|
Flip Chip
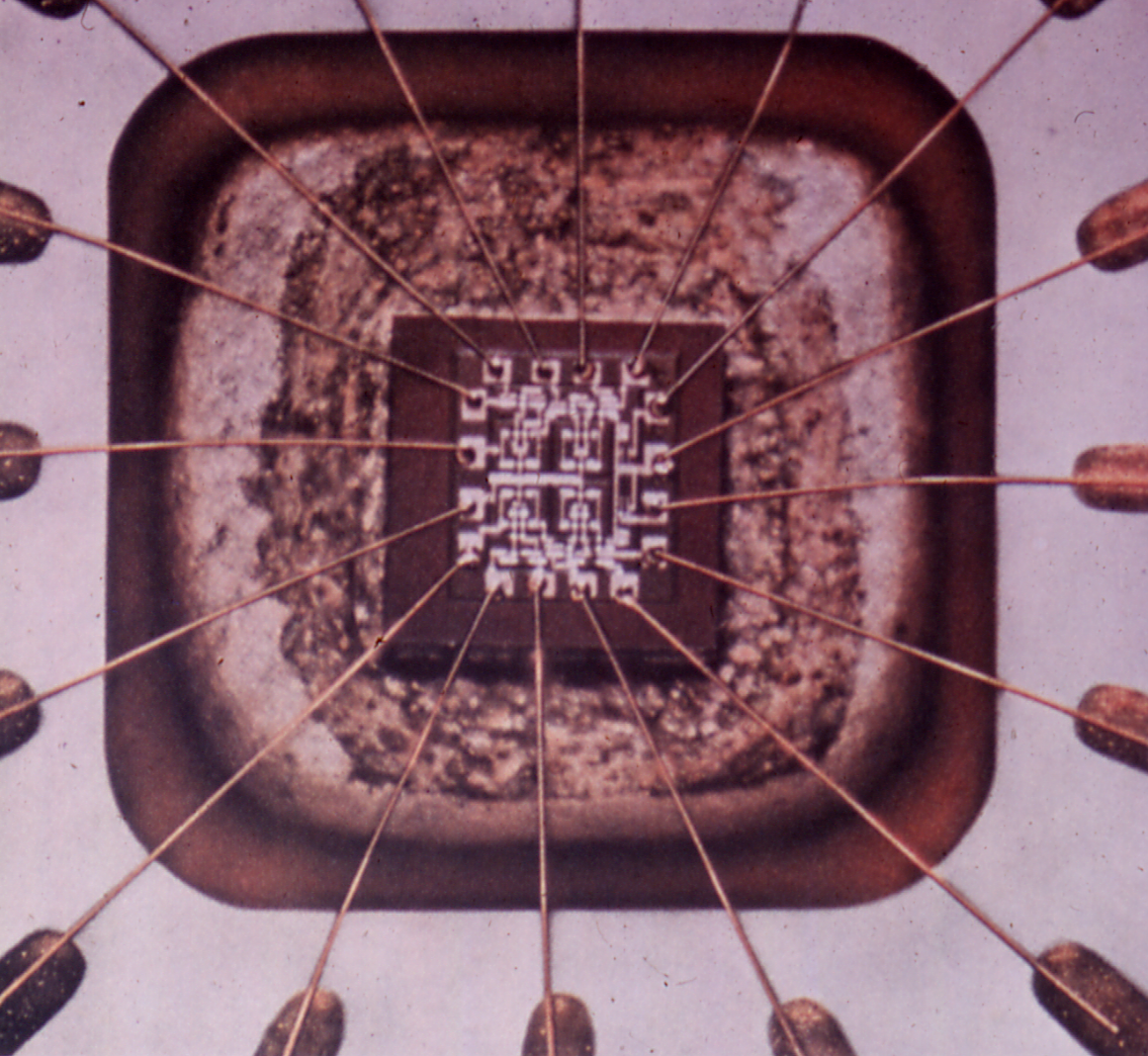
Flip chip, also known as controlled collapse chip connection or its abbreviation, C4, is a method for interconnecting dies such as semiconductor devices, IC chips, integrated passive devices and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), to external circuitry with solder bumps that have been deposited onto the chip pads. The technique was developed by General Electric's Light Military Electronics Department, Utica, New York. The solder bumps are deposited on the chip pads on the top side of the wafer during the final wafer processing step. In order to mount the chip to external circuitry (e.g., a circuit board or another chip or wafer), it is flipped over so that its top side faces down, and aligned so that its pads align with matching pads on the external circuit, and then the solder is reflowed to complete the interconnect. This is in contrast to wire bonding, in which the chip is mounted upright and fine wires are welded onto the chip pads and lead frame contacts to interconnect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celeron Mobile
Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers. Celeron processors are compatible with IA-32 software. They typically offer less performance per clock speed compared to flagship Intel CPU lines, such as the Pentium or Core brands. Celeron branded processors often have less cache or intentionally disabled advanced features, with variable impact on performance. While some Celeron designs have achieved strong performance for their segment, most of the Celeron line has exhibited noticeably degraded performance. This has been the primary justification for the higher cost of other Intel CPU brands versus the Celeron range. Introduced in April 1998, the first Celeron-branded CPU was based on the Pentium II. Subsequent Celeron-branded CPUs were based on the Pentium III, Pentium 4, Pentium M, and Intel Core. In September 2022, Intel announced that the Celeron brand, along with Pentium, will be replaced w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulator (electrical)
An electrical insulator is a material in which electric current does not flow freely. The atoms of the insulator have tightly bound electrons which cannot readily move. Other materials—semiconductors and conductors—conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. The most common examples are non-metals. A perfect insulator does not exist because even insulators contain small numbers of mobile charges (charge carriers) which can carry current. In addition, all insulators become electrically conductive when a sufficiently large voltage is applied that the electric field tears electrons away from the atoms. This is known as the breakdown voltage of an insulator. Some materials such as glass, paper and PTFE, which have high resistivity, are very good electrical insulators. A much larger class of materials, even though they may have lower bulk resistiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions. Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic energy of a substance. When a substance is heated, molecules begin to vibrate and move more, usually creating more distance between themselves. Substances which contract with increasing temperature are unusual, and only occur within limited temperature ranges (see examples below). The relative expansion (also called strain) divided by the change in temperature is called the material's coefficient of linear thermal expansion and generally varies with temperature. As energy in particles increases, they start moving faster and faster weakening the intermolecular forces between them, therefore expanding the substance. Overview Predicting expansion If an equation of state is available, it can be used to predict the values of the thermal expa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductance
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The flow of electric current creates a magnetic field around the conductor. The field strength depends on the magnitude of the current, and follows any changes in current. From Faraday's law of induction, any change in magnetic field through a circuit induces an electromotive force (EMF) (voltage) in the conductors, a process known as electromagnetic induction. This induced voltage created by the changing current has the effect of opposing the change in current. This is stated by Lenz's law, and the voltage is called '' back EMF''. Inductance is defined as the ratio of the induced voltage to the rate of change of current causing it. It is a proportionality factor that depends on the geometry of circuit conductors and the magnetic permeability of nearby materials. An electronic component designed to add inductance to a circuit is called an inductor. It typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roll-to-roll
In the field of electronic devices, roll-to-roll processing, also known as web processing, reel-to-reel processing or R2R, is the process of creating electronic devices on a roll of flexible plastic, metal foil, or flexible glass. In other fields predating this use, it can refer to any process of applying coating, printing, or performing other processes starting with a roll of a flexible material and re-reeling after the process to create an output roll. These processes, and others such as sheeting, can be grouped together under the general term converting. When the rolls of material have been coated, laminated or printed they can be subsequently slit to their finished size on a slitter rewinder. In electronic devices Large circuits made with thin-film transistors and other devices can be patterned onto these large substrates, which can be up to a few meters wide and long. Some of the devices can be patterned directly, much like an inkjet printer deposits ink. For most semico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tape-automated Bonding
Tape-automated bonding (TAB) is a process that places bare semiconductor chips (dies) like integrated circuits onto a flexible circuit board (FPC) by attaching them to fine conductors in a polyamide or polyimide (like trade names Kapton or UPILEX) film carrier. This FPC with the die(s) (TAB inner lead bonding, ILB) can be mounted on the system or module board or assembled inside a package (TAB outer lead bonding, OLB). Typically the FPC includes from one to three conductive layers and all inputs and outputs of the semiconductor die are connected simultaneously during the TAB bonding. Tape automated bonding is one of the methods needed for achieving chip-on-flex (COF) assembly and it is one of the first roll-to-roll processing (also called R2R, reel-to-reel) type methods in the electronics manufacturing. Process The TAB mounting is done such that the bonding sites of the die, usually in the form of bumps or balls made of gold, solder or anisotropic conductive material, are conne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printed Circuit Assembly
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers: each of the conductive layers is designed with an artwork pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto and/or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate. Electrical components may be fixed to conductive pads on the outer layers in the shape designed to accept the component's terminals, generally by means of soldering, to both electrically connect and mechanically fasten them to it. Another manufacturing process adds vias: plated-through holes that allow interconnections between layers. Printed circuit boards are used in nearly all electronic products. Alternatives to PCBs include wire wrap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens AG
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad. The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''Energy'', ''Healthcare'' (Siemens Healthineers), and ''Infrastructure & Cities'', which represent the main activities of the corporation. The corporation is a prominent maker of medical diagnostics equipment and its medical health-care division, which generates about 12 percent of the corporation's total sales, is its second-most profitable unit, after the industrial automation division. In this area, it is regarded as a pioneer and the company with the highest revenue in the world. The corporation is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index. Siemens and its subsidiaries employ approximately 303,000 people worldwide and reported global revenue of around €62 billion in 2021 according to its earnings release. History 1847 to 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Bridge
A thermal bridge, also called a cold bridge, heat bridge, or thermal bypass, is an area or component of an object which has higher thermal conductivity than the surrounding materials, creating a path of least resistance for heat transfer.Gorse, Christopher A., and David Johnston (2012). "Thermal bridge", in ''Oxford Dictionary of Construction, Surveying, and Civil Engineering''. 3rd ed. Oxford: Oxford UP, 2012 pp. 440-441. Print. Thermal bridges result in an overall reduction in thermal resistance of the object. The term is frequently discussed in the context of a building's thermal envelope where thermal bridges result in heat transfer into or out of conditioned space. Thermal bridges in buildings may impact the amount of energy required to heat and cool a space, cause condensation (moisture) within the building envelope, and result in thermal discomfort. In colder climates (such as the United Kingdom), thermal heat bridges can result in additional heat losses and require additiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflow Solder
Reflow soldering is a process in which a solder paste (a sticky mixture of powdered solder and flux) is used to temporarily attach one or thousands of tiny electrical components to their contact pads, after which the entire assembly is subjected to controlled heat. The solder paste reflows in a molten state, creating permanent solder joints. Heating may be accomplished by passing the assembly through a reflow oven, under an infrared lamp, or (unconventionally) by soldering individual joints with a desoldering hot air pencil. Reflow soldering with long industrial convection ovens is the preferred method of soldering surface mount technology components or SMT to a printed circuit board or PCB. Each segment of the oven has a regulated temperature, according to the specific thermal requirements of each assembly. Reflow ovens meant specifically for the soldering of surface mount components may also be used for through-hole components by filling the holes with solder paste and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flip Chip Side-view
Flip, FLIP, or flips may refer to: People * Flip (nickname), a list of people * Lil' Flip (born 1981), American rapper * Flip Simmons, Australian actor and musician * Flip Wilson, American comedian Arts and entertainment Fictional characters * Flip (''Little Nemo''), a cartoon character * Flip, the title character of '' Flip's Twisted World'', a video game * Flip the Frog, a cartoon character * Flip the grasshopper, a character in the children's book '' The Adventures of Maya the Bee'' Music * Flip Records (1950s), a rhythm and blues and doo-wop label based in Los Angeles * Flip Records (1994), a record label in California * Flips, a short name of The Flaming Lips, an American rock band formed in 1983 * ''Flip'' (album), a 1985 solo album by Nils Lofgren * ''The Flip'' (album), a 1969 album by jazz saxophonist Hank Mobley Business * Flip or Flipping, an American term for buying and reselling something quickly, particularly real estate * Flip Burger Boutique, a chain of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermosonic Bonding
Thermosonic bonding is widely used to wire bond silicon integrated circuits into computers. Alexander Coucoulas was named "Father of Thermosonic Bonding" by George Harman, the world's foremost authority on wire bonding, where he referenced Coucoulas's leading edge publications in his book, ''Wire Bonding In Microelectronics''.Coucoulas, A., Trans. Metallurgical Society Of AIME, "Ultrasonic Welding of Aluminum Leads to Tantalum Thin Films", 1966, pp. 587–589. abstract https://sites.google.com/site/coucoulasthermosonicbondaltaCoucoulas, A., "Hot Work Ultrasonic Bonding – A Method Of Facilitating Metal Flow By Restoration Processes", Proc. 20th IEEE Electronic Components Conf. Washington, D.C., May 1970, pp. 549–556.https://sites.google.com/site/hotworkultrasonicbonding Owing to the well proven reliability of thermosonic bonds, it is extensively used to connect the central processing units (CPUs), which are encapsulated silicon integrated circuits that serve as the "brains" of to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(JPG).jpg)