|
Flow Separation
In fluid dynamics, flow separation or boundary layer separation is the detachment of a boundary layer from a surface into a wake. A boundary layer exists whenever there is relative movement between a fluid and a solid surface with viscous forces present in the layer of fluid close to the surface. The flow can be externally, around a body, or internally, in an enclosed passage. Boundary layers can be either laminar or turbulent. A reasonable assessment of whether the boundary layer will be laminar or turbulent can be made by calculating the Reynolds number of the local flow conditions. Separation occurs in flow that is slowing down, with pressure increasing, after passing the thickest part of a streamline body or passing through a widening passage, for example. Flowing against an increasing pressure is known as flowing in an adverse pressure gradient. The boundary layer separates when it has travelled far enough in an adverse pressure gradient that the speed of the bounda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbulator
A turbulator is a device that turns a laminar boundary layer into a turbulent boundary layer. Device Turbulent flow can be desired on parts of the surface of an aircraft wing (airfoil) or in industrial applications such as heat exchangers and the mixing of fluids. The term “turbulator” is applied to a variety of applications and is used as a derivative of the word turbulent. However, the word has no commonly accepted technical or scientific meaning. It has been approved as a trademark in the U.S. and other countries in conjunction with machine parts used within rotating drums, sterilizers, heat transfer ovens, mixing and pelletizing machines, and air destratification fans for horticultural and agricultural uses, among others. In gliders the turbulator is often a thin zig-zag strip that is placed on the lower side of the wing and sometimes on the vertical stabilizer. In wind sensors ( anemometers), the use of turbulators reduces inaccuracies in the measurement of wind sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple-deck Theory
Triple deck theory is a theory that describes a three-layered boundary-layer structure when sufficiently large disturbances are present in the boundary layer. This theory is able to successfully explain the phenomenon of boundary layer separation, but it has found applications in many other flow setups as well, including the scaling of the lower-branch instability ( T-S) of the Blasius flow, etc. James Lighthill, Lev Landau and others were the first to realize that to explain boundary layer separation, different scales other than the classical boundary-layer scales need to be introduced. These scales were first introduced independently by James Lighthill and E. A. Müller in 1953. The triple-layer structure itself was independently discovered by Keith Stewartson (1969) and V. Y. Neiland (1969) and by A. F. Messiter (1970). Stewartson and Messiter considered the separated flow near the trailing edge of a flat plate, whereas Neiland studied the case of a shock impinging on a boundary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance Frequency
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximum amplitude response in the system. When this happens, the object or system absorbs energy from the external force and starts vibrating with a larger amplitude. Resonance can occur in various systems, such as mechanical, electrical, or acoustic systems, and it is often desirable in certain applications, such as musical instruments or radio receivers. However, resonance can also be detrimental, leading to excessive vibrations or even structural failure in some cases. All systems, including molecular systems and particles, tend to vibrate at a natural frequency depending upon their structure; when there is very little damping this frequency is approximately equal to, but slightly above, the resonant frequency. When an oscillating force, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kármán Vortex Street
In fluid dynamics, a Kármán vortex street (or a von Kármán vortex street) is a repeating pattern of swirling vortices, caused by a process known as '' vortex shedding,'' which is responsible for the unsteady separation of flow of a fluid around blunt bodies. It is named after the engineer and fluid dynamicist Theodore von Kármán, and is responsible for such phenomena as the "singing" of suspended telephone or power lines and the vibration of a car antenna at certain speeds. Mathematical modeling of von Kármán vortex street can be performed using different techniques including but not limited to solving the full Navier-Stokes equations with k-epsilon, SST, k-omega and Reynolds stress, and large eddy simulation (LES) turbulence models, by numerically solving some dynamic equations such as the Ginzburg–Landau equation, or by use of a bicomplex variable. Analysis A vortex street forms only at a certain range of flow velocities, specified by a range of Reynolds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressor Stall
A compressor stall is a local disruption of the airflow in the compressor of a gas turbine or turbocharger. A stall that results in the complete disruption of the airflow through the compressor is referred to as a compressor surge. The severity of the phenomenon ranges from a momentary power drop barely registered by the engine instruments to a complete loss of compression in case of a surge, requiring adjustments in the fuel flow to recover normal operation. Compressor stalls were a common problem on early jet engines with simple aerodynamics and manual or mechanical fuel control units, but they have been virtually eliminated by better design and the use of hydromechanical and electronic control systems such as full authority digital engine control. Modern compressors are carefully designed and controlled to avoid or limit stall within an engine's operating range. Types There are two types of compressor stall: Rotating stall Rotating stall is a local disruption of airflow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stall (flight)
In fluid dynamics, a stall is a reduction in the lift coefficient generated by a foil as angle of attack exceeds its critical value.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', p. 486. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. The critical angle of attack is typically about 15°, but it may vary significantly depending on the fluid, foil – including its shape, size, and finish – and Reynolds number. Stalls in fixed-wing aircraft are often experienced as a sudden reduction in lift. It may be caused either by the pilot increasing the wing's angle of attack or by a decrease in the critical angle of attack. The former may be due to slowing down (below stall speed), the latter by accretion of ice on the wings (especially if the ice is rough). A stall does not mean that the engine(s) have stopped working, or that the aircraft has stopped moving—the effect is the same even in an unpowered glider aircraft. Vectored thrust in aircraft is used to maintain alti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
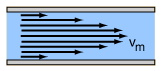
Laminar Flow
Laminar flow () is the property of fluid particles in fluid dynamics to follow smooth paths in layers, with each layer moving smoothly past the adjacent layers with little or no mixing. At low velocities, the fluid tends to flow without lateral mixing, and adjacent layers slide past one another smoothly. There are no cross-currents perpendicular to the direction of flow, nor eddies or swirls of fluids. In laminar flow, the motion of the particles of the fluid is very orderly with particles close to a solid surface moving in straight lines parallel to that surface. Laminar flow is a flow regime characterized by high momentum diffusion and low momentum convection. When a fluid is flowing through a closed channel such as a pipe or between two flat plates, either of two types of flow may occur depending on the velocity and viscosity of the fluid: laminar flow or turbulent flow. Laminar flow occurs at lower velocities, below a threshold at which the flow becomes turbulent. The thresh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers with no disruption between those layers. Turbulence is commonly observed in everyday phenomena such as surf, fast flowing rivers, billowing storm clouds, or smoke from a chimney, and most fluid flows occurring in nature or created in engineering applications are turbulent. Turbulence is caused by excessive kinetic energy in parts of a fluid flow, which overcomes the damping effect of the fluid's viscosity. For this reason, turbulence is commonly realized in low viscosity fluids. In general terms, in turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear of many sizes which interact with each other, consequently drag due to friction effects increases. The onset of turbulence can be predicted by the dimensionless Reynolds number, the ratio of kinetic energy to viscous damping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
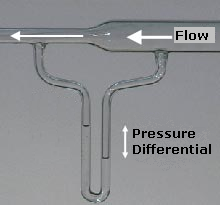
Bernoulli Principle
Bernoulli's principle is a key concept in fluid dynamics that relates pressure, speed and height. For example, for a fluid flowing horizontally Bernoulli's principle states that an increase in the speed occurs simultaneously with a decrease in pressure The principle is named after the Swiss mathematician and physicist Daniel Bernoulli, who published it in his book ''Hydrodynamica'' in 1738. Although Bernoulli deduced that pressure decreases when the flow speed increases, it was Leonhard Euler in 1752 who derived Bernoulli's equation in its usual form. Bernoulli's principle can be derived from the principle of conservation of energy. This states that, in a steady flow, the sum of all forms of energy in a fluid is the same at all points that are free of viscous forces. This requires that the sum of kinetic energy, potential energy and internal energy remains constant. Thus an increase in the speed of the fluid—implying an increase in its kinetic energy—occurs with a simultan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh (, ; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a Public university, public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Founded by the City of Edinburgh Council, town council under the authority of a royal charter from King James VI and I, James VI in 1582 and officially opened in 1583, it is one of Scotland's Ancient universities of Scotland, four ancient universities and the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, sixth-oldest university in continuous operation in the English-speaking world. The university played a crucial role in Edinburgh becoming a leading intellectual centre during the Scottish Enlightenment and contributed to the city being nicknamed the "Etymology of Edinburgh#Athens of the North, Athens of the North". The three main global university rankings (Academic Ranking of World Universities, ARWU, Times Higher Education World University Rankings, THE, and QS World University Rankings, QS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |