|
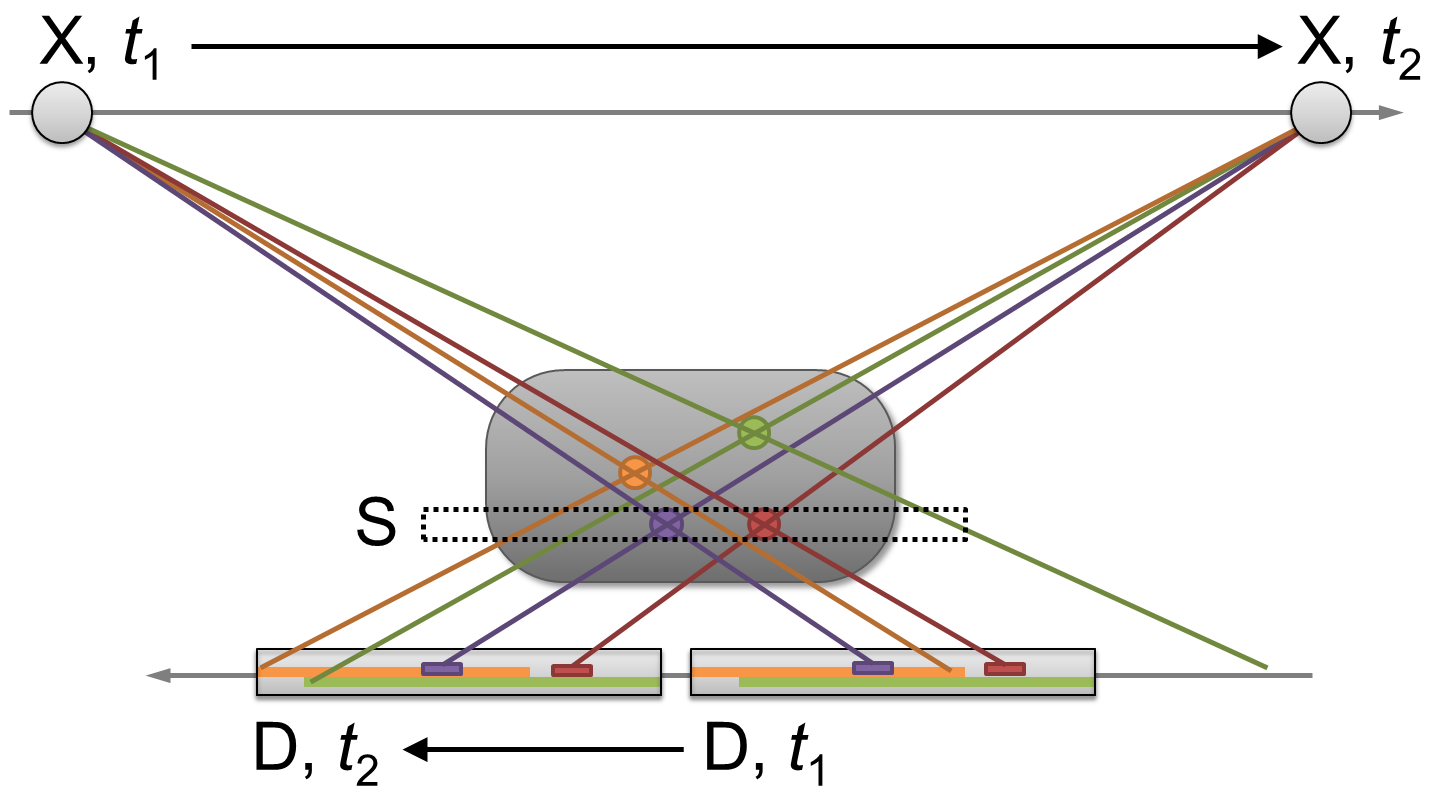
Focal Plane Tomography
In radiography, focal plane tomography is tomography (imaging a single plane, or slice, of an object) by simultaneously moving the X-ray generator and X-ray detector so as to keep a consistent exposure of only the plane of interest during image acquisition. This was the main method of obtaining tomographs in medical imaging until the late-1970s. It has since been largely replaced by more advanced imaging techniques such as CT and MRI. It remains in use today in a few specialized applications, such as for acquiring orthopantomographs of the jaw in dental radiography. Focal plane tomography’s development began in the 1930s as a means of reducing the problem of superimposition of structures which is inherent to projectional radiography. It was invented in parallel by, among others, by the French physician Bocage, the Italian radiologist Alessandro Vallebona and the Dutch radiologist Bernard George Ziedses des Plantes. Technique Focal plane tomography generally uses mechanical mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panoramic Radiograph
A panoramic radiograph is a panoramic scanning dental X-ray of the upper and lower jaw. It shows a two-dimensional view of a half-circle from ear to ear. Panoramic radiography is a form of focal plane tomography; thus, images of multiple planes are taken to make up the composite panoramic image, where the maxilla and mandible are in the focal trough and the structures that are superficial and deep to the trough are blurred. Other nonproprietary names for a panoramic radiograph are dental panoramic radiograph and pantomogram; Abbreviations include PAN, DPR, OPT, and OPG (the latter, based on genericizing a trade name, are often avoided in medical editing). Types Dental panoramic radiography equipment consists of a horizontal rotating arm which holds an X-ray source and a moving film mechanism (carrying a film) arranged at opposed extremities. The patient's skull sits between the X-ray generator and the film. The X-ray source is rectangular collimated beam. Also the height ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Plane
In Gaussian optics, the cardinal points consist of three pairs of points located on the optical axis of a rotationally symmetric, focal, optical system. These are the '' focal points'', the principal points, and the nodal points. For ''ideal'' systems, the basic imaging properties such as image size, location, and orientation are completely determined by the locations of the cardinal points; in fact only four points are necessary: the focal points and either the principal or nodal points. The only ideal system that has been achieved in practice is the plane mirror, however the cardinal points are widely used to ''approximate'' the behavior of real optical systems. Cardinal points provide a way to analytically simplify a system with many components, allowing the imaging characteristics of the system to be approximately determined with simple calculations. Explanation The cardinal points lie on the optical axis of the optical system. Each point is defined by the effect the opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Pyelogram
Pyelogram (or pyelography or urography) is a form of imaging of the renal pelvis and ureter. Types include: * Intravenous pyelogram – In which a contrast solution is introduced through a vein into the circulatory system. * Retrograde pyelogram – Any pyelogram in which contrast medium is introduced from the lower urinary tract and flows toward the kidney (i.e. in a "retrograde" direction, against the normal flow of urine). * Anterograde pyelogram (also antegrade pyelogram) – A pyelogram where a contrast medium passes from the kidneys toward the bladder, mimicking the normal flow of urine. * Gas pyelogram – A pyelogram that uses a gaseous rather than liquid contrast medium. It may also form without the injection of a gas, when gas producing micro-organisms infect the most upper parts of urinary system. Intravenous pyelogram An intravenous pyelogram (IVP), also called an intravenous urogram (IVU), is a radiological procedure used to visualize abnormalities of the urinary sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philips
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), commonly shortened to Philips, is a Dutch multinational conglomerate corporation that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, it has been mostly headquartered in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarters is still in Eindhoven. Philips was formerly one of the largest electronics companies in the world, but is currently focused on the area of health technology, having divested its other divisions. The company was founded in 1891 by Gerard Philips and his father Frederik, with their first products being light bulbs. It currently employs around 80,000 people across 100 countries. The company gained its royal honorary title (hence the ''Koninklijke'') in 1998 and dropped the "Electronics" in its name in 2013, due to its refocusing from consumer electronics to healthcare technology. Philips is organized into three main divisions: Personal Health (formerly Philips Consumer Electronics and Philips Domestic Appliances and Personal Care), Connecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focus (geometry), focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in which the two focal points are the same. The elongation of an ellipse is measured by its eccentricity (mathematics), eccentricity e, a number ranging from e = 0 (the Limiting case (mathematics), limiting case of a circle) to e = 1 (the limiting case of infinite elongation, no longer an ellipse but a parabola). An ellipse has a simple algebraic solution for its area, but only approximations for its perimeter (also known as circumference), for which integration is required to obtain an exact solution. Analytic geometry, Analytically, the equation of a standard ellipse centered at the origin with width 2a and height 2b is: : \frac+\frac = 1 . Assuming a \ge b, the foci are (\pm c, 0) for c = \sqrt. The standard parametric e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRI Contrast Agent
MRI contrast agents are contrast agents used to improve the visibility of internal body structures in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The most commonly used compounds for contrast enhancement are gadolinium-based. Such MRI contrast agents shorten the relaxation times of nuclei within body tissues following oral or intravenous administration. In MRI scanners, sections of the body are exposed to a strong magnetic field causing primarily the hydrogen nuclei ("spins") of water in tissues to be polarized in the direction of the magnetic field. An intense radiofrequency pulse is applied that tips the magnetization generated by the hydrogen nuclei in the direction of the receiver coil where the spin polarization can be detected. Random molecular rotational oscillations matching the resonance frequency of the nuclear spins provide the "relaxation" mechanisms that bring the net magnetization back to its equilibrium position in alignment with the applied magnetic field. The magnitude of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibular Schwannoma
A vestibular schwannoma (VS), also called acoustic neuroma, is a benign tumor that develops on the vestibulocochlear nerve that passes from the inner ear to the brain. The tumor originates when Schwann cells that form the insulating myelin sheath on the nerve malfunction. Normally, Schwann cells function beneficially to protect the nerves which transmit balance and sound information to the brain. However, sometimes a mutation in the tumor suppressor gene, NF2, located on chromosome 22, results in abnormal production of the cell protein named ''Merlin'', and Schwann cells multiply to form a tumor. The tumor originates mostly on the vestibular division of the nerve rather than the cochlear division, but hearing as well as balance will be affected as the tumor enlarges. The great majority of these VSs (95%) are unilateral, in one ear only. They are called "sporadic" (i.e., by-chance, non-hereditary). Although non-cancerous, they can do harm or even become life-threatening if they grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelography
Myelography is a type of radiographic examination that uses a contrast medium to detect pathology of the spinal cord, including the location of a spinal cord injury, cysts, and tumors. Historically the procedure involved the injection of a radiocontrast agent into the cervical or lumbar spine, followed by several X-ray projections. Today, myelography has largely been replaced by the use of MRI scans, although the technique is still sometimes used under certain circumstances – though now usually in conjunction with CT rather than X-ray projections. Types Cervical myelography This procedure is used to look for the level of where spinal cord disease occurs or compression of the spinal cord at the neck region for those who are unable or unwilling to undergone MRI scan of the spine. Lumbar myelography This procedure is to look for the level of spinal cord disease such as lumbar nerve root compression, cauda equina syndrome, conus medullaris lesions, and spinal stenosis. This is do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Ear Institute
The House Institute Foundation (HIF), formerly the House Ear Institute, is a non-profit 501(c)(3) organization, based in Los Angeles, California, and dedicated to advancing hearing science through research, education, and global hearing health to improve quality of life. History Established in 1946 by Howard P. House, as the Los Angeles Foundation of Otology, and later renamed for its founder, the House Institute Foundation has been engaged in the scientific exploration of the auditory system from the ear canal to the cortex of the brain for over 70 years. Since 1946, the House Institute Foundation has led the way in defining the causes of hearing and balance disorders, improving medical/surgical procedures and prosthetic devices. The Institute's discoveries have helped millions of people receive successful treatments. House Institute Foundation scientists have been involved in many firsts in the fields of otology, neurotology, skull base surgery, implantable auditory prosthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
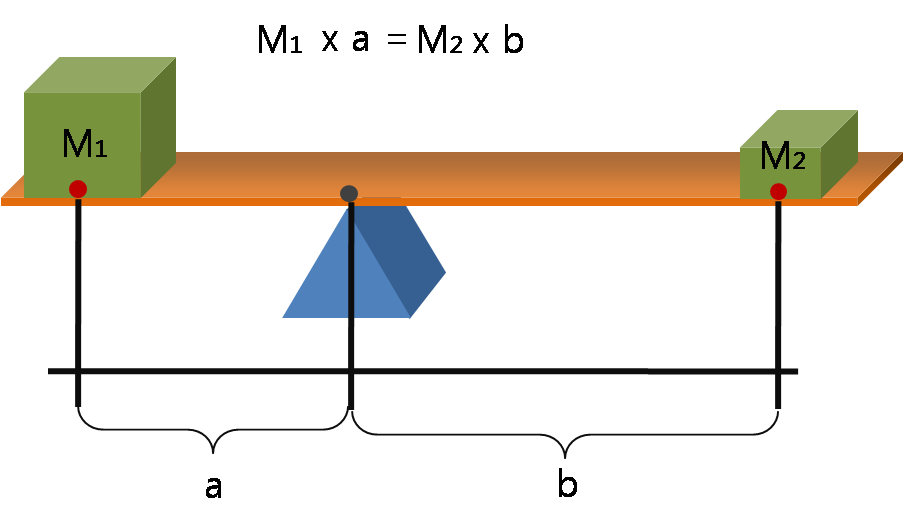
Lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or ''fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided into three types. Also, leverage is mechanical advantage gained in a system. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage. The ratio of the output force to the input force is the mechanical advantage of the lever. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement. Etymology The word "lever" entered English around 1300 from Old French, in which the word was ''levier''. This sprang from the stem of the verb ''lever'', meaning "to raise". The verb, in turn, goes back to the Latin ''levare'', itself from the adjective ''levis'', meaning "light" (as in "not heavy"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |