|
Geometrical Frustration
In condensed matter physics, geometrical frustration (or in short, frustration) is a phenomenon where the combination of conflicting inter-atomic forces leads to complex structures. Frustration can imply a plenitude of distinct ground states at absolute zero, zero temperature, and usual thermal ordering may be suppressed at higher temperatures. Much-studied examples include amorphous materials, glasses, and dilute magnets. The term ''frustration'', in the context of magnetism, magnetic systems, was introduced by Gerard Toulouse in 1977. Frustrated magnetism, magnetic systems had been studied even before. Early work includes a study of the Ising model on a triangular lattice with nearest-neighbor Spin (physics), spins coupled Antiferromagnetism, antiferromagnetically, by Gregory Wannier, G. H. Wannier, published in 1950. Related features occur in magnets with ''competing interactions'', where both ferromagnetic as well as antiferromagnetic couplings between pairs of Spin (physics), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Condensed Matter Physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid State of matter, phases, that arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms and electrons. More generally, the subject deals with condensed phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions among them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconductivity, superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at extremely low cryogenic temperatures, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of Spin (physics), spins on crystal lattices of atoms, the Bose–Einstein condensates found in ultracold atomic systems, and liquid crystals. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other theoretical physics, physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stoichiometric
Stoichiometry () is the relationships between the masses of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions. Stoichiometry is based on the law of conservation of mass; the total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products, so the relationship between reactants and products must form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of the products can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated. This is illustrated in the image here, where the unbalanced equation is: : : However, the current equation is imbalanced. The reactants have 4 hydrogen and 2 oxygen atoms, while the product has 2 hydrogen and 3 oxygen. To balance the hydrogen, a coefficient of 2 is added to the product H2O, and to fix the imbalance of oxygen, it is also added ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
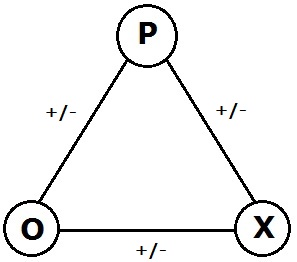
Signed Graph
In the area of graph theory in mathematics, a signed graph is a graph in which each edge has a positive or negative sign. A signed graph is balanced if the product of edge signs around every cycle is positive. The name "signed graph" and the notion of balance appeared first in a mathematical paper of Frank Harary in 1953. Dénes Kőnig had already studied equivalent notions in 1936 under a different terminology but without recognizing the relevance of the sign group. At the Center for Group Dynamics at the University of Michigan, Dorwin Cartwright and Harary generalized Fritz Heider's psychological theory of balance in triangles of sentiments to a psychological theory of balance in signed graphs. Signed graphs have been rediscovered many times because they come up naturally in many unrelated areas. For instance, they enable one to describe and analyze the geometry of subsets of the classical root systems. They appear in topological graph theory and group theory. They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quantum Chromodynamics
In theoretical physics, quantum chromodynamics (QCD) is the study of the strong interaction between quarks mediated by gluons. Quarks are fundamental particles that make up composite hadrons such as the proton, neutron and pion. QCD is a type of quantum field theory called a non-abelian gauge theory, with symmetry group special unitary group, SU(3). The QCD analog of electric charge is a property called ''color''. Gluons are the force carriers of the theory, just as photons are for the electromagnetic force in quantum electrodynamics. The theory is an important part of the Standard Model of particle physics. A large body of Quantum chromodynamics#Experimental tests, experimental evidence for QCD has been gathered over the years. QCD exhibits three salient properties: * Color confinement. Due to the force between two color charges remaining constant as they are separated, the energy grows until a quark–antiquark pair is mass–energy equivalence, spontaneously produced, turning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wilson Loop
In quantum field theory, Wilson loops are gauge invariant operators arising from the parallel transport of gauge variables around closed loops. They encode all gauge information of the theory, allowing for the construction of loop representations which fully describe gauge theories in terms of these loops. In pure gauge theory they play the role of order operators for confinement, where they satisfy what is known as the area law. Originally formulated by Kenneth G. Wilson in 1974, they were used to construct links and plaquettes which are the fundamental parameters in lattice gauge theory. Wilson loops fall into the broader class of loop operators, with some other notable examples being 't Hooft loops, which are magnetic duals to Wilson loops, and Polyakov loops, which are the thermal version of Wilson loops. Definition To properly define Wilson loops in gauge theory requires considering the fiber bundle formulation of gauge theories. Here for each point in the d-dim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Magnetic Moment
In electromagnetism, the magnetic moment or magnetic dipole moment is the combination of strength and orientation of a magnet or other object or system that exerts a magnetic field. The magnetic dipole moment of an object determines the magnitude of torque the object experiences in a given magnetic field. When the same magnetic field is applied, objects with larger magnetic moments experience larger torques. The strength (and direction) of this torque depends not only on the magnitude of the magnetic moment but also on its orientation relative to the direction of the magnetic field. Its direction points from the south pole to the north pole of the magnet (i.e., inside the magnet). The magnetic moment also expresses the magnetic force effect of a magnet. The magnetic field of a magnetic dipole is proportional to its magnetic dipole moment. The dipole component of an object's magnetic field is symmetric about the direction of its magnetic dipole moment, and decreases as the inverse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ferromagnetic
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) that results in a significant, observable magnetic permeability, and in many cases, a significant magnetic coercivity, allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials are noticeably attracted to a magnet, which is a consequence of their substantial magnetic permeability. Magnetic permeability describes the induced magnetization of a material due to the presence of an external magnetic field. For example, this temporary magnetization inside a steel plate accounts for the plate's attraction to a magnet. Whether or not that steel plate then acquires permanent magnetization depends on both the strength of the applied field and on the coercivity of that particular piece of steel (which varies with the steel's chemical composition and any heat treatment it may have undergone). In physics, multiple types of material magnetism have been distinguished. Ferromagnetism (along with the similar effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Line (geometry)
In geometry, a straight line, usually abbreviated line, is an infinitely long object with no width, depth, or curvature, an idealization of such physical objects as a straightedge, a taut string, or a ray (optics), ray of light. Lines are space (mathematics), spaces of dimension one, which may be Embedding, embedded in spaces of dimension two, three, or higher. The word ''line'' may also refer, in everyday life, to a line segment, which is a part of a line delimited by two Point (geometry), points (its ''endpoints''). Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements'' defines a straight line as a "breadthless length" that "lies evenly with respect to the points on itself", and introduced several postulates as basic unprovable properties on which the rest of geometry was established. ''Euclidean line'' and ''Euclidean geometry'' are terms introduced to avoid confusion with generalizations introduced since the end of the 19th century, such as Non-Euclidean geometry, non-Euclidean, Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular Face (geometry), faces, six straight Edge (geometry), edges, and four vertex (geometry), vertices. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polytope, convex polyhedra. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean geometry, Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid (geometry), pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron, the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such net (polyhedron), nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Degenerate Energy Level
In quantum mechanics, an energy level is degenerate if it corresponds to two or more different measurable states of a quantum system. Conversely, two or more different states of a quantum mechanical system are said to be degenerate if they give the same value of energy upon measurement. The number of different states corresponding to a particular energy level is known as the ''degree of degeneracy'' (or simply the ''degeneracy'') of the level. It is represented mathematically by the Hamiltonian (quantum mechanics), Hamiltonian for the system having more than one linear independence, linearly independent eigenstate with the same energy eigenvalue. When this is the case, energy alone is not enough to characterize what state the system is in, and other quantum numbers are needed to characterize the exact state when distinction is desired. In classical mechanics, this can be understood in terms of different possible trajectories corresponding to the same energy. Degeneracy plays a fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Antiferromagnetism
In materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism, the magnetic moments of atoms or molecules, usually related to the spins of electrons, align in a regular pattern with neighboring spins (on different sublattices) pointing in opposite directions. This is, like ferromagnetism and ferrimagnetism, a manifestation of ordered magnetism. The phenomenon of antiferromagnetism was first introduced by Lev Landau in 1933. Generally, antiferromagnetic order may exist at sufficiently low temperatures, but vanishes at and above the Néel temperature – named after Louis Néel, who had first identified this type of magnetic ordering. Above the Néel temperature, the material is typically paramagnetic. Measurement When no external field is applied, the antiferromagnetic structure corresponds to a vanishing total magnetization. In an external magnetic field, a kind of ferrimagnetic behavior may be displayed in the antiferromagnetic phase, with the absolute value of one of the sublattice magne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Frustrated Magnetism
In condensed matter physics, geometrical frustration (or in short, frustration) is a phenomenon where the combination of conflicting inter-atomic forces leads to complex structures. Frustration can imply a plenitude of distinct ground states at zero temperature, and usual thermal ordering may be suppressed at higher temperatures. Much-studied examples include amorphous materials, glasses, and dilute magnets. The term ''frustration'', in the context of magnetic systems, was introduced by Gerard Toulouse in 1977. Frustrated magnetic systems had been studied even before. Early work includes a study of the Ising model on a triangular lattice with nearest-neighbor spins coupled antiferromagnetically, by G. H. Wannier, published in 1950. Related features occur in magnets with ''competing interactions'', where both ferromagnetic as well as antiferromagnetic couplings between pairs of spins or magnetic moments are present, with the type of interaction depending on the separation dista ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |