|
Geocentrism
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric models, the Sun, Moon, stars, and planets all orbit Earth. The geocentric model was the predominant description of the cosmos in many European ancient civilizations, such as those of Aristotle in Classical Greece and Ptolemy in Roman Egypt, as well as during the Islamic Golden Age. Two observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. First, from anywhere on Earth, the Sun appears to revolve around Earth once per day. While the Moon and the planets have their own motions, they also appear to revolve around Earth about once per day. The stars appeared to be fixed on a celestial sphere rotating once each day about an axis through the geographic poles of Earth. Second, Earth seems to be unmoving from the perspective of an earthbound observer; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliocentric Model
Heliocentrism (also known as the heliocentric model) is a superseded astronomical model in which the Earth and planets orbit around the Sun at the center of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth at the center. The notion that the Earth revolves around the Sun had been proposed as early as the 3rd century BC by Aristarchus of Samos, who had been influenced by a concept presented by Philolaus of Croton (c. 470 – 385 BC). In the 5th century BC the Greek philosophers Philolaus and Hicetas had the thought on different occasions that the Earth was spherical and revolving around a "mystical" central fire, and that this fire regulated the universe. In medieval Europe, however, Aristarchus' heliocentrism attracted little attention—possibly because of the loss of scientific works of the Hellenistic period. It was not until the 16th century that a mathematical model of a heliocentric system was presented by the Renaissance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
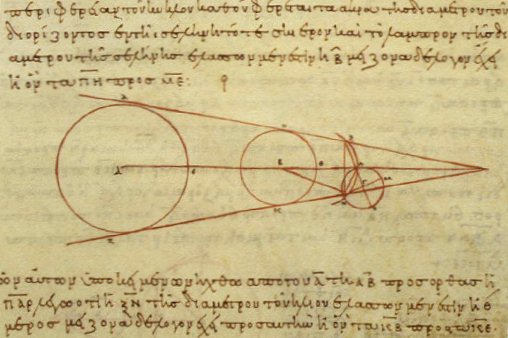
Aristarchus Of Samos
Aristarchus of Samos (; , ; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician who presented the first known heliocentric model that placed the Sun at the center of the universe, with the Earth revolving around the Sun once a year and rotating about its axis once a day. He also supported the theory of Anaxagoras according to which the Sun was just another star. He likely moved to Alexandria, and he was a student of Strato of Lampsacus, who later became the third head of the Peripatetic school in Greece. According to Ptolemy, he observed the summer solstice of 280 BC. Along with his contributions to the heliocentric model, as reported by Vitruvius, he created two separate sundials: one that is a flat disc; and one hemispherical. Aristarchus estimated the sizes of the Sun and Moon as compared to Earth's size. He also estimated the distances from the Earth to the Sun and Moon. His estimate that the Sun was 7 times larger than Earth (while inaccurate by an order of magnitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his Kepler's laws of planetary motion, laws of planetary motion, and his books ''Astronomia nova'', ''Harmonice Mundi'', and ''Epitome Astronomiae Copernicanae'', influencing among others Isaac Newton, providing one of the foundations for his theory of Newton's law of universal gravitation, universal gravitation. The variety and impact of his work made Kepler one of the founders and fathers of modern astronomy, the scientific method, Natural science, natural and modern science. He has been described as the "father of science fiction" for his novel ''Somnium (novel), Somnium''. Kepler was a mathematics teacher at a seminary school in Graz, where he became an associate of Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg, Prince Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg. Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Stars
In astronomy, the fixed stars () are the luminary points, mainly stars, that appear not to move relative to one another against the darkness of the night sky in the background. This is in contrast to those lights visible to the naked eye, namely the planets and comets, which appear to move slowly among those "fixed" stars. The fixed stars include all the stars visible to the naked eye other than the Sun, as well as the faint band of the Milky Way. Due to their star-like appearance when viewed with the naked eye, the few visible individual nebulae and other deep-sky objects are also counted among the fixed stars. Approximately 6,000 stars are visible to the naked eye under optimal conditions. The term ''fixed stars'' is a misnomer because those celestial objects are not actually fixed with respect to one another or to Earth. Due to their immense distance from Earth, these objects appear to move so slowly in the sky that the change in their relative positions is nearly imperce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartolomeu Velho 1568
Bartolomeu is a given name of Portuguese people, Portuguese, Galician language, Galician or Romanians, Romanian origin. It is a cognate of Bartholomew (name), Bartholomew. Notable people with this name include: * Bartolomeu Anania – Romanian Orthodox monk who was the Metropolitan of Cluj (1993–2011) * Bartolomeu Chaves - Brazilian para-athlete * Bartolomeu Cid dos Santos - Portuguese artist * Bartolomeu Dias - Portuguese explorer, and the first European navigator to round the southern tip of Africa * Bartolomeu de Gusmão – Portuguese priest * Bartolomeu Perestrello – 1st Capitão Donatário, Lord and Governor of the Island of Porto Santo (c. 1395–1457) * Bartolomeu Português – Portuguese buccaneer * Bartolomeu Velho – Sixteenth-century Portuguese mapmaker and cosmographer * Edgar Bartolomeu – Former Angolan professional soccer player See also * * * Barthélemy (other), Barthélemy – French * Bartholomew – English * Bartolomeo – Italian * Bartol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Pole
A geographical pole or geographic pole is either of the two points on Earth where its axis of rotation intersects its surface. The North Pole lies in the Arctic Ocean while the South Pole is in Antarctica. North and South poles are also defined for other planets or satellites in the Solar System, with a North pole being on the same side of the invariable plane as Earth's North pole. Relative to Earth's surface, the geographic poles move by a few metres over periods of a few years. This is a combination of Chandler wobble, a free oscillation with a period of about 433 days; an annual motion responding to seasonal movements of air and water masses; and an irregular drift towards the 80th west meridian. As cartography requires exact and unchanging coordinates, the averaged locations of geographical poles are taken as fixed ''cartographic poles'' and become the points where the body's great circles of longitude intersect. See also * Earth's rotation * Polar motion * Poles of astr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler's Laws Of Planetary Motion
In astronomy, Kepler's laws of planetary motion, published by Johannes Kepler in 1609 (except the third law, which was fully published in 1619), describe the orbits of planets around the Sun. These laws replaced circular orbits and epicycles in the heliocentric theory of Nicolaus Copernicus with elliptical orbits and explained how planetary velocities vary. The three laws state that: # The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci. # A line segment joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time. # The square of a planet's orbital period is proportional to the cube of the length of the semi-major axis of its orbit. The elliptical orbits of planets were indicated by calculations of the orbit of Mars. From this, Kepler inferred that other bodies in the Solar System, including those farther away from the Sun, also have elliptical orbits. The second law establishes that when a planet is closer to the Sun, it travels fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
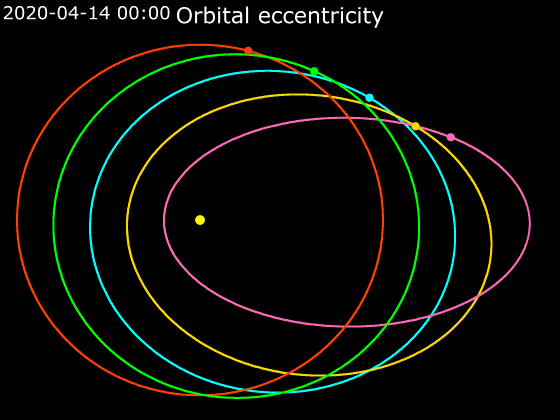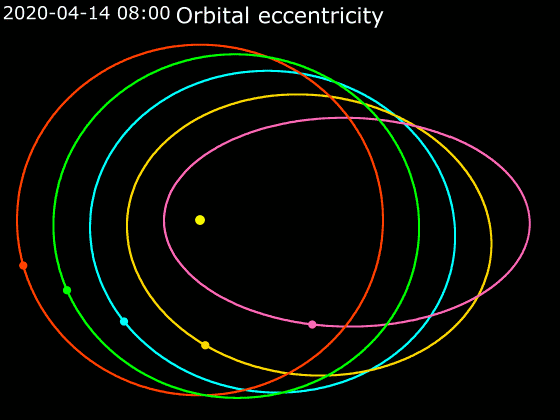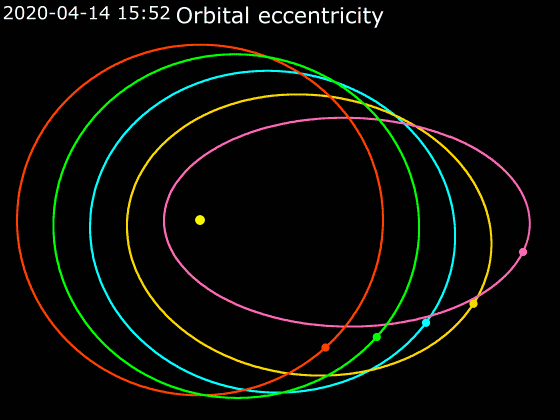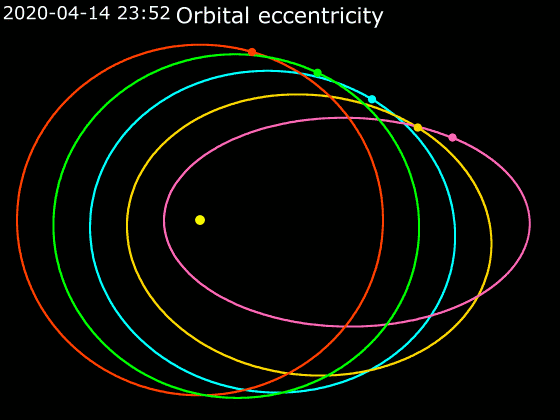
Elliptic Orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, an elliptical orbit or eccentric orbit is an orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to 0. Some orbits have been referred to as "elongated orbits" if the eccentricity is "high" but that is not an explanatory term. For the simple two body problem, all orbits are ellipses. In a gravitational two-body problem, both bodies follow similar elliptical orbits with the same orbital period around their common barycenter. The relative position of one body with respect to the other also follows an elliptic orbit. Examples of elliptic orbits include Hohmann transfer orbits, Molniya orbits, and tundra orbits. Velocity Under standard assumptions, no other forces acting except two spherically symmetrical bodies (m_1) and (m_2), the orbital speed (v\,) of one body traveling along an elliptical orbit can be computed from the vis-viva equation as: :v = \sqrt where: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Culture
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the Cultural heritage, internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompasses the social norms, ethical values, Tradition, traditional customs, belief systems, political systems, Cultural artifact, artifacts and technology, technologies primarily rooted in History of Europe, European and History of the Mediterranean region, Mediterranean histories. A broad concept, "Western culture" does not relate to a region with fixed members or geographical confines. It generally refers to the classical era cultures of Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome that expanded across the Mediterranean basin and Europe, and later circulated around the world predominantly through colonization and globalization. Historically, scholars have closely associated the idea of Western culture with the classical era of Greco-Roman antiquity. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Orbit
A circular orbit is an orbit with a fixed distance around the barycenter; that is, in the shape of a circle. In this case, not only the distance, but also the speed, angular speed, Potential energy, potential and kinetic energy are constant. There is no periapsis or apoapsis. This orbit has no Radial orbit, radial version. Listed below is a circular orbit in astrodynamics or celestial mechanics under standard assumptions. Here the centripetal force is the gravitational force, and the axis mentioned above is the line through the Center of mass, center of the central mass perpendicular to the orbital plane. Circular acceleration :wikt:transverse, Transverse acceleration (perpendicular to velocity) causes a change in direction. If it is constant in magnitude and changing in direction with the velocity, circular motion ensues. Taking two derivatives of the particle's coordinates concerning time gives the centripetal acceleration : a\, = \frac \, = where: *v\, is Kinetic e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mythology
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the veracity of a myth is not a defining criterion. Myths are often endorsed by religious (when they are closely linked to religion or spirituality) and secular authorities. Many societies group their myths, legends, and history together, considering myths and legends to be factual accounts of their remote past. In particular, creation myths take place in a primordial age when the world had not achieved its later form. Origin myths explain how a society's customs, institutions, and taboos were established and sanctified. National myths are narratives about a nation's past that symbolize the nation's values. There is a complex relationship between recital of myths and the enactment of rituals. Etymology The word "myth" comes from Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat Earth
Flat Earth is an archaic and scientifically disproven conception of the Figure of the Earth, Earth's shape as a Plane (geometry), plane or Disk (mathematics), disk. Many ancient cultures, notably in the cosmology in the ancient Near East, ancient Near East, subscribed to a flat-Earth cosmography. The model has undergone a modern flat Earth beliefs, recent resurgence as a conspiracy theory in the 21st century. The idea of a spherical Earth appeared in ancient Greek philosophy with Pythagoras (6th century BC). However, the Early Greek cosmology, early Greek cosmological view of a flat Earth persisted among most Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratics (6th–5th century BC). In the early 4th century BC, Plato wrote about a spherical Earth. By about 330 BC, his former student Aristotle had provided strong empirical evidence for a spherical Earth. Knowledge of the Earth's global shape gradually began to spread beyond the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic world. By the early period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |