|
Glass Lizards
Anguinae is a subfamily of legless lizards in the family Anguidae, commonly called glass lizards, glass snakes or slow worms. The first two names come from the fact their tails easily break or snap off. Members of Anguinae are native to North America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa. Evolution They first appeared in Europe during the early Eocene, approximately 48.6 million years ago, originating from North American ancestors that crossed over from Greenland via the Thule Land Bridge and spread toward Asia sometime after the drying of the Turgai Strait at the beginning of the Oligocene, and then across the Bering Land Bridge to North America during the Miocene. Description Very vestigial hindlegs are present in '' Hyalosaurus'' and '' Pseudopus'', but are entirely absent in the other genera.Lavin, & Girman, D. J. (2019). Phylogenetic relationships and divergence dating in the Glass Lizards (Anguinae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution., 133, 128–140. Members of the group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophisaurus Ventralis
The eastern glass lizard (''Ophisaurus ventralis'') is a species of legless lizard in the family Anguidae and the longest and heaviest species of glass lizards in the genus ''Ophisaurus'', endemic to the Southeastern United States. The streamlined, legless species is often confused with snakes. Glass lizards differ from snakes as they possess a moveable eyelid and an external ear opening as well as a lateral groove that separates the different types of scales on the animal, all three of these features are absent in snakes. Snakes also have flexible jaws while lizards do not. ''Ventralis'' comes from the Latin "venter" meaning belly; this is in reference to the snake-like movement. Description Adults of ''O. ventralis'' grow to in total length, although the head-body length is only at most. There are 99 or more scales along the lateral groove. In this species, no dark longitudinal stripes are present below the lateral groove or under the tail, and there is no distinct mid-dorsal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thule Land Bridge
The Thule Land Bridge (also called the Thulean North Atlantic Bridge) was a land bridge, now submerged beneath the Atlantic Ocean, that connected the British Isles to central Greenland. The land bridge appeared during the Late Paleocene and disappeared during the early Eocene. The Thule Land Bridge is theorized to have connected northern Europe to North America by way of the British Isles and Greenland. The Faroe Islands, the Iceland-Faroe Ridge, Iceland, and the shallow portion of the Denmark Strait may have been parts of the Thule Land Bridge. Relation to other land bridges While it existed, the Thule Land Bridge would have connected Doggerland to Greenland. It is also theorized that the land bridge from Europe to North America was completed with an unnamed crossing at the southern portion of the Davis Strait, connecting Greenland to Baffin Island Baffin Island (formerly Baffin Land), in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada, the second-la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus '' Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should clearly demonstrate both monophyly and validity as a separate lineag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on comparison with homologous features in related species. The emergence of vestigiality occurs by normal evolutionary processes, typically by loss of function of a feature that is no longer subject to positive selection pressures when it loses its value in a changing environment. The feature may be selected against more urgently when its function becomes definitively harmful, but if the lack of the feature provides no advantage, and its presence provides no disadvantage, the feature may not be phased out by natural selection and persist across species. Examples of vestigial structures (also called degenerate, atrophied, or rudimentary organs) are the loss of functional wings in island-dwelling birds; the human vomeronasal organ; and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
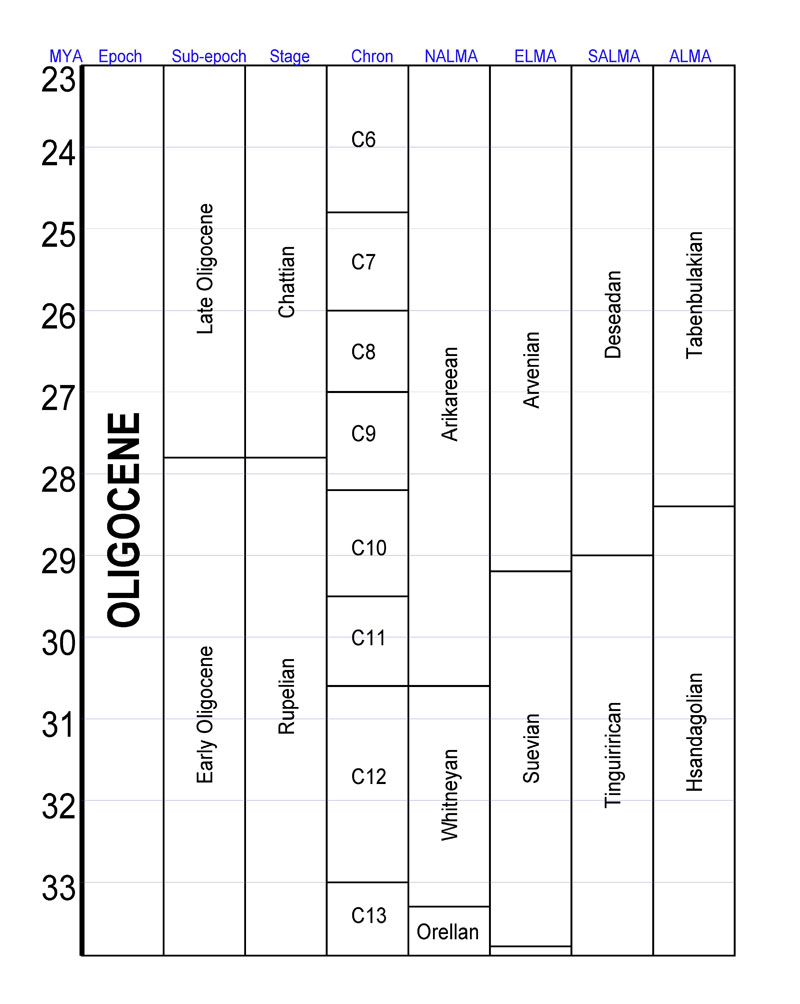
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
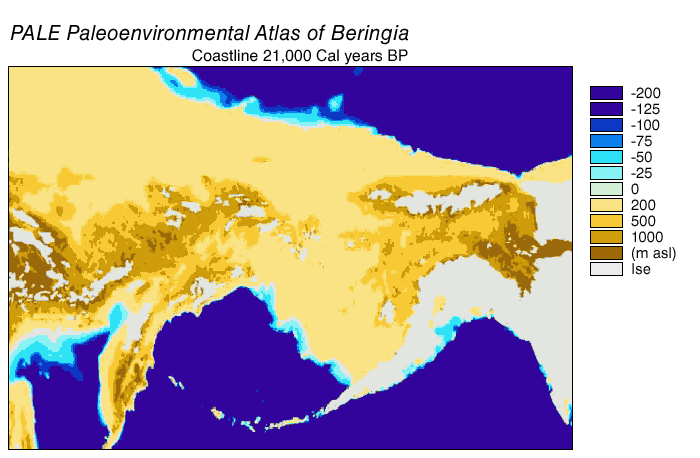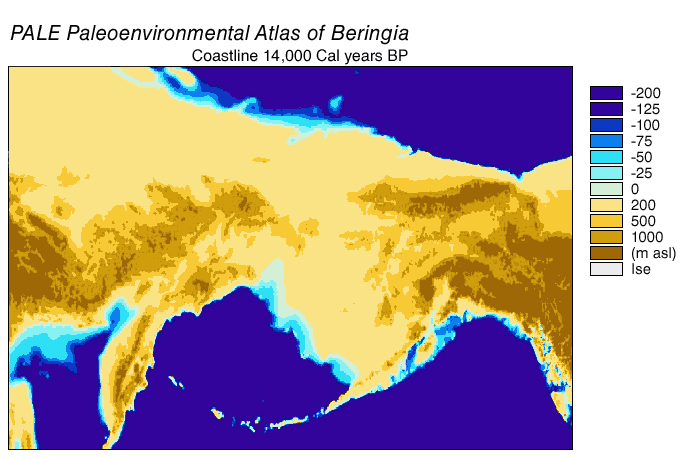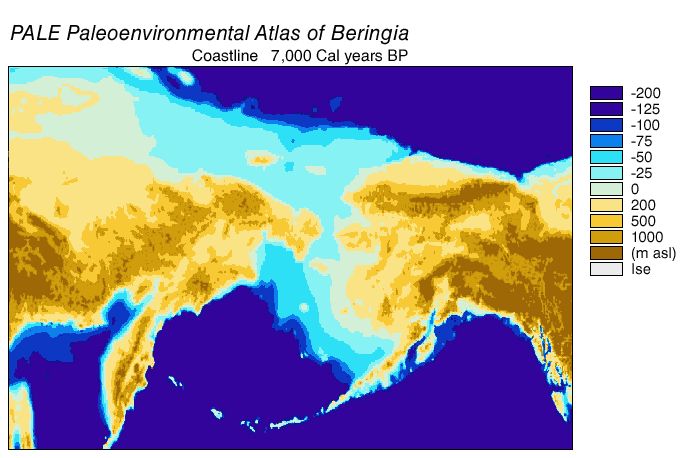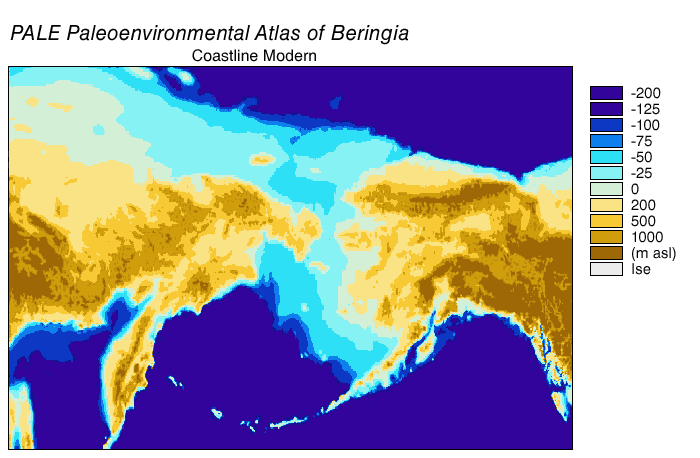
Bering Land Bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72° north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It includes the Chukchi Sea, the Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi and Kamchatka peninsulas in Russia as well as Alaska in the United States and Yukon in Canada. The area includes land lying on the North American Plate and Siberian land east of the Chersky Range. At various times, it formed a land bridge referred to as the Bering land bridge, that was up to wide at its greatest extent and which covered an area as large as British Columbia and Alberta together, totaling about , allowing biological dispersal to occur between Asia and North America. Today, the only land that is visible from the central part of the Bering land bridge are the Diomede Islands, the Pribilof Islands of St. Paul and St. Georg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turgai Strait
The Turgai Strait, also known as the Turgay/Turgai Sea, Obik Sea, Ural Sea or West Siberian Sea, was a large shallow body of salt water (an epicontinental or epeiric sea) during the Mesozoic through Cenozoic Eras. It extended north of the present-day Caspian Sea to the "paleo-Arctic" region, and was in existence from the Middle Jurassic to Oligocene, approximately 160 to 29 million years ago. The Turgai Strait was not absolutely continuous throughout this entire era, though it was a persistent and predominating feature in its region; it "fragmented southern Europe and southwestern Asia into many large islands, and separated Europe from Asia." The division of the Eurasian landmass by the Turgai Sea had the effect of isolating terrestrial animal populations. Notably, the isolation of Europe by the Turgai Sea led to it developing its own unique fauna via a mixture of Europe-endemic and African-originating lineages. Following the Turgai Strait's disappearance and the extinction of muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', 'Eos, Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
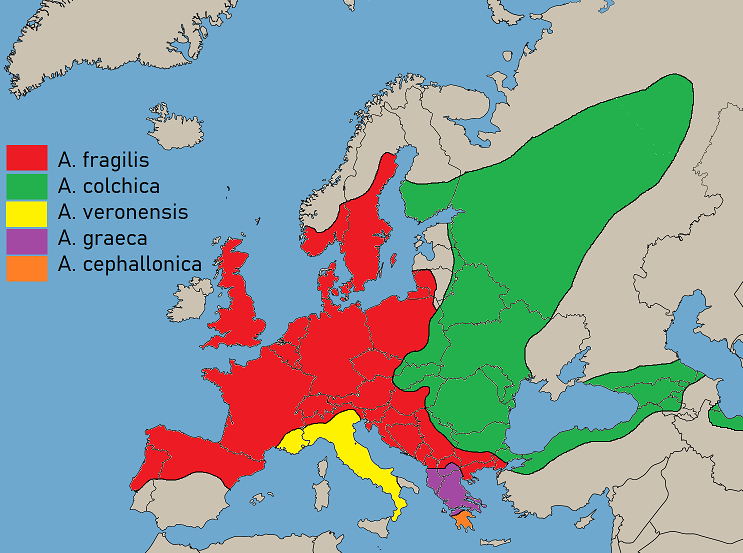
Anguis
Slow wormsThe "slow-" in slowworm is distinct from the English adjective ''slow'' ("not fast"); the word comes from Old English ''slāwyrm'', where ''slā-'' means "slowworm" and ''wyrm'' means "serpent, reptile". () (also called blindworms and hazelworms) are a small genus (''Anguis'') of snake-like legless lizards in the family Anguidae. The genus contains five extant living species, including the Anguis fragilis, common slow worm (''A. fragilis''), the Anguis colchica, eastern slow worm (''A. colchica''), the Anguis graeca, Greek slow worm (''A. graeca''), the Peloponnese slow worm (''A. cephalonnica''), and the Anguis veronensis, Italian slow worm (''A. veronensis''). There are also known fossil species. Description Slow worms are typically grey-brown, with the females having a coppery sheen and two lateral black stripes, and the males displaying Electric blue (color), electric blue spots, particularly in the breeding season. They viviparous, give birth to live young, which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slow Worm
The common slow worm (''Anguis fragilis'') is a species of legless lizard native to western Eurasia. It is also called a deaf adder, blindworm, or regionally, a long-cripple, steelworm, and hazelworm. The "blind" in blindworm refers to the lizard's small eyes, similar to a blindsnake (although the slow worm's eyes are functional). The common slow worm, i.e. the species ''Anguis fragilis'', is often called simply "slow worm", though all species of the species complex comprising the genus ''Anguis'' are also called "slow worms". Common slow worms are semifossorial (burrowing) lizards that spend much of their time hiding underneath objects. The skin of slow worms is smooth, with scales that do not overlap. Like many other lizards, they autotomize, meaning that they have the ability to shed their tails to escape predators. While the tail regrows, it does not reach its original length. In the UK, slow worms are commonly encountered in gardens and allotments, where they can be enco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguidae
Anguidae refers to a large and diverse family of lizards native to the Northern Hemisphere. It contains 9 genera and 89 extant species. Common characteristics of this group include a reduced supratemporal arch, striations on the medial faces of tooth crowns, osteoderms, and a lateral fold in the skin of most taxa. The group is divided into two living subfamilies, the legless Anguinae, which contains slow worms and glass lizards, among others, found across the Northern Hemisphere, and Gerrhonotinae, which contains the alligator lizards, native to North and Central America. The family Diploglossidae (which contains the galliwasps) was also formerly included. Morphology and reproduction Anguids have hard osteoderms beneath their scales giving them an armored appearance. Members of the subfamily Anguinae have reduced or absent limbs, giving them a snake-like appearance, while members of Gerrohonotinae are fully limbed. Body type varies among species, with sizes ranging from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |