|
Farriers
A farrier is a specialist in equine hoof care, including the trimming and balancing of horses' hooves and the placing of shoes on their hooves, if necessary. A farrier combines some blacksmith's skills (fabricating, adapting, and adjusting metal shoes) with some veterinarian's skills (knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the lower limb) to care for horses' feet. Traditionally an occupation for men, in a number of countries women have now become farriers. History While the practice of putting protective hoof coverings on horses dates back to the first century, evidence suggests that the practice of nailing iron shoes into a horse's hoof is a much later invention. One of the first archaeological discoveries of an iron horseshoe was found in the tomb of Merovingian king Childeric I, who reigned from 458 to 481 or 482. The discovery was made by Adrien Quinquin in 1653, and the findings were written about by Jean-Jacques Chifflet in 1655. Chifflet wrote that the iron h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farrier Tools
A farrier is a specialist in equine hoof care, including the trimming and balancing of horses' hooves and the placing of shoes on their hooves, if necessary. A farrier combines some blacksmith's skills (fabricating, adapting, and adjusting metal shoes) with some veterinarian's skills (knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the lower limb) to care for horses' feet. Traditionally an occupation for men, in a number of countries women have now become farriers. History While the practice of putting protective hoof coverings on horses dates back to the first century, evidence suggests that the practice of nailing iron shoes into a horse's hoof is a much later invention. One of the first archaeological discoveries of an iron horseshoe was found in the tomb of Merovingian king Childeric I, who reigned from 458 to 481 or 482. The discovery was made by Adrien Quinquin in 1653, and the findings were written about by Jean-Jacques Chifflet in 1655. Chifflet wrote that the iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horseshoe
A horseshoe is a product designed to protect a horse hoof from wear. Shoes are attached on the palmar surface (ground side) of the hooves, usually nailed through the insensitive hoof wall that is anatomically akin to the human toenail, although much larger and thicker. However, there are also cases where shoes are glued. Horseshoes are available in a wide variety of materials and styles, developed for different types of horses and for the work they do. The most common materials are steel and aluminium, but specialized shoes may include use of rubber, plastic, magnesium, titanium, or copper.Price, Steven D. (ed.) ''The Whole Horse Catalog: Revised and Updated'' New York:Fireside 1998 , pp. 84–87. Steel tends to be preferred in sports in which a strong, long-wearing shoe is needed, such as polo, eventing, show jumping, and western riding events. Aluminium shoes are lighter, making them common in horse racing where a lighter shoe is desired, and often facilitate certain ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veterinary Medicine
Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, management, medical diagnosis, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, disorder, and injury in non-human animals. The scope of veterinary medicine is wide, covering all animal species, both List of domesticated animals, domesticated and wildlife, wild, with a wide range of conditions that can affect different species. Veterinary medicine is widely practiced, both with and without professional supervision. Professional care is most often led by a veterinarian, veterinary physician (also known as a veterinarian, veterinary surgeon, or "vet"), but also by paraveterinary workers, such as veterinary nurses, veterinary technicians, and veterinary assistants. This can be augmented by other paraprofessionals with specific specialties, such as animal physiotherapy or dentistry, and species-relevant roles such as farriers. Veterinary science helps human health through the monitoring and control of Zoonosis, zoonoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marechal Ferrant
Leopoldo Marechal (June 11, 1900 – June 26, 1970) was one of the most important Argentine writers of the twentieth century. Biographical notes Born in Buenos Aires into a family of French and Basque descent, Marechal became a primary school teacher and a high school professor after obtaining his degree despite enormous economic difficulties. During the 1920s he was among the poets who rallied around the movement represented by the literary journal '' Martín Fierro''. While his first published works of poetry, ''Los aguiluchos'' (1922) and ''Días como flechas'' (1926), tended towards vanguardism, his ''Odas para el hombre y la mujer'' showed a blend of novelty and a more classical style. It is with this collection of poems that Marechal obtained his first official recognition as a poet in 1929, the ''Premio Municipal de Poesía'' of the city of Buenos Aires. He traveled to Europe for the first time in 1926 and in Paris met important intellectuals and artists such as Pic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English period. Scholarly opinion varies, but the University of Valencia states the period when Middle English was spoken as being from 1150 to 1500. This stage of the development of the English language roughly coincided with the High Middle Ages, High and Late Middle Ages. Middle English saw significant changes to its vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and orthography. Writing conventions during the Middle English period varied widely. Examples of writing from this period that have survived show extensive regional variation. The more standardized Old English literary variety broke down and writing in English became fragmented and localized and was, for the most part, being improvised. By the end of the period (about 1470), and aided by the movabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old French
Old French (, , ; ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France approximately between the late 8th [2-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it was deemed no longer make to think of the varieties spoken in Gaul as Latin. Although a precise date can't be given, there is a general consensus (see Wright 1982, 1991, Lodge 1993) that an awareness of a vernacular, distinct from Latin, emerged at the end of the eighth century.] and mid-14th centuries. Rather than a unified Dialect#Dialect or language, language, Old French was a Dialect cluster, group of Romance languages, Romance dialects, Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible yet Dialect continuum, diverse. These dialects came to be collectively known as the , contrasting with the , the emerging Occitano-Romance languages of Occitania, now the south of France. The mid-14th century witnessed the emergence of Middle French, the lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance activity, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its basic premise – to identify which of two or more horses is the fastest over a set course or distance – has been mostly unchanged since at least classical antiquity. Horse races vary widely in format, and many countries have developed their own particular traditions around the sport. Variations include restricting races to particular breeds, running over obstacles, running over different distances, running on different track surfaces, and running in different gaits. In some races, horses are assigned different weights to carry to reflect differences in ability, a process known as handicapping. While horses are sometimes raced purely for sport, a major part of horse racing's interest and economic importance is in the gambling associated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anvil
An anvil is a metalworking tool consisting of a large block of metal (usually Forging, forged or Steel casting, cast steel), with a flattened top surface, upon which another object is struck (or "worked"). Anvils are massive because the higher their inertia, the more efficiently they cause the energy of striking tools to be transferred to the work piece. In most cases the anvil is used as a forge, forging tool. Before the advent of modern welding technology, it was the primary tool of metal workers. The great majority of modern anvils are made of cast steel that has been heat treated by either Case-hardening, flame or Induction_hardening, electric induction. Inexpensive anvils have been made of cast iron and low-quality steel, but are considered unsuitable for serious use, as they deform and lack rebound when struck. The largest single piece tool steel anvil that is heat treated is 1600 pounds. This anvil was made in 2023 by Oak Lawn Blacksmith. There are larger anvils tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
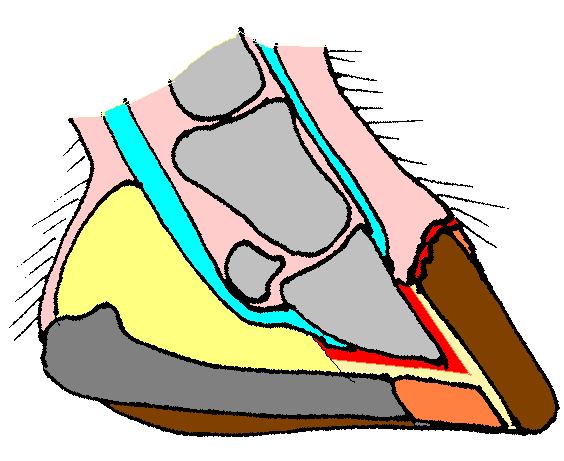
Hoof Knife
The hoof (: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits; the ruminants with two digits are the most numerous, e.g. giraffe, deer, bison, cattle, goats, gazelles, pigs, and sheep. The feet of perissodactyl mammals have an odd number of toes, e.g. the horse, the rhinoceros, and the tapir. Although hooves are limb structures primarily found in placental mammals, hadrosaurs such as '' Edmontosaurus'' possessed hoofed forelimbs. The marsupial '' Chaeropus'' also had hooves. Description The hoof surrounds the distal end of the second phalanx, the distal phalanx, and the navicular bone. The hoof consists of the hoof wall, the bars of the hoof, the sole and frog and soft tissue shock absorption structures. The weight of the animal is normally borne by both the sole and the edge of the hoof wall. Hooves perf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. The disease is caused by the Bacteria, bacterium ''Yersinia pestis'' and spread by Flea, fleas and through the air. One of the most significant events in European history, the Black Death had far-reaching population, economic, and cultural impacts. It was the beginning of the second plague pandemic. The plague created religious, social and economic upheavals, with profound effects on the course of European history. The origin of the Black Death is disputed. Genetic analysis suggests ''Yersinia pestis'' bacteria evolved approximately 7,000 years ago, at the beginning of the Neolithic, with flea-mediated strains emerging around 3,800 years ago during the late Bronze Age. The immediate territorial origins of the Black Death and its outbreak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |