|
Glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase. Mechanism In the muscles, glycogenolysis begins due to the binding of cAMP to phosphorylate kinase, converting the latter to its active form so it can convert phosphorylase b to phosphorylase a, which is responsible for catalyzing the breakdown of glycogen. The overall reaction for the breakdown of glycogen to glucose-1-phosphate is: : glycogen(n residues) + Pi glycogen(n-1 residues) + glucose-1-phosphate Here, glycogen phosphorylase cleaves the bond linking a terminal glucose residue to a glycogen branch by substitution of a phosphoryl group for the α →4linkage. Glucose-1-phosphate is converted to glucose-6-phosphate (which often ends up in glycolysis) by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase. Glucose residues are phosphorolysed from bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and NADH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes. The wide occurrence of glycolysis in other species indicates that it is an ancient metabolic pathway. Indeed, the reactions that make up glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, can occur in the Great Oxygenation Event, oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes, catalyzed by metal ions, meaning this is a plausible prebiotic pathway for abiogenesis. The most common type of glycolysis is the ''Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP) pathway'', which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms of energy reserves, creatine phosphate being for very short-term, glycogen being for short-term and the triglyceride stores in adipose tissue (i.e., body fat) being for long-term storage. Protein, broken down into amino acids, is seldom used as a main energy source except during starvation and glycolytic crisis ''(see bioenergetic systems)''. In humans, glycogen is made and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and skeletal muscle. In the liver, glycogen can make up 5–6% of the organ's fresh weight: the liver of an adult, weighing 1.5 kg, can store roughly 100–120 grams of glycogen. In skeletal muscle, glycogen is found in a low concentration (1–2% of the muscle mass): the skeletal muscle of an adult weighing 70 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose-6-phosphate
Glucose 6-phosphate (G6P, sometimes called the Robison ester) is a glucose sugar phosphorylated at the hydroxy group on carbon 6. This dianion is very common in cells as the majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this way. Because of its prominent position in cellular chemistry, glucose 6-phosphate has many possible fates within the cell. It lies at the start of two major metabolic pathways: glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway. In addition to these two metabolic pathways, glucose 6-phosphate may also be converted to glycogen or starch for storage. This storage is in the liver and muscles in the form of glycogen for most multicellular animals, and in intracellular starch or glycogen granules for most other organisms. Production From glucose Within a cell, glucose 6-phosphate is produced by phosphorylation of glucose on the sixth carbon. This is catalyzed by the enzyme hexokinase in most cells, and, in higher animals, glucokinase in certain cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms of energy reserves, creatine phosphate being for very short-term, glycogen being for short-term and the triglyceride stores in adipose tissue (i.e., body fat) being for long-term storage. Protein, broken down into amino acids, is seldom used as a main energy source except during starvation and glycolytic crisis ''(see bioenergetic systems)''. In humans, glycogen is made and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and skeletal muscle. In the liver, glycogen can make up 5–6% of the organ's fresh weight: the liver of an adult, weighing 1.5 kg, can store roughly 100–120 grams of glycogen. In skeletal muscle, glycogen is found in a low concentration (1–2% of the muscle mass): the skeletal muscle of an adult weighing 70 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fight-or-flight Response
The fight-or-flight or the fight-flight-freeze-or-fawn (also called hyperarousal or the acute stress response) is a physiological reaction that occurs in response to a perceived harmful event, attack, or threat to survival. It was first described by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1915. His theory states that animals react to threats with a general discharge of the sympathetic nervous system, preparing the animal for fighting or fleeing. More specifically, the adrenal medulla produces a hormonal cascade that results in the secretion of catecholamines, especially norepinephrine and epinephrine. The hormones estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol, as well as the neurotransmitters dopamine and serotonin, also affect how organisms react to stress. The hormone osteocalcin might also play a part. This response is recognised as the first stage of the general adaptation syndrome that regulates stress responses among vertebrates and other organisms. Name Originally understood as the "figh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoglucomutase
Phosphoglucomutase () is an enzyme that transfers a phosphate group on an α-D-glucose monomer from the 1 to the 6 position in the forward direction or the 6 to the 1 position in the reverse direction. More precisely, it facilitates the interconversion of glucose 1-phosphate and glucose 6-phosphate. Function Role in glycogenolysis After glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the phosphorolytic cleavage of a glucosyl residue from the glycogen polymer, the freed glucose has a phosphate group on its 1-carbon. This glucose 1-phosphate molecule is not itself a useful metabolic intermediate, but phosphoglucomutase catalyzes the conversion of this glucose 1-phosphate to glucose 6-phosphate (see below for the mechanism of this reaction). Glucose 6-phosphate’s metabolic fate depends on the needs of the cell at the time it is generated. If the cell is low on energy, then glucose 6-phosphate will travel down the glycolytic pathway, eventually yielding two molecules of adenosine tripho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
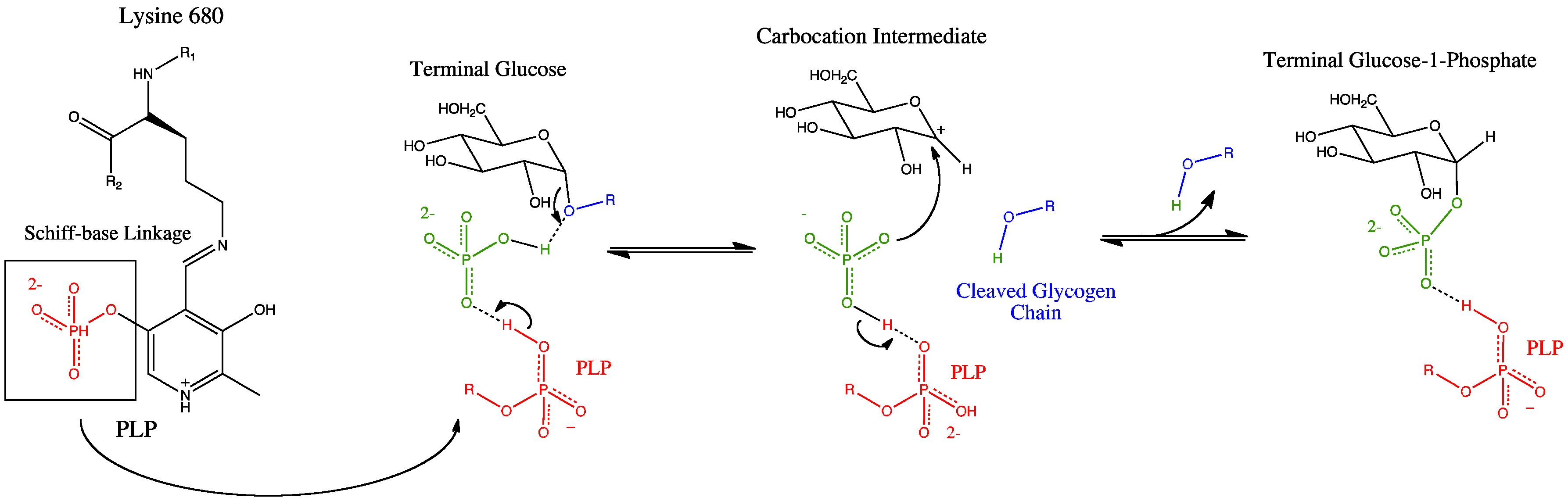
Glycogen Phosphorylase
Glycogen phosphorylase is one of the phosphorylase enzymes (). Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogenolysis in animals by releasing glucose-1-phosphate from the terminal alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond. Glycogen phosphorylase is also studied as a model protein regulated by both reversible phosphorylation and allosteric effects. Mechanism Glycogen phosphorylase breaks up glycogen into glucose subunits (see also figure below): (α-1,4 glycogen chain)n + Pi ⇌ (α-1,4 glycogen chain)n-1 + α-D-glucose-1-phosphate. Glycogen is left with one fewer glucose molecule, and the free glucose molecule is in the form of glucose-1-phosphate. In order to be used for metabolism, it must be converted to glucose-6-phosphate by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase. Although the reaction is reversible in vitro, within the cell the enzyme only works in the forward direction as shown below because the concentration of inorganic phosphate is much higher than that of gluco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen Debranching Enzyme
The glycogen debranching enzyme, in humans, is the protein encoded by the gene ''AGL''. This enzyme is essential for the Glycogenolysis, breakdown of glycogen, which serves as a store of glucose in the body. It has separate glucosyltransferase and glucosidase activities. Together with phosphorylases, the enzyme mobilize glucose reserves from glycogen deposits in the muscles and liver. This constitutes a major source of energy reserves in most organisms. Glycogen breakdown is highly regulated in the body, especially in the liver, by various hormones including insulin and glucagon, to maintain a homeostatic balance of blood-glucose levels. When glycogen breakdown is compromised by mutations in the glycogen debranching enzyme, metabolic diseases such as Glycogen storage disease type III can result. The two steps of glycogen breakdown, glucosyltransferase and glucosidase, are performed by a single enzyme in mammals, yeast, and some bacteria, but by two distinct enzymes in ''E. coli'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoglucomutase
Phosphoglucomutase () is an enzyme that transfers a phosphate group on an α-D-glucose monomer from the 1 to the 6 position in the forward direction or the 6 to the 1 position in the reverse direction. More precisely, it facilitates the interconversion of glucose 1-phosphate and glucose 6-phosphate. Function Role in glycogenolysis After glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the phosphorolytic cleavage of a glucosyl residue from the glycogen polymer, the freed glucose has a phosphate group on its 1-carbon. This glucose 1-phosphate molecule is not itself a useful metabolic intermediate, but phosphoglucomutase catalyzes the conversion of this glucose 1-phosphate to glucose 6-phosphate (see below for the mechanism of this reaction). Glucose 6-phosphate’s metabolic fate depends on the needs of the cell at the time it is generated. If the cell is low on energy, then glucose 6-phosphate will travel down the glycolytic pathway, eventually yielding two molecules of adenosine tripho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose-1-phosphate
Glucose 1-phosphate (also called Cori ester) is a glucose molecule with a phosphate group on the 1'-carbon. It can exist in either the α- or β-anomeric form. Reactions of α-glucose 1-phosphate Catabolic In glycogenolysis, it is the direct product of the reaction in which glycogen phosphorylase cleaves off a molecule of glucose from a greater glycogen structure. A deficiency of muscle glycogen phosphorylase is known as glycogen storage disease type V (McArdle Disease). To be utilized in cellular catabolism it must first be converted to glucose 6-phosphate by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase in a free equilibrium. One reason that cells form glucose 1-phosphate instead of glucose during glycogen breakdown is that the very polar phosphorylated glucose cannot leave the cell membrane and so is marked for intracellular catabolism. Phosphoglucomutase-1 deficiency is known as glycogen storage disease type 14 (GSD XIV). Anabolic In glycogenesis, free glucose 1-phosphate can also react w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen Phosphorylase
Glycogen phosphorylase is one of the phosphorylase enzymes (). Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogenolysis in animals by releasing glucose-1-phosphate from the terminal alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond. Glycogen phosphorylase is also studied as a model protein regulated by both reversible phosphorylation and allosteric effects. Mechanism Glycogen phosphorylase breaks up glycogen into glucose subunits (see also figure below): (α-1,4 glycogen chain)n + Pi ⇌ (α-1,4 glycogen chain)n-1 + α-D-glucose-1-phosphate. Glycogen is left with one fewer glucose molecule, and the free glucose molecule is in the form of glucose-1-phosphate. In order to be used for metabolism, it must be converted to glucose-6-phosphate by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase. Although the reaction is reversible in vitro, within the cell the enzyme only works in the forward direction as shown below because the concentration of inorganic phosphate is much higher than that of gluco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridoxal Phosphate
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. The versatility of PLP arises from its ability to covalently bind the substrate, and then to act as an electrophilic catalyst, thereby stabilizing different types of carbanionic reaction intermediates. Role as a coenzyme PLP acts as a coenzyme in all transamination reactions, and in certain decarboxylation, deamination, and racemization reactions of amino acids. The aldehyde group of PLP forms a Schiff-base linkage (internal aldimine) with the ε-amino group of a specific lysine group of the aminotransferase enzyme. The α-amino group of the amino acid substrate displaces the ε-amino group of the active-site lysine residue in a process known as transaldimination. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |