|
Fire-damp
Firedamp is any flammable gas found in coal mines, typically coalbed methane. It is particularly found in areas where the coal is bituminous. The gas accumulates in pockets in the coal and adjacent strata and, when they are penetrated, the release of the gas can cause explosions. Historically, if such a pocket was highly pressurized, it was termed a "bag of foulness". Name Damp is the collective name given to all gases (other than air) found in coal mines in Great Britain and North America. As well as firedamp, other damps include ''blackdamp'' (nonbreathable mixture of carbon dioxide, water vapour and other gases); whitedamp (carbon monoxide and other gases produced by combustion); poisonous, explosive ''stinkdamp'' (hydrogen sulfide), with its characteristic rotten-egg odour; and the insidiously lethal ''afterdamp'' (carbon monoxide and other gases) which are produced following explosions of firedamp or coal dust. Etymology Often hyphenated as fire-damp, this term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flammable
A combustible material is a material that can burn (i.e., sustain a flame) in air under certain conditions. A material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable material catches fire immediately on exposure to flame. The degree of flammability in air depends largely upon the volatility of the material this is related to its composition-specific vapour pressure, which is temperature dependent. The quantity of vapour produced can be enhanced by increasing the surface area of the material forming a mist or dust. Take wood as an example. Finely divided wood dust can undergo explosive flames and produce a blast wave. A piece of paper (made from pulp) catches on fire quite easily. A heavy oak desk is much harder to ignite, even though the wood fibre is the same in all three materials. Common sense (and indeed scientific consensus until the mid-1700s) would seem to suggest that mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Dust
Coal dust is a fine-powdered form of coal which is created by the crushing, grinding, or pulverizer, pulverization of coal rock. Because of the brittle nature of coal, coal dust can be created by mining, transporting, or mechanically handling it. Grinding or pulverizing coal to a dust form before combusting it improves the speed and efficiency of burning, which makes the coal easier to handle. However, coal dust is dangerous goods, hazardous to workers if it is suspended in air outside the controlled environment of grinding and combustion equipment. It poses the acute hazard of forming an explosive mixture in air and the chronic hazard of causing pulmonary illness in people who inhale excessive quantities of it. The distribution of the particle-size of coal dust is frequently measured in Mesh (scale), mesh. The British slang term for cheap fuel consisting of coal dust (slack) containing small lumps of coal (nuts) is wikt:nutty slack, nutty slack. Energy generation For use in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firedamp Whistle
A firedamp whistle (German: ''Schlagwetterpfeife'') is an instrument for the prophylactic indication of firedamp — flammable gases often present in coal mines. History The German Emperor Wilhelm II, German Emperor, Wilhelm II asked Fritz Haber in 1912, shortly after the opening of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physical Chemistry and Electrochemistry in Berlin, for the construction of a warning system for the presence of firedamp. Within a year Haber developed the methane whistle and presented it to the emperor in a lecture on October 28, 1913. Haber tried hard to market the device and eventually signed a contract with the Auergesellschaft. Unfortunately, the device did not prevail, since the calibration of the pipes under working conditions in a Coal mining, colliery was not practical. Mode of operation The simultaneous use of two equally-tuned pipes, of which one is blown with atmospheric air and the second with another gas, results in two only slightly different t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauze
Gauze is a thin, translucent Textile, fabric with a wikt:loose, loose open Weaving, weave. In technical terms, "gauze" is a weave structure in which the weft yarns are arranged in pairs and are crossed before and after each Warp (weaving), warp yarn, keeping the weft firmly in place. This weave structure is used to add stability to the fabric, which is important when using fine yarns loosely spaced. However, this weave structure can be used with any weight of yarn, and can be seen in some rustic textiles made from coarse hand-spun plant fiber yarns. Gauze is widely used for medical dressings. Gauze can also be made of non-woven fabric. Etymology and history The word ''gauze'' came into English in the 16th century via French ''gaze'', beyond which its history is uncertain. Most scholars trace ''gauze'' to a Persian language, Persian word for thin cloth or an Arabic word for raw silk. The Philip III, Bishop of Fermo#Hungary, 1279 Council of Baden banned clergy from wearing " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle Upon Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne, or simply Newcastle ( , Received Pronunciation, RP: ), is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. It is England's northernmost metropolitan borough, located on the River Tyne's northern bank opposite Gateshead to the south. It is the most populous settlement in the Tyneside conurbation and North East England. Newcastle developed around a Roman Empire, Roman settlement called Pons Aelius. The settlement became known as ''Monkchester'' before taking on the name of The Castle, Newcastle, a castle built in 1080 by William the Conqueror's eldest son, Robert Curthose. It was one of the world's largest ship building and repair centres during the Industrial Revolution. Newcastle was historically part of the county of Northumberland, but governed as a county corporate after 1400. In 1974, Newcastle became part of the newly-created metropolitan county of Tyne and Wear. The local authority is Newcastle Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felling Mine Disaster
Felling is the process of cutting down trees,"Feller" def. 2. and "Felling", def. 1. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' 2nd ed. via CD-ROM (v. 4.0) © Oxford University Press. 2009. an element of the task of logging. The person cutting the trees is a lumberjack. A feller buncher is a machine capable of felling a single large tree or grouping and felling several small ones simultaneously. Methods Hand felling In hand felling, an axe, saw, or chainsaw is used to fell a tree, followed up by limbing and bucking in traditional applications. In the modern commercial logging industry, felling is typically followed by limbing and skidding. Feller buncher A feller-buncher is a motorized vehicle with an attachment which rapidly cuts and gathers several trees in the process of felling them. In cut-to-length logging Cut-to-length logging (CTL) is a mechanized harvesting system in which trees are delimbed and ''cut to length'' directly at the tree stump, stump. CTL is typically a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
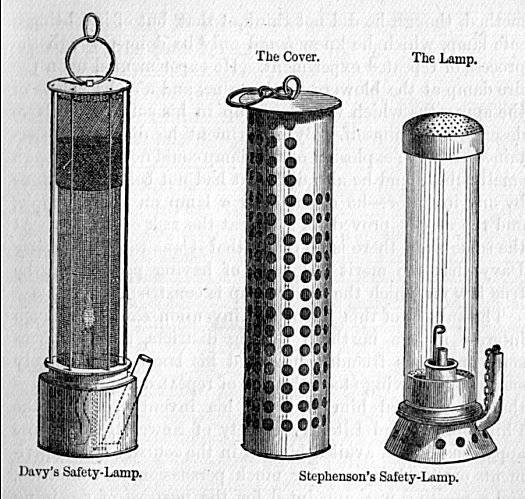
Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several Chemical element, elements for the first time: potassium and sodium in 1807 and calcium, strontium, barium, magnesium and boron the following year, as well as for discovering the elemental nature of chlorine and iodine. Davy also studied the forces involved in these separations, inventing the new field of electrochemistry. Davy is also credited with discovering clathrate hydrates. In 1799, he experimented with nitrous oxide and was astonished at how it made him laugh. He nicknamed it "laughing gas" and wrote about its potential as an Anesthesia, anaesthetic to relieve pain during surgery. Davy was a baronet, President of the Royal Society (PRS), Member of the Royal Irish Academy (MRIA), a founder member and Fellow of the Geological Society of London, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was an English civil engineer and Mechanical engineering, mechanical engineer during the Industrial Revolution. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorian era, Victorians as a great example of diligent application and thirst for improvement. His chosen Track gauge#The Stockton and Darlington Railway, rail gauge, sometimes called "Stephenson gauge", was the basis for the standard gauge used by most of the world's railways. Pioneered by Stephenson, rail transport was one of the most important technological inventions of the 19th century and a key component of the Industrial Revolution. Built by George and his son Robert Stephenson, Robert's company Robert Stephenson and Company, the Locomotion No. 1, ''Locomotion'' No. 1 was the first steam locomotive to carry passengers on a public rail line, the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1825. George also built the first public inter-city railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Lamp
A safety lamp is any of several types of lamp that provides illumination in places such as coal mines where the air may carry coal dust or a build-up of flammable gases, which may explode if ignited, possibly by an electric spark. Until the development of effective electric lamps in the early 1900s, miners used flame lamps to provide illumination. Open flame lamps could ignite flammable gases which collected in mines, causing explosions; safety lamps were developed to enclose the flame to prevent it from igniting the explosive gases. Flame safety lamps have been replaced for lighting in mining with sealed explosion-proof electric lights, but continue to be used to detect gases. Background Damps or gases Miners have traditionally referred to the various gases encountered during mining as damps, from the Middle Low German word ''dampf'' (meaning "vapour"). Damps are variable mixtures and are historic terms. * '' Firedamp'' Naturally occurring flammable mixtures, principally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitehaven
Whitehaven is a town and civil parish in the Cumberland (unitary authority), Cumberland district of Cumbria, England. It is a port on the north-west coast, and lies outside the Lake District National parks of England and Wales, National Park. It is south-west of Carlisle. The parish also includes the small village of Sandwith, Cumbria, Sandwith. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census the parish had a population of 24,040 and the Whitehaven built up area had a population of 22,945. The town's growth was largely due to the exploitation of the extensive coal measures by the Lowther family, driving a growing export of coal through the harbour from the 17th century onwards. It was also a major port for trading with the Thirteen Colonies, American colonies, and was, after London, the second busiest port of England by tonnage from 1750 to 1772. This prosperity led to the creation of a Georgian architecture, Georgian planned town in the 18th century which has left an architect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir James Lowther, 4th Baronet
Sir James Lowther, 4th Baronet, FRS (1673 – 2 January 1755) was an English landowner, industrialist and Whig politician who sat in the House of Commons for 54 years between 1694 and 1755. His ownership and development of coal mines around Whitehaven in Cumberland gave him substantial revenues, and he was reputed the richest commoner in England. Early life Lowther was baptised on 5 August 1673 at St Giles in the Fields, London, the second son of Sir John Lowther, 2nd Baronet and Jane Leigh. Educated privately in London, he attended Queen's College, Oxford and the Middle Temple. On the death of his father in 1706, the baronetcy was inherited by James's elder brother Christopher, but Christopher (whose drinking and gambling had led his father to disinherit him) was cut off with an annuity of about £100 a year and the family properties passed to James, who subsequently inherited the baronetcy in 1731, when his brother died without children. Politics In 1694, Lowther was ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mostyn
Mostyn is a village and Community (Wales), community in Flintshire, Wales, and Wards and electoral divisions of the United Kingdom, electoral ward lying on the estuary of the River Dee, Wales, River Dee, located near the town of Holywell, Flintshire, Holywell. It has a privately owned port that has in the past had a Mostyn Colliery, colliery and ironworks and was involved in the export of commodities, and in present times services the offshore wind industry and shipped the wings for the Airbus A380 which were manufactured at Broughton, Flintshire, Broughton. History Mostyn was mentioned in the Doomsday Book of 1086. Henry Bolingbroke (later Henry IV) landed here in 1399 before attacking Richard II at Flint Castle. Coal was mined at Mostyn Colliery and iron production started in the mid nineteenth century. The combination of a colliery, iron works and the docks made this a profitable enterprise. Nineteen hundred people were employed at one time. The coal eventually became exhaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |