|
Form-factor
Form factor is a hardware design aspect that defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of components, particularly in electronics. A form factor may represent a broad class of similarly sized components, or it may prescribe a specific standard. It may also define an entire system, as in a computer form factor. Evolution and standardization As electronic hardware has become smaller following Moore's law and related patterns, ever-smaller form factors have become feasible. Specific technological advances, such as PCI Express, have had a significant design impact, though form factors have historically been slower to evolve than individual components. Standardization of form factors is vital for compatibility of hardware from different manufacturers. Trade-offs Smaller form factors may offer more efficient use of limited space, greater flexibility in the placement of components within a larger assembly, reduced use of material, and greater ease of tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Form Factor (desktop And Motherboard)
Small form factor (SFF or SFX) is a term used for desktop computers, and their enclosures and motherboards, to indicate that they are designed in accordance with one of several standardized computer form factors intended to minimize the volume and footprint of a desktop computer compared to the standard ATX form factor. For comparison purposes, the size of an SFF case is usually measured in litres. SFFs are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, including shoeboxes, cubes, and book-sized PCs. Their smaller and often lighter construction has made them popular as home theater PCs and as gaming computers for attending LAN parties. Manufacturers also emphasize the aesthetic and ergonomic design of SFFs since users are more likely to place them on top of a desk or carry them around. Advancements in component technology together with reductions in size means a powerful computer is no longer restricted to the huge towers of old. Small form factors do not include computing dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
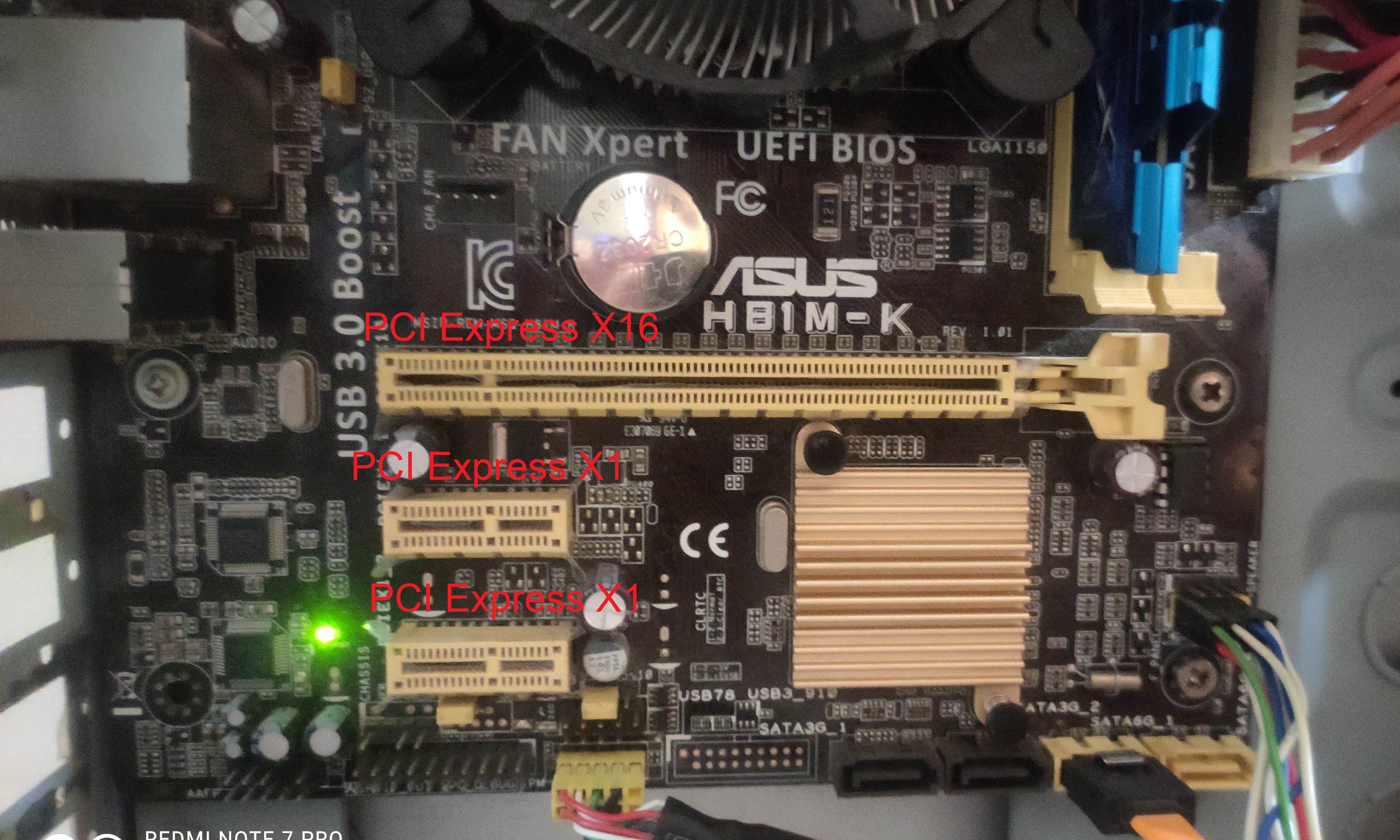
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism (Advanced Error Reporting, AER), and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization. The PCI Express electrical interface is measured by the number of simultaneous lanes. (A lane is a single send/receive line of data. The analogy is a highway with traffic in both direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra-mobile PC
An ultra-mobile PC, or ultra-mobile personal computer (UMPC), is a miniature version of a pen computer, a class of laptop whose specifications were launched by Microsoft and Intel in spring 2006. Sony had already made a first attempt in this direction in 2004 with its Vaio U series, which was only sold in Asia. UMPCs are generally smaller than subnotebooks, have a TFT display measuring (diagonally) about , are operated like tablet PCs using a touchscreen or a stylus, and can also have a physical keyboard. There is no clear boundary between subnotebooks and ultra-mobile PCs, but UMPCs commonly have Major factors other than the common clamshell laptop design, such as having small keys on either side of the screen, or having a slide-out keyboard. The first-generation UMPCs were simple PCs running Linux or an adapted version of Microsoft's tablet PC operating system. With the announcement of the UMPC, Microsoft dropped the licensing requirement that tablet PCs must support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subnotebook
Subnotebook, also called ultraportable, superportable, or mini notebook, was a marketing term for laptop computers that are smaller and lighter than a typical notebook-sized laptop. Types and sizes As typical laptop sizes have decreased over the course of the 2010s, and other distinguishing features have become mainstream, the distinction between regular-size and 'subnotebook' laptops has largely disappeared. To the extent that it still exists, 'subnotebook' could be defined as machines with screen smaller than 13" but with a permanently-attached keyboard intended for two-handed typing. Prior to this convergence, subnotebooks were also distinguished from netbooks and ultra-mobile PCs, based on both size and market position. Classic subnotebooks were smaller than full sized laptops but larger than handheld computers. They were distinguished by smaller screens and bodies and lighter weights relative to contemporaneous laptops. The savings in size and weight were often achieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
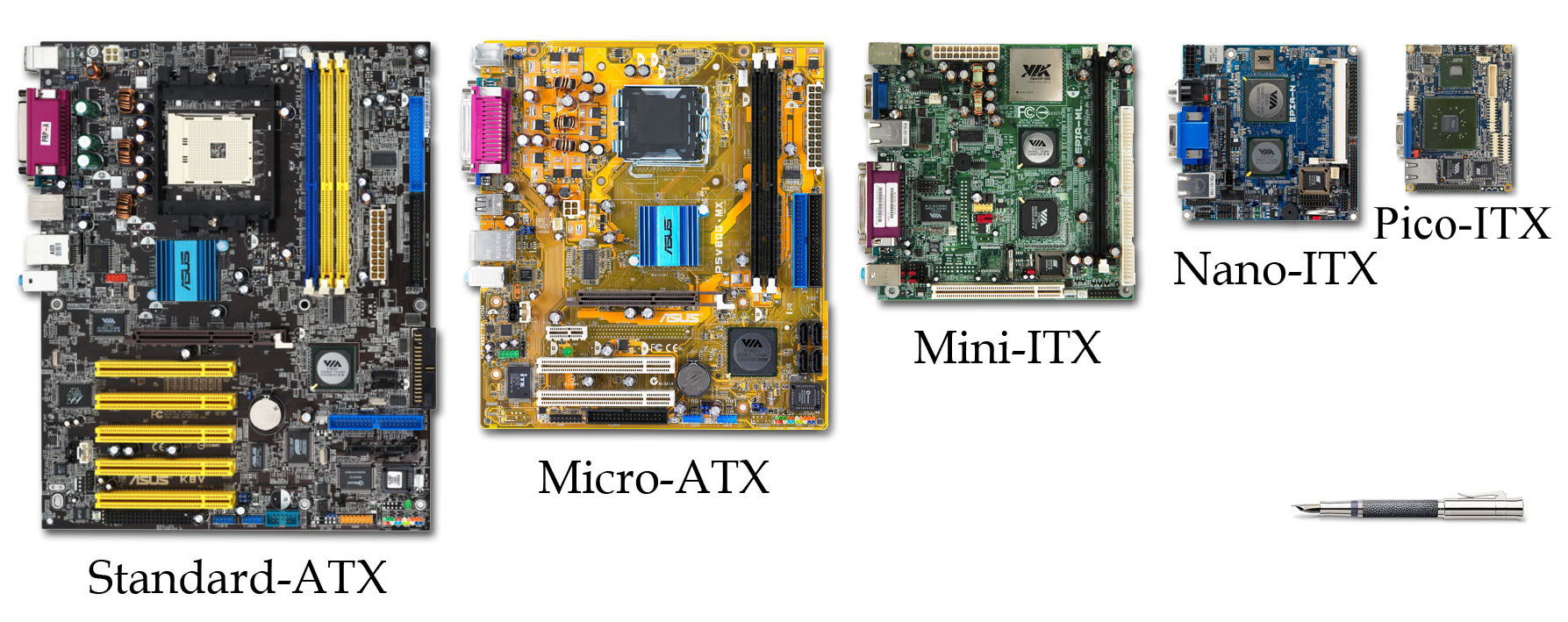
Motherboard Form Factor
In computing, the motherboard form factor is the specification of a motherboard – the dimensions, power supply type, location of mounting holes, number of ports on the back panel, etc. Specifically, in the IBM PC compatible industry, standard form factors ensure that parts are interchangeable across competing vendors and generations of technology, while in enterprise computing, form factors ensure that server modules fit into existing rackmount systems. Traditionally, the most significant specification is for that of the motherboard, which generally dictates the overall size of the case. Small form factors have been developed and implemented. Overview of form factors A PC motherboard is the main circuit board within a typical desktop computer, laptop or server. Its main functions are as follows: * To serve as a central backbone to which all other modular parts such as CPU, RAM, and hard drives can be attached as required to create a computer * To be interchangeable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk Drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box. Introduced by IBM in 1956, HDDs were the dominant secondary storage device for general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of servers and personal computers, though personal computing devices produced in large volume, like cell phones and tablets, rely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Cooling
Computer cooling is required to remove the waste heat produced by computer components, to keep components within permissible operating temperature limits. Components that are susceptible to temporary malfunction or permanent failure if overheated include integrated circuits such as central processing units (CPUs), chipsets, graphics cards, and hard disk drives. Components are often designed to generate as little heat as possible, and computers and operating systems may be designed to reduce power consumption and consequent heating according to workload, but more heat may still be produced than can be removed without attention to cooling. Use of heatsinks cooled by airflow reduces the temperature rise produced by a given amount of heat. Attention to patterns of airflow can prevent the development of hotspots. Computer fans are widely used along with heatsink fans to reduce temperature by actively exhausting hot air. There are also more exotic cooling techniques, such as liq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clamshell Design
The flip phone or clamshell is a form factor of a mobile phone or other device which is in two or more sections that fold via a hinge. If the hinge is on a long edge the device is more likely to be called clamshell than flip phone (e.g., Nokia Communicators). Generally speaking, the interface components such as keys and display are kept inside the closed clamshell, protecting them from damage and unintentional use while also making the device shorter or narrower so it is easier to carry around. In many cases, opening the clamshell offers more surface area than when the device is closed, allowing interface components to be larger and easier to use than on devices which do not flip open. A disadvantage of the clamshell design is the connecting hinge, which is prone to fatigue or failure. Etymology The clamshell form factor is most closely associated with the cell phone market, as Motorola used to have a trademark on the term "flip phone", but the term "flip phone" has becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laptop
A laptop, laptop computer, or notebook computer is a small, portable personal computer (PC) with a screen and alphanumeric keyboard. Laptops typically have a clam shell form factor with the screen mounted on the inside of the upper lid and the keyboard on the inside of the lower lid, although 2-in-1 PCs with a detachable keyboard are often marketed as laptops or as having a "laptop mode". Laptops are folded shut for transportation, and thus are suitable for mobile use. They are so named because they can be practically placed on a person's lap when being used. Today, laptops are used in a variety of settings, such as at work, in education, for playing games, web browsing, for personal multimedia, and for general home computer use. As of 2022, in American English, the terms ''laptop computer'' and ''notebook computer'' are used interchangeably; in other dialects of English, one or the other may be preferred. Although the terms ''notebook computers'' or ''notebooks'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Enclosure
A disk enclosure is a specialized casing designed to hold and power disk drives while providing a mechanism to allow them to communicate to one or more separate computers. Drive enclosures provide power to the drives therein and convert the data sent across their native data bus into a format usable by an external connection on the computer to which it is connected. In some cases, the conversion is as trivial as carrying a signal between different connector types. In others, it is complicated enough to require a separate embedded system to retransmit data over connector and signal of a different standard. Factory-assembled external hard disk drives, external DVD-ROM drives, and others consist of a storage device in a disk enclosure. Benefits Key benefits to using external disk enclosures include: *Adding additional storage space and media types to small form factor and laptop computers, as well as sealed embedded systems such as digital video recorders and video game con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portable Computer
A portable computer is a computer designed to be easily moved from one place to another and included a display and keyboard together, with a single plug, much like later desktop computers called '' all-in-ones'' (AIO), that integrate the system's internal components into the same case as the display. The first commercially sold portable might be the MCM/70, released 1974. The next major portables were the IBM 5100 (1975), Osborne's CP/M-based Osborne 1 (1981) and Compaq's , advertised as 100% IBM PC compatible Compaq Portable (1983). These luggable computers still required a continuous connection to an external power source; this limitation was later overcome by the laptop. Laptops were followed by lighter models, so that in the 2000s mobile devices and by 2007 smartphones made the term almost meaningless. The 2010s introduced wearable computers such as smartwatches. Portable computers, by their nature, are generally microcomputers. Larger portable computers were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All-in-one PC
An all-in-one computer or all-in-one PC (AIO) is a personal computer that integrates the system's internal components into the same case as the display, thus occupying a smaller footprint (with fewer cables) than desktops that incorporate a tower. Advantages and disadvantages Some advantages of the all-in-one computer compared to other form factors include being easier to set up, a reduced physical footprint, ease of transportation, and the option to interface with the computer via touchscreen (a now-common fixture on all-in-ones). Some disadvantages include generally being more expensive than desktop computers, a lack of customizability—most of the internal hardware such as the RAM and the SSD, especially in post-late-2010s machines, is soldered onto the system board—a lack of upgrade paths for the CPU, RAM, and technology of the display, and the difficulty of repair. History This form factor was popular during the early 1980s for personal computers intended for professi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |