|
Fluoridation
Water fluoridation is the controlled addition of fluoride to public water supplies to reduce tooth decay. Fluoridated water maintains fluoride levels effective for cavity prevention, achieved naturally or through supplementation. In the mouth, fluoride slows tooth enamel demineralization and enhances remineralization in early-stage cavities. Defluoridation is necessary when natural fluoride exceeds recommended limits. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends fluoride levels of 0.5–1.5 mg/L, depending on climate and other factors. In the U.S., the recommended level has been 0.7 mg/L since 2015, lowered from 1.2 mg/L. Bottled water often has unknown fluoride levels. Tooth decay affects 60–90% of schoolchildren worldwide. Fluoridation reduces cavities in children, with Cochrane reviews estimating reductions of 35% in baby teeth and 26% in permanent teeth when no other fluoride sources are available, though efficacy in adults is less clear. In Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic, Monatomic ion, monatomic Ion#Anions and cations, anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts typically have distinctive bitter tastes, and are odorless. Its salts and minerals are important Reagent, chemical reagents and industrial chemicals, mainly used in the production of hydrogen fluoride for fluorocarbons. Fluoride is classified as a weak base since it only partially associates in solution, but concentrated fluoride is corrosive and can attack the skin. Fluoride is the simplest fluorine anion. In terms of charge and size, the fluoride ion resembles the hydroxide ion. Fluoride ions occur on Earth in several minerals, particularly fluorite, but are present only in trace quantities in bodies of water in nature. Nomenclature Fluorides include compounds that contain ionic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major Tissue (biology), tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the Crown (tooth), crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and Pulp (tooth), dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface. Features Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and contains the highest percentage of minerals (at 96%),Ross ''et al.'', p. 485 with water and organic material composing the rest.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nancy, Elsevier, pp. 70–94 The primary mineral is hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. Enamel is formed on the tooth while the tooth develops wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottled Water
Bottled water is drinking water (e.g., Water well, well water, distilled water, Reverse osmosis, reverse osmosis water, mineral water, or Spring (hydrology), spring water) packaged in Plastic bottle, plastic or Glass bottle, glass water bottles. Bottled water may be Carbonated water, carbonated or not, with packaging sizes ranging from small single serving bottles to large carboys for water coolers. The consumption of bottled water is influenced by factors such as convenience, taste, perceived safety, and concerns over the quality of municipal tap water. Concerns about the environmental impact of bottled water, including the production and disposal of plastic bottles, have led to calls for more sustainable practices in the industry. History Although vessels to bottle and transport water were part of the earliest human civilizations, bottling water began in the United Kingdom with the first water bottling at the Holy Well, Malvern, Holy Well in 1622. The demand for bottled wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topical Fluoride
Topical fluorides are fluoride-containing drugs indicated in prevention and treatment of dental caries, particularly in children's primary dentitions. The dental-protecting property of topical fluoride can be attributed to multiple mechanisms of action, including the promotion of remineralization of decalcified enamel, the inhibition of the cariogenic microbial metabolism in dental plaque and the increase of tooth resistance to acid dissolution. Topical fluoride is available in a variety of dose forms, for example, toothpaste, mouth rinses, varnish and silver diamine solution. These dosage forms possess different absorption mechanisms and consist of different active ingredients. Common active ingredients include sodium fluoride, stannous fluoride, silver diamine fluoride. These ingredients account for different pharmacokinetic profiles, thereby having varied dosing regimes and therapeutic effects. A minority of individuals may experience certain adverse effects, including dermatolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is a measurement used by economics, economists and sociology, sociologsts. The measurement combines a person's work experience and their or their family's access to economic resources and social position in relation to others. In common parlance, "socioeconomic status" is synonymous with social class. However, academics distinguish social class from socioeconomic status, using the former to refer to one's relatively stable cultural background and the latter to refer to one's current social and economic situation which is consequently more changeable over time. When analyzing a family's SES, the household income and the education and occupations of its members are examined, whereas for an individual's SES only their own attributes are assessed. Recently, research has revealed a lesser-recognized attribute of SES as perceived financial stress, as it defines the "balance between income and necessary expenses". Perceived financial stress can be tested by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
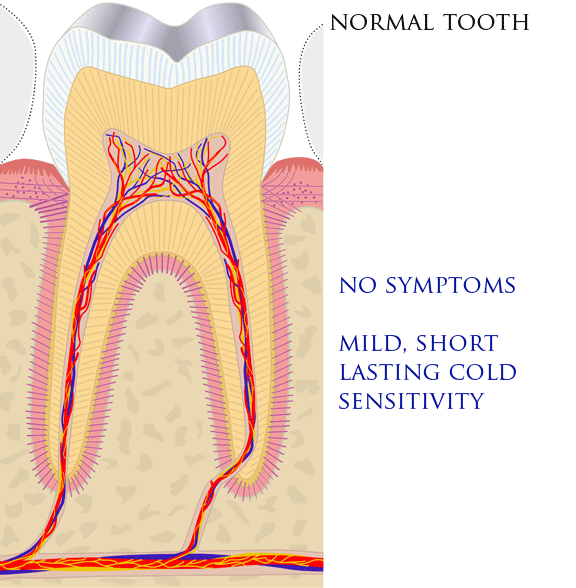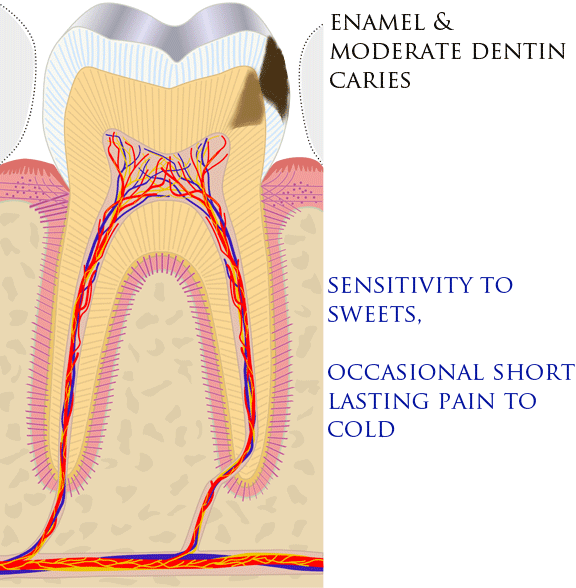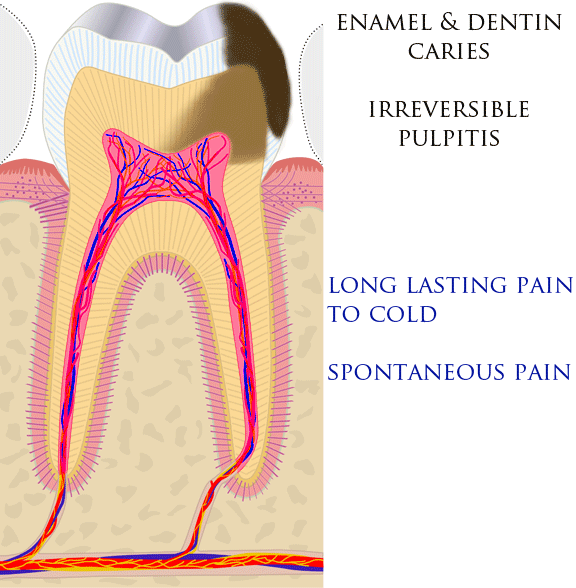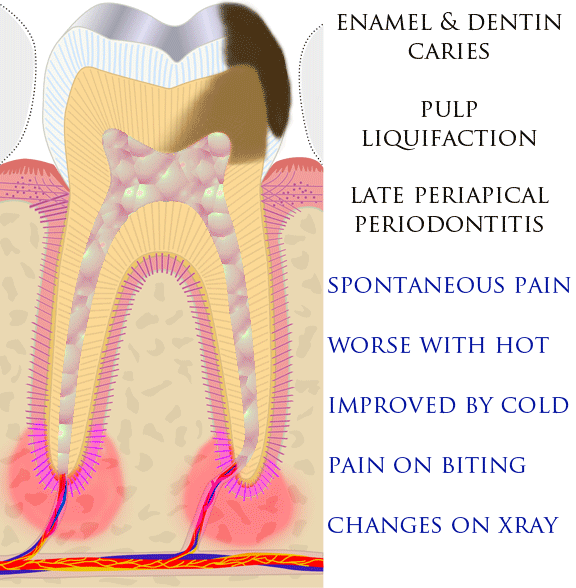
Tooth Pain
Toothaches, also known as dental pain or tooth pain,Segen JC. (2002). ''McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine''. The McGraw-Hill Companies. is pain in the teeth or their supporting structures, caused by dental diseases or pain referred to the teeth by non-dental diseases. When severe it may impact sleep, eating, and other daily activities. Common causes include inflammation of the pulp, (usually in response to tooth decay, dental trauma, or other factors), dentin hypersensitivity, apical periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone around the root apex), dental abscesses (localized collections of pus), alveolar osteitis ("dry socket", a possible complication of tooth extraction), acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (a gum infection), and temporomandibular disorder. Pulpitis is reversible when the pain is mild to moderate and lasts for a short time after a stimulus (for instance cold); or irreversible when the pain is severe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eating
Eating (also known as consuming) is the ingestion of food. In biology, this is typically done to provide a heterotrophic organism with energy and nutrients and to allow for growth. Animals and other heterotrophs must eat in order to survive – carnivores eat other animals, herbivores eat plants, omnivores consume a mixture of both plant and animal matter, and detritivores eat detritus. Fungi digest organic matter outside their bodies as opposed to animals that digest their food inside their bodies. For humans, eating is more complex, but is typically an activity of daily living. Physicians and dieticians consider a healthful diet essential for maintaining peak physical condition. Some individuals may limit their amount of nutritional intake. This may be a result of a lifestyle choice: as part of a diet or as religious fasting. Limited consumption may be due to hunger or famine. Overconsumption of calories may lead to obesity and the reasons behind it are myriad, however, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Of Life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards and concerns". Standard indicators of the quality of life include wealth, employment, the environment, physical and mental health, education, recreation and leisure time, social belonging, religious beliefs, safety, security and freedom. QOL has a wide range of contexts, including the fields of international development, healthcare, politics and employment. Health related QOL (HRQOL) is an evaluation of QOL and its relationship with health. Engaged theory One approach, called the engaged theory, outlined in the journal of ''Applied Research in the Quality of Life'', posits four domains in assessing quality of life: ecology, economics, politics and culture. In the domain of culture, for example, it includes the following subd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrialized Countries
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are the gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), the per capita income, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living. Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate. Different definitions of developed countries are provided by the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank; moreover, HDI ranking is used to reflect the composite index of life expectancy, education, and income per capita. In 2025, 40 countries fit all three criteria, while an additional 21 countries fit two out of three. Developed countries have generally more advanced post-industrial economies, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Diseases
A chronic condition (also known as chronic disease or chronic illness) is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term ''chronic'' is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. Common chronic diseases include diabetes, functional gastrointestinal disorder, eczema, arthritis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, autoimmune diseases, genetic disorders and some viral diseases such as hepatitis C and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. An illness which is lifelong because it ends in death is a terminal illness. It is possible and not unexpected for an illness to change in definition from terminal to chronic as medicine progresses. Diabetes and HIV for example were once terminal yet are now considered chronic, due to the availability of insulin for diabetics and daily drug treatment for individuals with HIV, which allow these individuals to live wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amalgam (dentistry)
In dentistry, amalgam is an alloy of Mercury (element), mercury used to fill Tooth decay, teeth cavities. It is made by mixing a combination of liquid mercury and particles of solid metals such as silver, copper or tin. The amalgam is mixed by the dentist just before use. It remains soft for a short while after mixing, which facilitates it being snugly packed into the cavity and shaped before it sets hard. Dental amalgams were first documented in a Tang dynasty medical text written by Su Gong (苏恭) in 659, and appeared in Germany in 1528. In the 1800s, amalgam became the dental restorative material of choice due to its low cost, ease of application, strength, and durability. History of use There are, according to Geir Bjørklund, indications that dental amalgam was used in the first part of the Tang dynasty in China (AD 618–907), and in Germany by Strockerus in about 1528. Evidence of a dental amalgam first appears in the Tang dynasty medical text ''Xinxiu bencao'' (新 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |