|
F Shell
In chemistry and atomic physics, an electron shell may be thought of as an orbit that electrons follow around an atom's nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the "1 shell" (also called the "K shell"), followed by the "2 shell" (or "L shell"), then the "3 shell" (or "M shell"), and so on further and further from the nucleus. The shells correspond to the principal quantum numbers (''n'' = 1, 2, 3, 4 ...) or are labeled alphabetically with the letters used in X-ray notation (K, L, M, ...). Each period on the conventional periodic table of elements represents an electron shell. Each shell can contain only a fixed number of electrons: the first shell can hold up to two electrons, the second shell can hold up to eight electrons, the third shell can hold up to 18, continuing as the general formula of the ''n''th shell being able to hold up to 2( ''n''2) electrons. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-sub
The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems. Description, nomenclature, and variants A D-sub contains two or more parallel rows of pins or sockets usually surrounded by a D-shaped metal shield, or shell, that provides mechanical support, ensures correct orientation, and may screen against electromagnetic interference. Calling that shield a shell (or D-shell) can be ambiguous, as the term shell is also short for the cable shell, or backshell. D-sub connectors have gender: parts with pin contacts are called ''male connectors'' or ''plugs'', while those with socket contacts are called ''female connectors'' or ''sockets''. The socket's shield fits tightly inside the plug's shield. Panel-mounted connectors usually have #4-40 UNC (as designated with the Unified Thread Standard) jackscrews that ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Spectrum
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to electrons making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The photon energy of the emitted photons is equal to the energy difference between the two states. There are many possible electron transitions for each atom, and each transition has a specific energy difference. This collection of different transitions, leading to different radiated wavelengths, make up an emission spectrum. Each element's emission spectrum is unique. Therefore, spectroscopy can be used to identify elements in matter of unknown composition. Similarly, the emission spectra of molecules can be used in chemical analysis of substances. Emission In physics, emission is the process by which a higher energy quantum mechanical state of a particle becomes converted to a lower one through the emission of a photon, resulting in the production of light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is the foundation of all quantum physics, which includes quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Quantum mechanics can describe many systems that classical physics cannot. Classical physics can describe many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic and Microscopic scale, (optical) microscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at very small submicroscopic (atomic and subatomic) scales. Classical mechanics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation that is valid at ordinary scales. Quantum systems have Bound state, bound states that are Quantization (physics), quantized to Discrete mathematics, discrete values of energy, momentum, angular momentum, and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azimuthal Quantum Number
In quantum mechanics, the azimuthal quantum number is a quantum number for an atomic orbital that determines its angular momentum operator, orbital angular momentum and describes aspects of the angular shape of the orbital. The azimuthal quantum number is the second of a set of quantum numbers that describe the unique quantum state of an electron (the others being the principal quantum number , the magnetic quantum number , and the spin quantum number ). For a given value of the principal quantum number (''electron shell''), the possible values of are the integers from 0 to . For instance, the shell has only orbitals with \ell=0, and the shell has only orbitals with \ell=0, and \ell=1. For a given value of the azimuthal quantum number , the possible values of the magnetic quantum number are the integers from to , including 0. In addition, the spin quantum number can take two distinct values. The set of orbitals associated with a particular value of are som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann Constant
The Boltzmann constant ( or ) is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative thermal energy of particles in a ideal gas, gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin (K) and the molar gas constant, in Planck's law of black-body radiation and Boltzmann's entropy formula, and is used in calculating Johnson–Nyquist noise, thermal noise in resistors. The Boltzmann constant has Dimensional analysis, dimensions of energy divided by temperature, the same as entropy and heat capacity. It is named after the Austrian scientist Ludwig Boltzmann. As part of the 2019 revision of the SI, the Boltzmann constant is one of the seven "Physical constant, defining constants" that have been defined so as to have exact finite decimal values in SI units. They are used in various combinations to define the seven SI base units. The Boltzmann constant is defined to be exactly joules per kelvin, with the effect of defining the SI unit ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
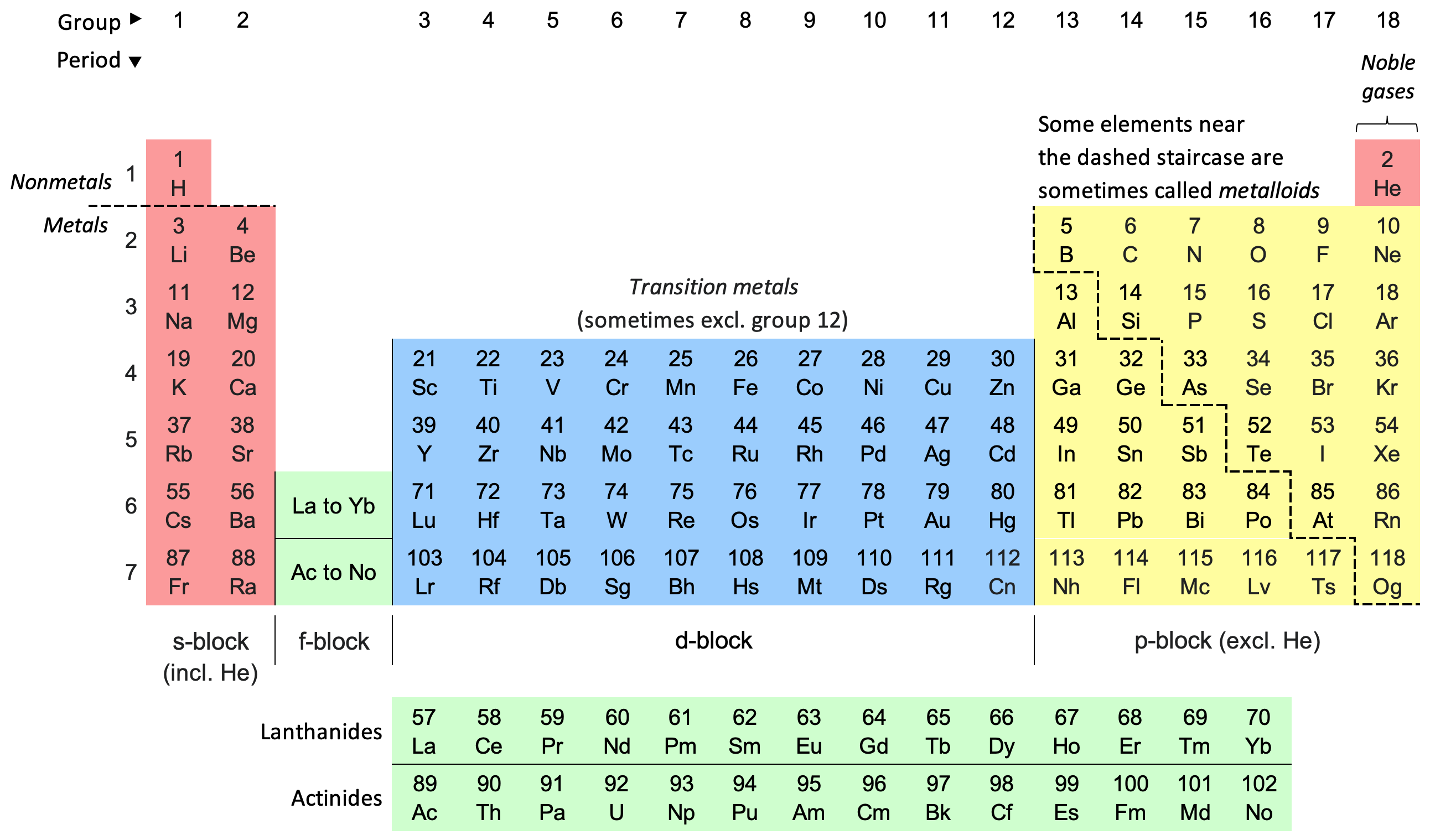
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top right. The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilbert N
Gilbert may refer to: People and fictional characters *Gilbert (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters * Gilbert (surname), including a list of people Places Australia * Gilbert River (Queensland) * Gilbert River (South Australia) Kiribati * Gilbert Islands, a chain of atolls and islands in the Pacific Ocean United States * Gilbert, Arizona, a town * Gilbert, Arkansas, a town * Gilbert, Florida, the airport of Winterhaven * Gilbert, Iowa, a city * Gilbert, Louisiana, a village * Gilbert, Michigan, and unincorporated community * Gilbert, Minnesota, a city * Gilbert, Nevada, ghost town * Gilbert, Ohio, an unincorporated community * Gilbert, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community * Gilbert, South Carolina, a town * Gilbert, West Virginia, a town * Gilbert, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community * Mount Gilbert (other), various mountains * Gilbert River (Oregon) Outer space * Gilbert (lunar crater) * Gilbert (Martian crater) Arts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Rugeley Bury
Charles Rugeley Bury (29 June 1890 – 30 December 1968) was an English physical chemist who proposed an early model of the atom with the arrangement of electrons, which explained their chemical properties, alongside the more dominant model of Niels Bohr. In some early papers, the model was called the "Bohr-Bury Atom". He introduced the word ''transition'' to describe the elements now known as transition metals or transition elements. Bury was born in Henley-on-Thames and grew up in Ellfield, Wotton-under-Edge. His father had studied law but did not continue in the field and died when he was young. A grandmother in Leamington took care of him and his early education was at Malvern College. He then went to Trinity College, Oxford where D.H. Nagel was a tutor. His chemistry teachers included Harold Hartley. Bury worked as a demonstrator in Balliol and Trinity College labs. In 1912 he went to Göttingen and worked with Walther Nernst. He then joined the chemistry department at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irving Langmuir
Irving Langmuir (; January 31, 1881 – August 16, 1957) was an American chemist, physicist, and metallurgical engineer. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1932 for his work in surface chemistry. Langmuir's most famous publication is the 1919 article "The Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms and Molecules" in which, building on Gilbert N. Lewis's cubical atom theory and Walther Kossel's chemical bonding theory, he outlined his "concentric theory of atomic structure". Langmuir became embroiled in a priority dispute with Lewis over this work; Langmuir's presentation skills were largely responsible for the popularization of the theory, although the credit for the theory itself belongs mostly to Lewis. While at General Electric from 1909 to 1950, Langmuir advanced several fields of physics and chemistry, inventing the gas-filled incandescent lamp and the hydrogen welding technique. The Langmuir Laboratory for Atmospheric Research near Socorro, New Mexico, was named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einstein
Albert Einstein (14 March 187918 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is best known for developing the theory of relativity. Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics. His mass–energy equivalence formula , which arises from special relativity, has been called "the world's most famous equation". He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics for . Born in the German Empire, Einstein moved to Switzerland in 1895, forsaking his German citizenship (as a subject of the Kingdom of Württemberg) the following year. In 1897, at the age of seventeen, he enrolled in the mathematics and physics teaching diploma program at the Swiss federal polytechnic school in Zurich, graduating in 1900. He acquired Swiss citizenship a year later, which he kept for the rest of his life, and afterwards secured a permanent position at the Swiss Patent Office in Bern. In 1905, he submitted a successful PhD dissertation to the University of Zurich. In 1914, he m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegbahn Notation
The Siegbahn notation is used in X-ray spectroscopy to name the spectral lines that are characteristic to elements. It was introduced by Manne Siegbahn. The characteristic lines in X-ray emission spectra correspond to atomic electronic transitions where an electron jumps down to a vacancy in one of the inner shells of an atom. Such a hole in an inner shell may have been produced by bombardment with electrons in an X-ray tube, by other particles as in PIXE, by other X-rays in X-ray fluorescence or by radioactive decay of the atom's nucleus. Although still widely used in spectroscopy, this notation is unsystematic and often confusing. For these reasons, International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends another nomenclature. History The use of the letters K and L to denote X-rays originates in a 1911 paper by Charles Glover Barkla, titled ''The Spectra of the Fluorescent Röntgen Radiations'' ("Röntgen radiation" is an archaic name for "X-rays"). By 1913, H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
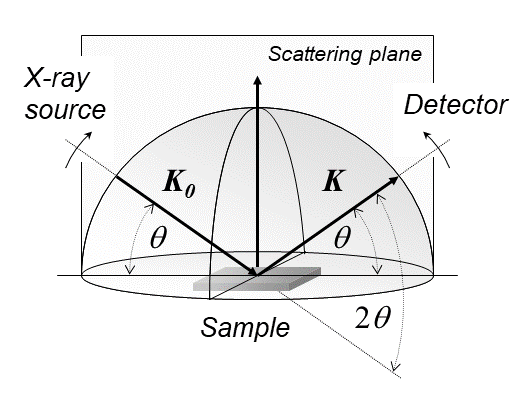
X-ray Diffraction
X-ray diffraction is a generic term for phenomena associated with changes in the direction of X-ray beams due to interactions with the electrons around atoms. It occurs due to elastic scattering, when there is no change in the energy of the waves. The resulting map of the directions of the X-rays far from the sample is called a diffraction pattern. It is different from X-ray crystallography which exploits X-ray diffraction to determine the arrangement of atoms in materials, and also has other components such as ways to map from experimental diffraction measurements to the positions of atoms. This article provides an overview of X-ray diffraction, starting with the early #History, history of x-rays and the discovery that they have the right spacings to be diffracted by crystals. In many cases these diffraction patterns can be #Introduction to x-ray diffraction theory, Interpreted using a single scattering or kinematical theory with conservation of energy (#Ewald's sphere, wave vecto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |