of an alternative route of galactose utiliza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
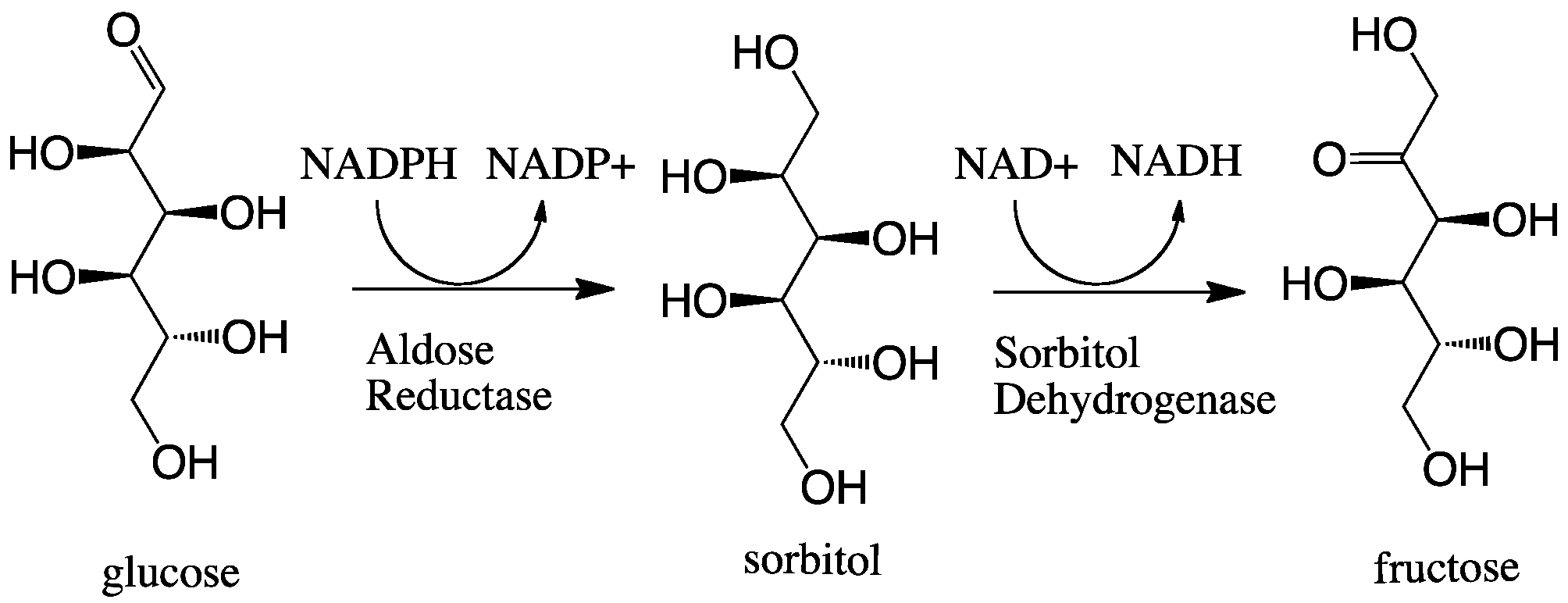
Aldose Reductase
In enzymology, aldose reductase (or aldehyde reductase) () is a cytosolic NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase that catalyzes the reduction of a variety of aldehydes and carbonyls, including monosaccharides. It is primarily known for catalyzing the reduction of glucose to sorbitol, the first step in polyol pathway of glucose metabolism. Reactions Aldose reductase catalyzes the NADPH-dependent conversion of glucose to sorbitol, the first step in polyol pathway of glucose metabolism. The second and last step in the pathway is catalyzed by sorbitol dehydrogenase, which catalyzes the NAD-linked oxidation of sorbitol to fructose. Thus, the polyol pathway results in conversion of glucose to fructose with stoichiometric utilization of NADPH and production of NADH. ;glucose + NADPH + H+ \rightleftharpoons sorbitol + NADP+ Galactose is also a substrate for the polyol pathway, but the corresponding keto sugar is not produced because sorbitol dehydrogenase is incapable of oxidizing galactitol. Nev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Alcohol
Sugar alcohols (also called polyhydric alcohols, polyalcohols, alditols or glycitols) are organic compounds, typically derived from sugars, containing one hydroxyl group (–OH) attached to each carbon atom. They are white, water-soluble solids that can occur naturally or be produced industrially by hydrogenation of sugars. Since they contain multiple –OH groups, they are classified as polyols. Sugar alcohols are used widely in the food industry as thickeners and sweeteners. In commercial foodstuffs, sugar alcohols are commonly used in place of table sugar (sucrose), often in combination with high-intensity artificial sweeteners, in order to offset their low sweetness. Xylitol and sorbitol are popular sugar alcohols in commercial foods. Chemical structure Sugar alcohols have the general formula HOCH2(CHOH)''n''CH2OH. In contrast, sugars have two fewer hydrogen atoms, for example HOCH2(CHOH)''n''CHO or HOCH2(CHOH)''n''−1C(O)CH2OH. The sugar alcohols differ in chain length. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bonds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactose
Galactose (, '' galacto-'' + ''-ose'', "milk sugar"), sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is about as sweet as glucose, and about 65% as sweet as sucrose. It is an aldohexose and a C-4 epimer of glucose. A galactose molecule linked with a glucose molecule forms a lactose molecule. Galactan is a polymeric form of galactose found in hemicellulose, and forming the core of the galactans, a class of natural polymeric carbohydrates. D-Galactose is also known as brain sugar since it is a component of glycoproteins (oligosaccharide-protein compounds) found in nerve tissue. Etymology The word ''galactose'' was coined by Charles Weissman in the mid-19th century and is derived from Greek ''galaktos'' (of milk) and the generic chemical suffix for sugars ''-ose''. The etymology is comparable to that of the word ''lactose'' in that both contain roots meaning "milk sugar". Lactose is a disaccharide of galactose plus glucose. Structure and isomerism Galactose exists in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Center For Biotechnology Information
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland, and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by US Congressman Claude Pepper. The NCBI houses a series of databases relevant to biotechnology and biomedicine and is an important resource for bioinformatics tools and services. Major databases include GenBank for DNA sequences and PubMed, a bibliographic database for biomedical literature. Other databases include the NCBI Epigenomics database. All these databases are available online through the Entrez search engine. NCBI was directed by David Lipman, one of the original authors of the BLAST sequence alignment program and a widely respected figure in bioinformatics. GenBank NCBI had responsibility for making available the GenBank DNA seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (anatomy)
The lens, or crystalline lens, is a transparent biconvex structure in the eye that, along with the cornea, helps to refract light to be focused on the retina. By changing shape, it functions to change the focal length of the eye so that it can focus on objects at various distances, thus allowing a sharp real image of the object of interest to be formed on the retina. This adjustment of the lens is known as '' accommodation'' (see also below). Accommodation is similar to the focusing of a photographic camera via movement of its lenses. The lens is flatter on its anterior side than on its posterior side. In humans, the refractive power of the lens in its natural environment is approximately 18 dioptres, roughly one-third of the eye's total power. Structure The lens is part of the anterior segment of the human eye. In front of the lens is the iris, which regulates the amount of light entering into the eye. The lens is suspended in place by the suspensory ligament of the lens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of falling and depression. Cataracts cause 51% of all cases of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide. Cataracts are most commonly due to aging but may also occur due to trauma or radiation exposure, be present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes, longstanding use of corticosteroid medication, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposure to sunlight, and alcohol. The underlying mechanism involves accumulation of clumps of protein or yellow-brown pigment in the lens that reduces transmission of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMedicine
eMedicine is an online clinical medical knowledge base founded in 1996 by doctors Scott Plantz and Jonathan Adler, and computer engineer Jeffrey Berezin. The eMedicine website consists of approximately 6,800 medical topic review articles, each of which is associated with a clinical subspecialty "textbook". The knowledge base includes over 25,000 clinically multimedia files. Each article is authored by board certified specialists in the subspecialty to which the article belongs and undergoes three levels of physician peer-review, plus review by a Doctor of Pharmacy. The article's authors are identified with their current faculty appointments. Each article is updated yearly, or more frequently as changes in practice occur, and the date is published on the article. eMedicine.com was sold to WebMD in January, 2006 and is available as the Medscape Reference. History Plantz, Adler and Berezin evolved the concept for eMedicine.com in 1996 and deployed the initial site via Boston Medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WebMD
WebMD is an American corporation known primarily as an online publisher of news and information pertaining to human health and well-being. The site includes information pertaining to drugs. It is one of the top healthcare websites. It was founded in 1998 by internet entrepreneur Jeff Arnold. In early 1999, it was part of a three way merger with Sapient Health Network (SHN) and Direct Medical Knowledge (DMK). SHN began in Portland, Oregon, in 1996 by Jim Kean, Bill Kelly, and Kris Nybakken, who worked together at a CD-ROM publishing firm, Creative Multimedia. Later in 1999, WebMD merged with Healtheon, founded by Netscape Communications founder James H. Clark. Traffic During March 2020, WebMD's network of websites reached more unique visitors each month than any other leading private or government healthcare website, making it the leading health publisher in the United States. In the fourth quarter of 2016, WebMD recorded an average of 179.5 million unique users per month, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactose-1-phosphate Uridylyltransferase
Galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase (or GALT, G1PUT) is an enzyme () responsible for converting ingested galactose to glucose. Galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase (GALT) catalyzes the second step of the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, namely: :UDP-glucose + galactose 1-phosphate \rightleftharpoons glucose 1-phosphate + UDP-galactose The expression of GALT is controlled by the actions of the FOXO3 gene. The absence of this enzyme results in classic galactosemia in humans and can be fatal in the newborn period if lactose is not removed from the diet. The pathophysiology of galactosemia has not been clearly defined. Image:D-galactose Fischer.png, galactose Image:D-glucose-chain-2D-Fischer.png, glucose Mechanism GALT catalyzes the second reaction of the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism through ping pong bi-bi kinetics with a double displacement mechanism. This means that the net reaction consists of two reactants and two products (see the reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_PHIL_4284_lores.jpg)