|
Glassine
Glassine is a smooth and glossy paper which is air-, water-, and grease-resistant. It is usually available in densities between . It is translucent unless dyes are added to the paper to color it or make it opaque. It is manufactured by supercalendering: after pressing and drying, the paper web is passed through a stack of alternating steel-covered and fiber-covered rolls called a supercalender at the end of the paper machine so that the paper fibers are oriented in the same direction. Usage Glassine is most commonly used as a base for further silicone coating for the manufacture of release liner. Glassine is also used as an interleaving paper in bookbinding, especially to protect fine illustrations from contact with facing pages; the paper can be manufactured with a neutral pH and can prevent damage from spilling, exposure, or rubbing. Glassine adhesive tape has been used in book repair. In chemistry, glassine is used as an inexpensive weighing paper. It is applied in foodser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firecracker
A firecracker (cracker, noise maker, banger) is a small explosive device primarily designed to produce a large amount of noise, especially in the form of a loud bang, usually for celebration or entertainment; any visual effect is incidental to this goal. They have fuses, and are wrapped in a heavy paper casing to contain the explosive compound. Firecrackers, along with fireworks, originated in China. History The predecessor of the firecracker was a type of heated bamboo, used as early as 200 BCE, that exploded when heated continuously. The Chinese name for firecrackers, ''baozhu'' (), literally means "exploding bamboo." After the invention of gunpowder, gunpowder firecrackers had a shape that resembled bamboo and produced a similar sound, so the name "exploding bamboo" was retained. In traditional Chinese culture, firecrackers were used to scare off enemies or evil spirits. Firecrackers production and sales Ingredients Firecrackers are generally made of cardboard or plas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighing Paper
Weighing paper is often used when weighing solid, powdery substances on an analytical balance. By preventing the substance from making contact with unwanted materials, the precision of the measurement may be increased. Production Weighing paper is usually made through a process called calendering. First, a chemically manufactured paper pulp fiber is broken down and squeezed into the mold where it will dry into the sheet. Then, this sheet will be rolled down by hot roller. As a result, the pulp fiber will be flat and in the same direction. To make the paper very smooth and moist-resistant, it goes through the process repetitively, called super-calendering. Uses Weighing paper can be folded into different shape depending on its uses. #Origami pouch: Origami pouch is a pocket-like shaped weighing paper that can be usually used for handling powdery, slippery samples. # Weighing boat: Weighing boat is a box-like folded weighing paper that can be usually used for handling solid, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Envelope
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter (message), letter or Greeting card, card. Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one of three shapes: a rhombus, a short-arm cross or a Kite (geometry), kite. These shapes allow the envelope structure to be made by folding the sheet sides around a central rectangular area. In this manner, a rectangle-faced enclosure is formed with an arrangement of four flaps on the reverse side. Overview A folding sequence such that the last flap closed is on a short side is referred to in commercial envelope #Manufacture, manufacture as a pocket – a format frequently employed in the packaging of small quantities of seeds. Although in principle the flaps can be held in place by securing the topmost flap at a single point (for example with a wax seal), generally they are pasted or gummed together at the overlaps. They are most commonly u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamp Hinge
In philately, stamp hinges, or mounts, are small, folded, transparent, rectangular pieces of paper coated with a mild gum. They are used by stamp collectors to affix postage stamps onto the pages of a stamp album. Mackay, James. ''Stamp Collecting: Philatelic Terms Illustrated''. 4th edition. London: Stanley Gibbons, 2003, p.68. Use The short end is moistened and affixed to the stamp, the long end is likewise affixed to the page. The hinge keeps the stamp on the page while still allowing it to be lifted to examine the back, for instance to see the watermark or expert marks. Abbreviation Collectors categorise their stamps as follows: * MUH/MNH – Mint Unhinged/Never Hinged * H – Hinged * LH – Lightly Hinged * HH – Heavily Hinged * HR – Hinge Remnant (portion of the hinge could not be removed and remains on the stamp) Risks The best stamp hinges are designed to be "peelable", meaning that the stamp may be removed from the page, and the hinge from the stamp, without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is drained through a fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distributed on the surface, it can be pressed and dried. The papermaking process developed in east Asia, probably China, at least as early as 105 Common Era, CE, by the Han Dynasty, Han court eunuch Cai Lun, although the earliest archaeological fragments of paper derive from the 2nd century BCE in China. Although paper was originally made in single sheets by hand, today it is mass-produced on large machines—some making reels 10 metres wide, running at 2,000 metres per minute and up to 600,000 tonnes a year. It is a versatile material with many uses, including printing, painting, graphics, signage, design, packaging, decorating, writing, and Housekeeping, cleaning. It may also be used a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Lay
Herman Warden Lay (March 6, 1909 – December 6, 1982) was an American businessman who was involved in potato chip manufacturing with his eponymous brand of Lay's potato chips. He started H.W. Lay Co., Inc., now part of the Frito-Lay corporation, a subsidiary of PepsiCo. By 1937, he had 25 employees, and had begun producing his own line of snack foods. The H.W. Lay & Company merged with The Frito Company in September 1961, creating the largest-selling snack food company in the United States, the Frito-Lay corporation. In 1965, Herman W. Lay (chairman and chief executive officer of Frito-Lay) and Donald M. Kendall (President and chief executive officer of Pepsi-Cola) merged the two companies and formed PepsiCo, Inc. A philanthropist, he helped found the Association of Private Enterprise Education (APEE). Personal life Lay married Sarah Amelia "Mimi" Harper and had four children. He died at the age of 73 on December 6, 1982. His late son, Herman Warden Lay Jr., was a Dallas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potato Chip
Potato chips (North American English and Australian English; often just chip) or crisp (British English and Hiberno-English) are thin slices of potato (or a thin deposit of potato paste) that has been deep frying, deep fried, baking, baked, or air frying, air fried until crunchy. They are commonly served as a snack, side dish, or appetizer. The basic chips are cooked and Edible salt, salted; additional varieties are manufactured using various flavorings and ingredients including herbs, spices, cheeses, other natural flavors, artificial flavours, artificial flavors, and Food additive, additives. Potato chips form a large part of the snack food and convenience food market in Western countries. The global potato chip market generated total revenue of US$16.49 billion in 2005. This accounted for 35.5% of the total savory snacks market in that year (which was $46.1 billion overall). History The earliest known recipe for potato chips is in the English cook William Kitchiner's b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Rocketry
A model rocket is a small rocket designed to reach low altitudes (e.g., for a model) and #Model rocket recovery methods, be recovered by a variety of means. According to the United States National Association of Rocketry, National Association of Rocketry (NAR)'s Safety Code, model rockets are constructed out of lightweight and non metallic parts. The materials are typically paper, cardboard, balsa wood or plastic. The code also provides guidelines for motor use, launch site selection, launch methods, launcher placement, recovery system design and deployment and more. Since the early 1960s, a copy of the Model Rocket Safety Code has been provided with most model rocket kits and motors. Despite its inherent association with extremely flammable substances and objects with a pointed tip traveling at high speeds, model rocketry historically has proven to be a very safe hobby and has been credited as a significant source of inspiration for children who have eventually become scient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paperboard
Paperboard is a thick paper-based material. While there is no rigid differentiation between paper and paperboard, paperboard is generally thicker (usually over 0.30 mm, 0.012 in, or 12 Inch#Equivalents, points) than paper and has certain superior attributes such as foldability and rigidity. According to International Organization for Standardization, ISO standards, paperboard is a paper with a grammage above 250 g/m2, but there are exceptions. Paperboard can be single- or multi-ply. Paperboard can be easily cut and formed, is lightweight, and because it is strong, is used in packaging. Another end-use is high quality graphic printing, such as book and magazine covers or postcards. Paperboard is also used in fine arts for creating sculptures. Sometimes it is referred to as ''cardboard'', which is a generic, lay term used to refer to any heavy pulp (paper), paper pulp–based board, however this usage is deprecated in the paper, printing, and packaging industries as it does not ade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tessellation
A tessellation or tiling is the covering of a surface, often a plane, using one or more geometric shapes, called ''tiles'', with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellation can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of geometries. A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include '' regular tilings'' with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and '' semiregular tilings'' with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called "non-periodic". An '' aperiodic tiling'' uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern (an aperiodic set of prototiles). A '' tessellation of space'', also known as a space filling or honeycomb, can be defined in the geometry of higher dimensions. A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
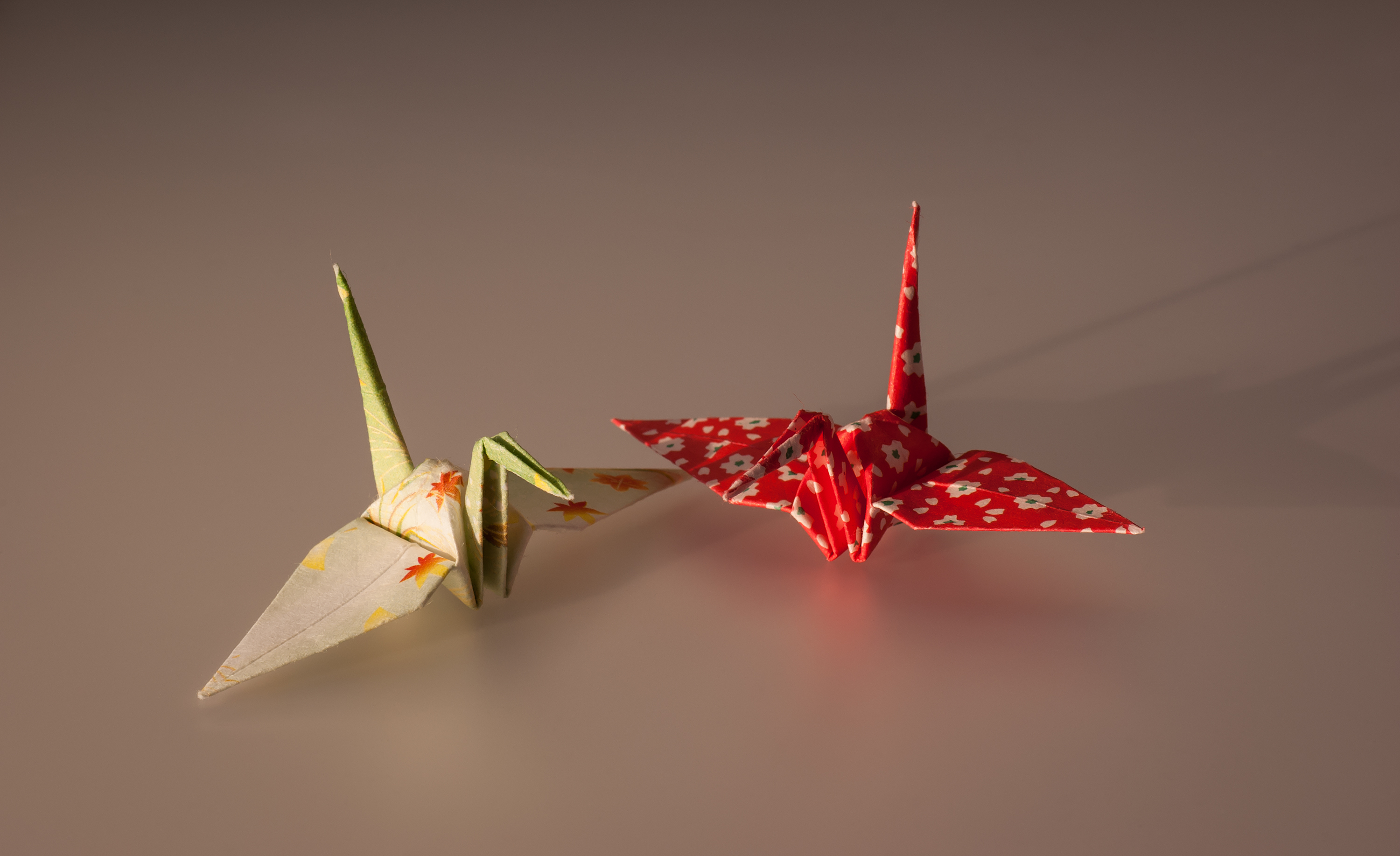
Origami
) is the Japanese art of paper folding. In modern usage, the word "origami" is often used as an inclusive term for all folding practices, regardless of their culture of origin. The goal is to transform a flat square sheet of paper into a finished sculpture through folding and sculpting techniques. Modern origami practitioners generally discourage the use of cuts, glue, or markings on the paper. Origami folders often use the Japanese word ' to refer to designs which use cuts. In the detailed Japanese classification, origami is divided into stylized ceremonial origami (儀礼折り紙, ''girei origami'') and recreational origami (遊戯折り紙, ''yūgi origami''), and only recreational origami is generally recognized as origami. In Japan, ceremonial origami is generally called "origata" ( :ja:折形) to distinguish it from recreational origami. The term "origata" is one of the old terms for origami. The small number of basic origami folds can be combined in a variety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a morphinan opioid substance synthesized from the Opium, dried latex of the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy; it is mainly used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. Heroin is used medically in several countries to Pain reliever, relieve pain, such as during childbirth or a heart attack, as well as in opioid replacement therapy. Medical-grade diamorphine is used as a pure Hydrochloride, hydrochloride salt. Various white and brown powders sold illegally around the world as ''heroin'' are routinely diluted with cutting agents. Black tar heroin is a variable admixture of morphine derivatives—predominantly 6-MAM (6-monoacetylmorphine), which is the result of crude acetylation during clandestine production of street heroin. Heroin is typically Drug injection, injected, usually into a vein, but it can also be snorted, smoked, or inhaled. In a clinical context, the route of administration is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |