|
Frontière De Fer
''Frontière de fer'' or ''pré carré'' is the name given in military historiography to the double line of fortresses that king Louis XIV of France had constructed after the Peace of Nijmegen in 1678 to protect what was then Northern France against foreign invasion, and to be used as operational bases against foreign enemies in the years of the Nine Years' War and the War of the Spanish Succession. This system of defensive lines was later extended to a so-called ''Ceinture de fer'' (Iron Belt) that also encompassed similar systems along the eastern and southern borders of France. The alternative term ''pré carré'' may be based on a misunderstanding.Bély, ''Pré carré'' The term ''pré carré'' was first used by the French military engineer Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban in a letter to the French minister of war François Michel Le Tellier de Louvois of January 1643 in which he wrote:Pujo, p. 63 In this quote Vauban not only introduced the term ''pré carré'' that can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from the High Middle Ages to 1848 during its dissolution. It was also an early French colonial empire, colonial power, with colonies in Asia and Africa, and the largest being New France in North America geographically centred around the Great Lakes. The Kingdom of France was descended directly from the West Francia, western Frankish realm of the Carolingian Empire, which was ceded to Charles the Bald with the Treaty of Verdun (843). A branch of the Carolingian dynasty continued to rule until 987, when Hugh Capet was elected king and founded the Capetian dynasty. The territory remained known as ''Francia'' and its ruler as ('king of the Franks') well into the High Middle Ages. The first king calling himself ('King of France') was Philip II of Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
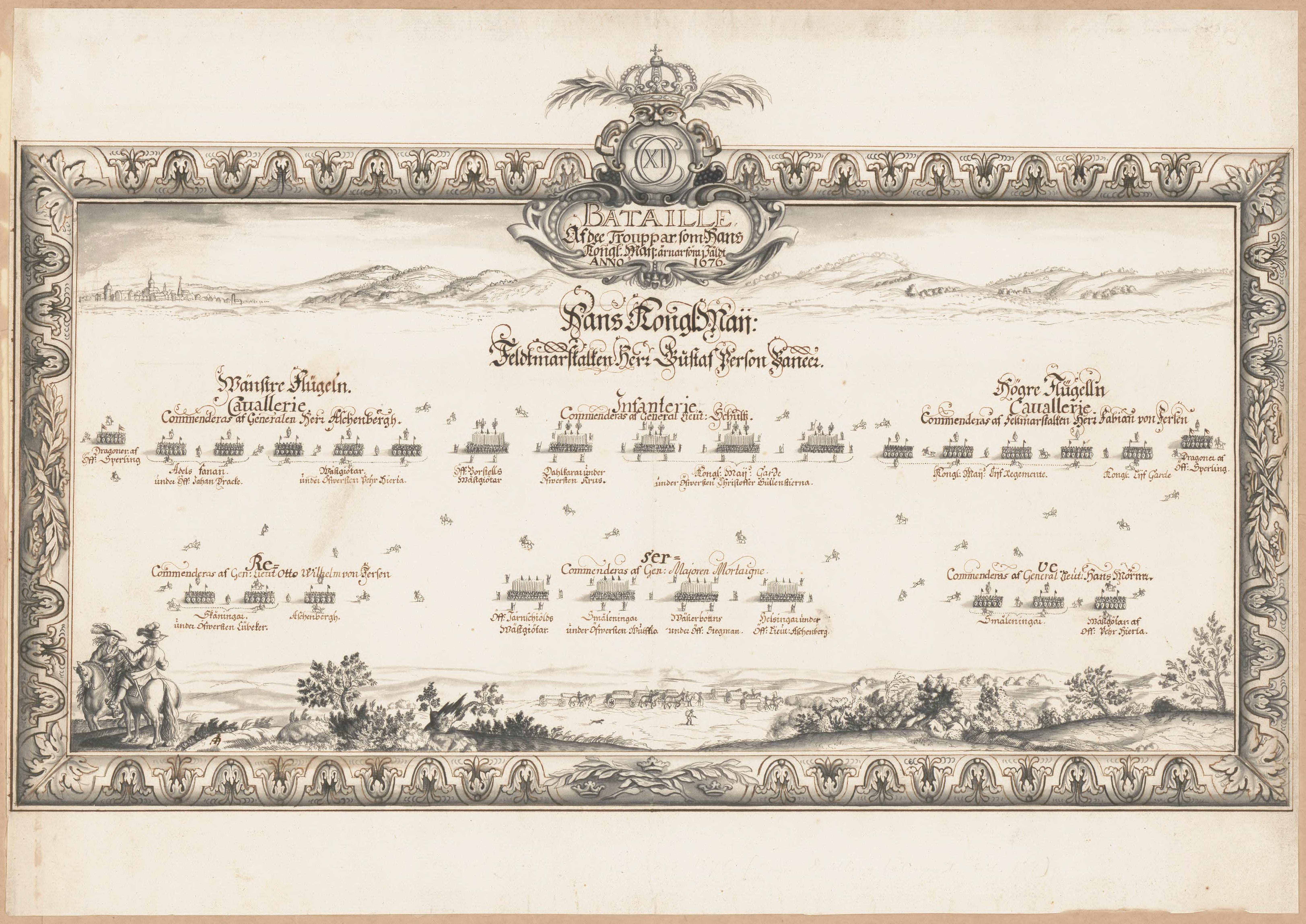
Order Of Battle
Order of battle of an armed force participating in a military operation or campaign shows the hierarchical organization, command structure, strength, disposition of personnel, and equipment of units and formations of the armed force. Various abbreviations are in use, including OOB, O/B, or OB, while ORBAT remains the most common in the United Kingdom. An order of battle is distinct from a Table of Organization and Equipment, table of organisation, which is the intended composition of a given unit or formation according to the military doctrine of its armed force. Historically, an order of battle was the order in which troops were positioned relative to the position of the army commander or the chronological order in which ships were deployed in naval situations. As combat operations develop during a campaign, orders of battle may be revised and altered in response to the military needs and challenges. Also the known details of an order of battle may change during the course of exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouchain
Bouchain (; ) is a commune in the Nord department in northern France. It lies halfway between Cambrai and Valenciennes. Bouchain, seat of the early medieval County of Ostrevent, was taken by Arnulf I, Count of Flanders, in the 10th century and eventually subsumed into the County of Hainaut. During the War of the Spanish Succession, when the town was fortified, Bouchain was besieged twice. On 12 September 1711 it was seized from the French after a 34 day siege by the Grand Alliance led by the Duke of Marlborough. It was again besieged, and recaptured by French forces, on 19 October 1712 after an 18 day siege. Population International relations It is twinned with Halesworth and Eitorf. Heraldry See also * Communes of the Nord department The following is a list of the 647 communes of the Nord department of the French Republic. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025): [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valenciennes
Valenciennes (, also , , ; ; or ; ) is a communes of France, commune in the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department, Hauts-de-France, France. It lies on the Scheldt () river. Although the city and region experienced a steady population decline between 1975 and 1990, it has since rebounded. History Early history In 923, it passed to the Duchy of Lower Lotharingia dependent on the Holy Roman Empire. Once the Empire of the Franks was established, the city began to develop, though the archaeological record has still not revealed all it has to reveal about this period. In 1259, Valenciennes was the site of a General Chapter of the Dominican Order at which Thomas Aquinas together with masters Bonushomo Britto, Florentius, Albert the Great, Albert, and Pope Innocent V, Peter took part in establishing a ''ratio studiorum'' or program of studies for the Dominican Order that featured the study of philosophy as an innovation for those not sufficiently trained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arras
Arras ( , ; ; historical ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department, which forms part of the region of Hauts-de-France; before the reorganization of 2014 it was in Nord-Pas-de-Calais. The historic centre of the Artois region, with a Baroque town square, Arras is in northern France at the confluence of the rivers Scarpe and Crinchon. The Arras plain is on a large chalk plateau bordered on the north by the Marqueffles fault, on the southwest by the Artois and Ternois hills, and on the south by the slopes of Beaufort-Blavincourt. On the east it is connected to the Scarpe valley. Saint Vedast (or St. Vaast) was the first Catholic bishop in the year 499 and tried to eliminate paganism among the Franks. By 843, Arras was seat of the County of Artois which became part of the Royal domain in 1191. The first mention of the name ''Arras'' appeared in the 12th century. Some hypothesize it is a contraction of '' Atrebates'', a Belgic tribe of Gaul and Britain that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douai
Douai ( , , ; ; ; formerly spelled Douay or Doway in English) is a city in the Nord (French department), Nord département in northern France. It is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture of the department. Located on the river Scarpe (river), Scarpe some from Lille and from Arras, Douai is home to one of the region's most impressive belfry (architecture), belfries. History Its site probably corresponds to that of a 4th-century Roman fortress known as Duacum. From the 10th century, the town was a Romance languages, romance fiefdom of the Count of Flanders, counts of County of Flanders, Flanders. The town became a flourishing textile market centre during the Middle Ages, historically known as Douay or Doway in English. In 1384, the county of Flanders passed into the domains of the Dukes of Burgundy and thence in 1477 into Habsburg possessions. In 1667, Douai was taken by the troops of Louis XIV of France, and by the 1668 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1668), Treaty of Aix-la-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tournai
Tournai ( , ; ; ; , sometimes Anglicisation (linguistics), anglicised in older sources as "Tournay") is a city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality of Wallonia located in the Hainaut Province, Province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies by road southwest of the centre of Brussels on the river Scheldt, and is part of Eurometropolis Lille–Kortrijk–Tournai, In 2022, the municipality of Tournai had an estimated population of 68,518 people. Tournai is one of the oldest cities in Belgium and has played an important role in the country's cultural history. It was the first capital of the Francia, Frankish Empire, with Clovis I being born here. Geography Tournai lies by road southwest of the centre of Brussels on the river Scheldt. Administratively, the town and municipality is part of the Hainaut Province, Province of Hainaut, in the Wallonia region of southwest Belgium. The municipality has an area of . Tournai has its own Arrondissements of Belgium, arrondissements, both ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condé-sur-l'Escaut
Condé-sur-l'Escaut (, literally ''Condé on the Escaut''; ) is a commune of the Nord department in northern France. It lies on the border with Belgium. The population as of 1999 was 10,527. Residents of the area are known as Condéens or Condéennes. The Mayor of Condé-sur-l'Escaut is Gregory Lelong, re-elected in 2020. Geography Condé-sur-l'Escaut is northeast of Valenciennes, from Lille, and from Brussels, Belgium. It is situated at the confluence of the Haine and Scheldt rivers. The region is noted for its coal mines, resources which made it a strategic objective in both world wars. History The name comes from a Celtic word, "Condate", meaning "confluence", referring to the two rivers. A Romanised form of the word, Condatum, was in use during the Roman period, and "Condé" was in use by the 14th century. The current name, Condé-sur-l'Escaut, dates from 1886. Being at the confluence of two rivers, the site has had military importance since before Roman times. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mons, Belgium
Mons (; German and , ; Walloon language, Walloon and ) is a City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities of Belgium, municipality of Wallonia, and the capital of the Hainaut Province, province of Hainaut, Belgium. Mons was made into a fortified city by Count Baldwin IV, Count of Hainaut, Baldwin IV of County of Hainaut, Hainaut in the 12th century. The population grew quickly, trade flourished, and several commercial buildings were erected near the Grand-Place. In 1814, King William I of the Netherlands increased the fortifications, following the fall of the First French Empire. The Industrial Revolution and coal mining made Mons a centre of heavy industry. In 1830, Belgium gained its independence and the decision was made to dismantle the fortifications, allowing the creation of large boulevards and other urban projects. In 1914, Mons was the location of the Battle of Mons. The British were forced to withdrawal (military), retreat by a numerically superior German force and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flood
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant concern in agriculture, civil engineering and public health. Environmental issues, Human changes to the environment often increase the intensity and frequency of flooding. Examples for human changes are land use changes such as deforestation and Wetland conservation, removal of wetlands, changes in waterway course or flood controls such as with levees. Global environmental issues also influence causes of floods, namely climate change which causes an Effects of climate change on the water cycle, intensification of the water cycle and sea level rise. For example, climate change makes Extreme weather, extreme weather events more frequent and stronger. This leads to more intense floods and increased flood risk. Natural types of floods include riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maneuver Warfare
Maneuver warfare, or manoeuvre warfare, is a military strategy which emphasizes movement, initiative and surprise to achieve a position of advantage. Maneuver seeks to inflict losses indirectly by envelopment, encirclement and disruption, while minimizing the need to engage in frontal combat. In contrast to attrition warfare where strength tends to be applied against strength, maneuver warfare attempts to apply strength against weakness in order to accomplish the mission. Maneuver warfare, the use of initiative, originality and the unexpected, combined with a ruthless determination to succeed, seeks to avoid opponents' strengths while exploiting their weaknesses and attacking their critical vulnerabilities and is the conceptual opposite of attrition warfare. Rather than seeking victory by applying superior force and mass to achieve physical destruction, maneuver uses preemption, deception, dislocation, and disruption to destroy the enemy's will and ability to fight. Historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince-Bishopric Of Liège
The Prince-Bishopric of Liège or Principality of Liège was a Roman Catholic ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that was situated for the most part in present-day Belgium. It was an Imperial Estate, so the bishop of Liège, as its prince, had a seat and a vote in the Imperial Diet. The Prince-Bishopric of Liège should not be confused with the Diocese of Liège, which was larger and over which the prince-bishop exercised only the usual responsibilities of a bishop. The bishops of Liège acquired their status as prince-bishops between 980 and 985 when Bishop Notker of Liège, who had been the bishop since 972, received secular control of the County of Huy from Emperor Otto II. From 1500, the prince-bishopric belonged to the Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle. Its territory included most of the present Belgian provinces of Liège and Limburg, and some exclaves in other parts of Belgium and the Netherlands. The ecclesiastical state briefly became a republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |