|
Flat-panel Detector
Flat-panel detectors are a class of solid-state x-ray digital radiography devices similar in principle to the image sensors used in digital photography and video. They are used in both projectional radiography and as an alternative to x-ray image intensifiers (IIs) in fluoroscopy equipment. Principles X-rays pass through the subject being imaged and strike one of two types of detectors. Indirect detectors Indirect detectors contain a layer of scintillator material, typically either gadolinium oxysulfide or cesium iodide, which converts the x-rays into light. Directly behind the scintillator layer is an amorphous silicon detector array manufactured using a process very similar to that used to make LCD televisions and computer monitors. Like a TFT-LCD display, millions of roughly 0.2 mm pixels each containing a thin-film transistor form a grid patterned in amorphous silicon on the glass substrate. Unlike an LCD, but similar to a digital camera's image sensor chip, each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin-film Transistor
A thin-film transistor (TFT) is a special type of field-effect transistor (FET) where the transistor is thin relative to the plane of the device. TFTs are grown on a supporting (but non-conducting) substrate. A common substrate is glass, because the traditional application of TFTs is in liquid-crystal displays (LCDs). This differs from the conventional bulk metal oxide field effect transistor ( MOSFET), where the semiconductor material typically ''is'' the substrate, such as a silicon wafer. Design and Manufacture TFTs can be fabricated with a wide variety of semiconductor materials. Because it is naturally abundant and well understood, amorphous or polycrystalline silicon was historically used as the semiconductor layer. However, because of the low mobility of amorphous silicon and the large device-to-device variations found in polycrystalline silicon, other materials have been studied for use in TFTs. These include cadmium selenide, metal oxides such as indium gallium zin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Detectors
X-ray detectors are devices used to measure the flux, spatial distribution, spectrum, and/or other properties of X-rays. Detectors can be divided into two major categories: imaging detectors (such as photographic plates and X-ray film (photographic film), now mostly replaced by various digitizing devices like image plates or flat panel detectors) and dose measurement devices (such as ionization chambers, Geiger counters, and dosimeters used to measure the local radiation exposure, dose, and/or dose rate, for example, for verifying that radiation protection equipment and procedures are effective on an ongoing basis). X-ray imaging To obtain an image with any type of image detector the part of the patient to be X-rayed is placed between the X-ray source and the image receptor to produce a shadow of the internal structure of that particular part of the body. X-rays are partially blocked ("attenuated") by dense tissues such as bone, and pass more easily through soft tissues. Areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
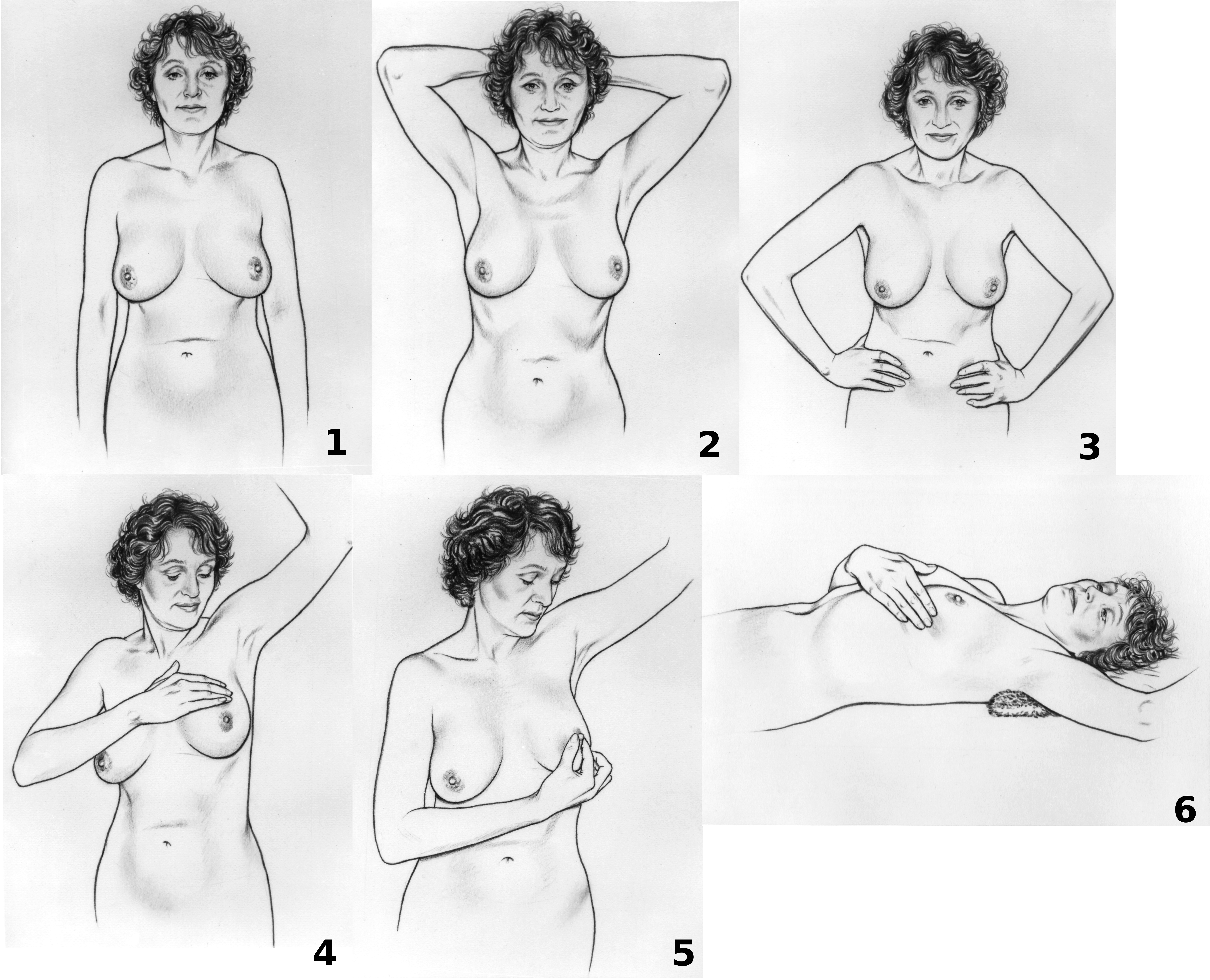
Breast Cancer Screening
Breast cancer screening is the medical screening of asymptomatic, apparently healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to achieve an earlier diagnosis. The assumption is that early detection will improve outcomes. A number of screening tests have been employed, including clinical and self breast exams, mammography, genetic screening, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging. A clinical or self breast exam involves feeling the breast for breast lump, lumps or other abnormalities. Medical evidence, however, does not support its use in women with a typical risk for breast cancer. Universal screening with mammography is controversial as it may not reduce all-cause mortality and may cause harms through unnecessary treatments and medical procedures. Many national organizations recommend it for most older women. The United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening mammography in women at normal risk for breast cancer, every two years between the ages of 50 and 74 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photostimulated Luminescence
Photostimulated luminescence (PSL) is the release of stored energy within a phosphor by stimulation with visible light, to produce a luminescent signal. X-rays may induce such an energy storage. A plate based on this mechanism is called a photostimulable phosphor (PSP) plate and is one type of X-ray detector used in projectional radiography. Creating an image requires illuminating the plate twice: the first exposure, to the radiation of interest, "writes" the image, and a later, second illumination (typically by a visible-wavelength laser) "reads" the image. The device to read such a plate is known as a phosphorimager (occasionally spelled phosphoimager, perhaps reflecting its common application in molecular biology for detecting radiolabeled phosphorylated proteins and nucleic acids). Projectional radiography using a photostimulable phosphor plate as an X-ray detector can be called "phosphor plate radiography" or "computed radiography" (not to be confused with computed tomography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projectional Radiography
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by x-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images are often examined by radiologists. Both the procedure and any resultant images are often simply called "X-ray". Plain radiography or roentgenography generally refers to projectional radiography (without the use of more advanced techniques such as computed tomography that can generate 3D-images). ''Plain radiography'' can also refer to radiography without a radiocontrast agent or radiography that generates single static images, as contrasted to fluoroscopy, which are technically also projectional. Equipment X-ray generator Projectional radiographs generally use X-rays created by X-ray generators, which generate X-rays from X-ray tubes. Grid An anti-scatter grid may be placed between the patient and the detector to reduce the quanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Film
X-ray detectors are devices used to measure the flux, spatial distribution, spectrum, and/or other properties of X-rays. Detectors can be divided into two major categories: imaging detectors (such as photographic plates and X-ray film (photographic film), now mostly replaced by various digitizing devices like image plates or flat panel detectors) and dose measurement devices (such as ionization chambers, Geiger counters, and dosimeters used to measure the local radiation exposure, dose, and/or dose rate, for example, for verifying that radiation protection equipment and procedures are effective on an ongoing basis). X-ray imaging To obtain an image with any type of image detector the part of the patient to be X-rayed is placed between the X-ray source and the image receptor to produce a shadow of the internal structure of that particular part of the body. X-rays are partially blocked ("attenuated") by dense tissues such as bone, and pass more easily through soft tissues. Areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat Panel Detector
Flat-panel detectors are a class of solid-state x-ray digital radiography devices similar in principle to the image sensors used in digital photography and video. They are used in both projectional radiography and as an alternative to x-ray image intensifiers (IIs) in fluoroscopy equipment. Principles X-rays pass through the subject being imaged and strike one of two types of detectors. Indirect detectors Indirect detectors contain a layer of scintillator material, typically either gadolinium oxysulfide or cesium iodide, which converts the x-rays into light. Directly behind the scintillator layer is an amorphous silicon detector array manufactured using a process very similar to that used to make LCD televisions and computer monitors. Like a TFT-LCD display, millions of roughly 0.2 mm pixels each containing a thin-film transistor form a grid patterned in amorphous silicon on the glass substrate. Unlike an LCD, but similar to a digital camera's image sensor chip, each pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Materials'' 12, 476-478 (2013). causing it to harden. Calcifications may be classified on whether there is mineral balance or not, and the location of the calcification. Calcification may also refer to the processes of normal mineral deposition in biological systems, such as the formation of stromatolites or mollusc shells (see Biomineralization). Signs and symptoms Calcification can manifest itself in many ways in the body depending on the location. In the pulpal structure of a tooth, calcification often presents asymptomatically, and is diagnosed as an incidental finding during radiographic interpretation. Individual teeth with calcified pulp will typically respond negatively to vitality testing; teeth with calcified pulp often lack sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
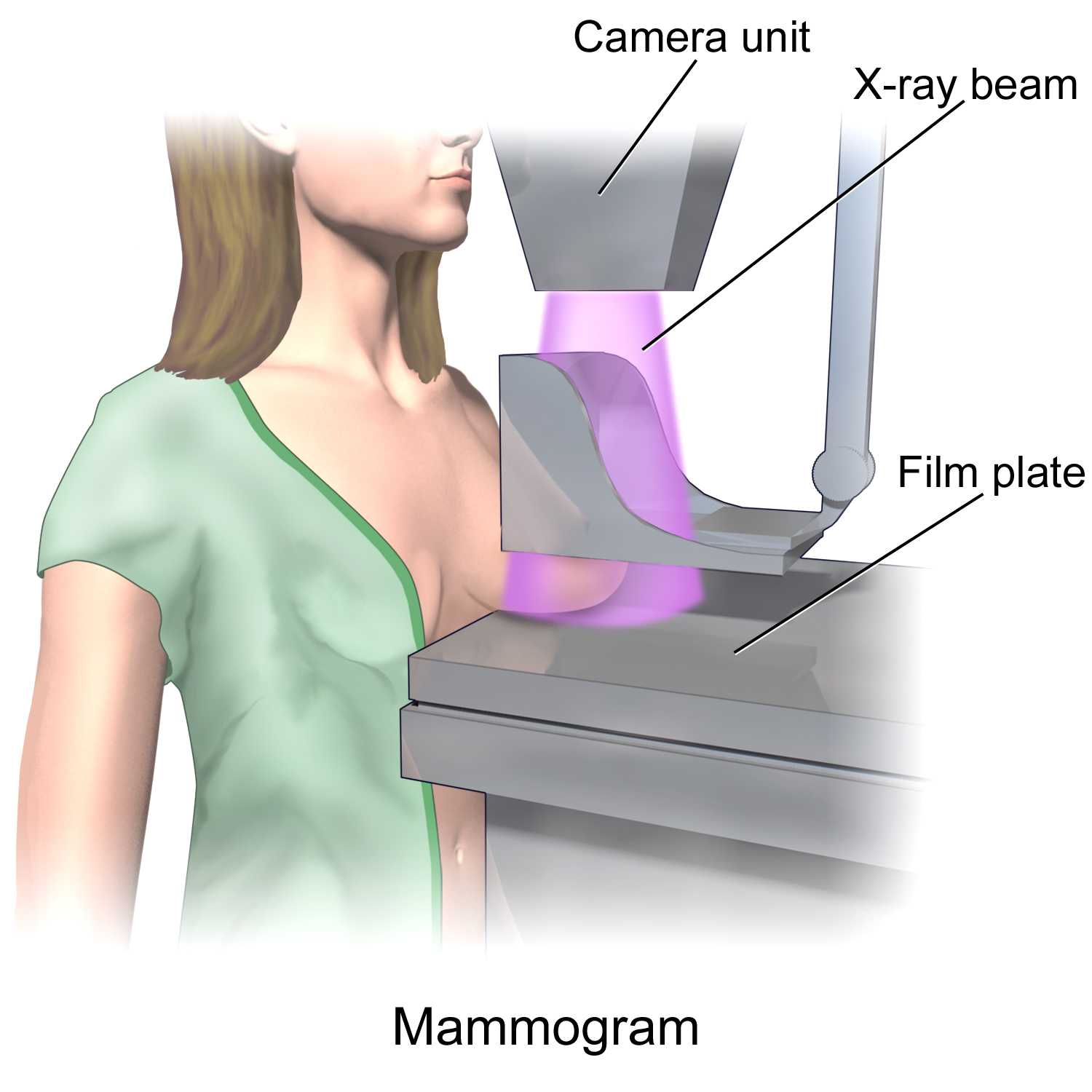
Mammography
Mammography (also called mastography) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses or microcalcifications. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D (tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment and/or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palpable masses that may or may not be seen on mammogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biasing
In electronics, biasing is the setting of DC (direct current) operating conditions (current and voltage) of an active device in an amplifier. Many electronic devices, such as diodes, transistors and vacuum tubes, whose function is processing time-varying ( AC) signals, also require a steady (DC) current or voltage at their terminals to operate correctly. This current or voltage is called ''bias''. The AC signal applied to them is superposed on this DC bias current or voltage. The operating point of a device, also known as bias point, quiescent point, or Q-point, is the DC voltage or current at a specified terminal of an active device (a transistor or vacuum tube) with no input signal applied. A bias circuit is a portion of the device's circuit which supplies this steady current or voltage. Overview In electronics, 'biasing' usually refers to a fixed DC voltage or current applied to a terminal of an electronic component such as a diode, transistor or vacuum tube in a circuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |