|
Eye Diagram
In telecommunication, an eye pattern, also known as an eye diagram, is an oscilloscope display in which a digital signal from a receiver is repetitively sampled and applied to the vertical input, while the data rate is used to trigger the horizontal sweep. It is so called because, for several types of coding, the pattern looks like a series of eyes between a pair of rails. It is a tool for the evaluation of the combined effects of channel noise, dispersion and intersymbol interference on the performance of a baseband pulse-transmission system. The technique was first used with the WWII SIGSALY secure speech transmission system. From a mathematical perspective, an eye pattern is a visualization of the probability density function (PDF) of the signal, modulo the unit interval (UI). In other words, it shows the probability of the signal being at each possible voltage across the duration of the UI. Typically a color ramp is applied to the PDF in order to make small brightness differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Lines
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmission must be taken into account. This applies especially to radio-frequency engineering because the short wavelengths mean that wave phenomena arise over very short distances (this can be as short as millimetres depending on frequency). However, the theory of transmission lines was historically developed to explain phenomena on very long telegraph lines, especially submarine telegraph cables. Transmission lines are used for purposes such as connecting radio transmitters and receivers with their antennas (they are then called feed lines or feeders), distributing cable television signals, trunklines routing calls between telephone switching centres, computer network connections and high speed computer data buses. RF engineers commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histogram
A histogram is an approximate representation of the distribution of numerical data. The term was first introduced by Karl Pearson. To construct a histogram, the first step is to " bin" (or "bucket") the range of values—that is, divide the entire range of values into a series of intervals—and then count how many values fall into each interval. The bins are usually specified as consecutive, non-overlapping intervals of a variable. The bins (intervals) must be adjacent and are often (but not required to be) of equal size. If the bins are of equal size, a bar is drawn over the bin with height proportional to the frequency—the number of cases in each bin. A histogram may also be normalized to display "relative" frequencies showing the proportion of cases that fall into each of several categories, with the sum of the heights equaling 1. However, bins need not be of equal width; in that case, the erected rectangle is defined to have its ''area'' proportional to the frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase-locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector in a feedback loop. The oscillator's frequency and phase are controlled proportionally by an applied voltage, hence the term voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The oscillator generates a periodic signal of a specific frequency, and the phase detector compares the phase of that signal with the phase of the input periodic signal, to adjust the oscillator to keep the phases matched. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same. Consequently, in addition to synchronizing signals, a phase-locked loop can track an input frequency, or it can generate a frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock Recovery
In serial communication of digital data, clock recovery is the process of extracting timing information from a serial data stream itself, allowing the timing of the data in the stream to be accurately determined without separate clock information. It is widely used in data communications; the similar concept used in analog systems like color television is known as carrier recovery. Basic concept Serial data is normally sent as a series of pulses with well-defined timing constraints. This presents a problem for the receiving side; if their own local clock is not precisely synchronized with the transmitter, they may sample the signal at the wrong time and thereby decode the signal incorrectly. This can be addressed with extremely accurate and stable clocks, like atomic clocks, but these are expensive and complex. More common low-cost clock systems, like quartz oscillators, are accurate enough for this task over short periods of time, but over a period of minutes or hours the drift in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Code
In telecommunication, a line code is a pattern of voltage, current, or photons used to represent digital data transmitted down a communication channel or written to a storage medium. This repertoire of signals is usually called a constrained code in data storage systems. Some signals are more prone to error than others as the physics of the communication channel or storage medium constrains the repertoire of signals that can be used reliably. Common line encodings are unipolar, polar, bipolar, and Manchester code. Transmission and storage After line coding, the signal is put through a physical communication channel, either a transmission medium or data storage medium.Karl Paulsen"Coding for Magnetic Storage Mediums".2007. The most common physical channels are: * the line-coded signal can directly be put on a transmission line, in the form of variations of the voltage or current (often using differential signaling). * the line-coded signal (the ''baseband signal'') underg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET. The original 10BASE5 Ethernet uses coaxial cable as a shared medium, while the newer Ethernet variants use twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with switches. Over the course of its history, Ethernet data transfer rates have been increased from the original to the latest , with rates up to under development. The Ethernet standards include several wiring and signaling variants of the OSI physical layer. Systems communicating over Ethernet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DisplayPort
DisplayPort (DP) is a digital display interface developed by a consortium of PC and chip manufacturers and standardized by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). It is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a computer monitor A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls. The di .... It can also carry audio signal, audio, USB, and other forms of data. DisplayPort was designed to replace VGA connector, VGA, FPD-Link, and Digital Visual Interface (DVI). It is backward compatibility, backward compatible with other interfaces, such as HDMI and DVI, through the use of either active or passive adapters. It is the first display interface to rely on packetized data transmission, a form of digital communication found in technologies such as Ethernet, U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
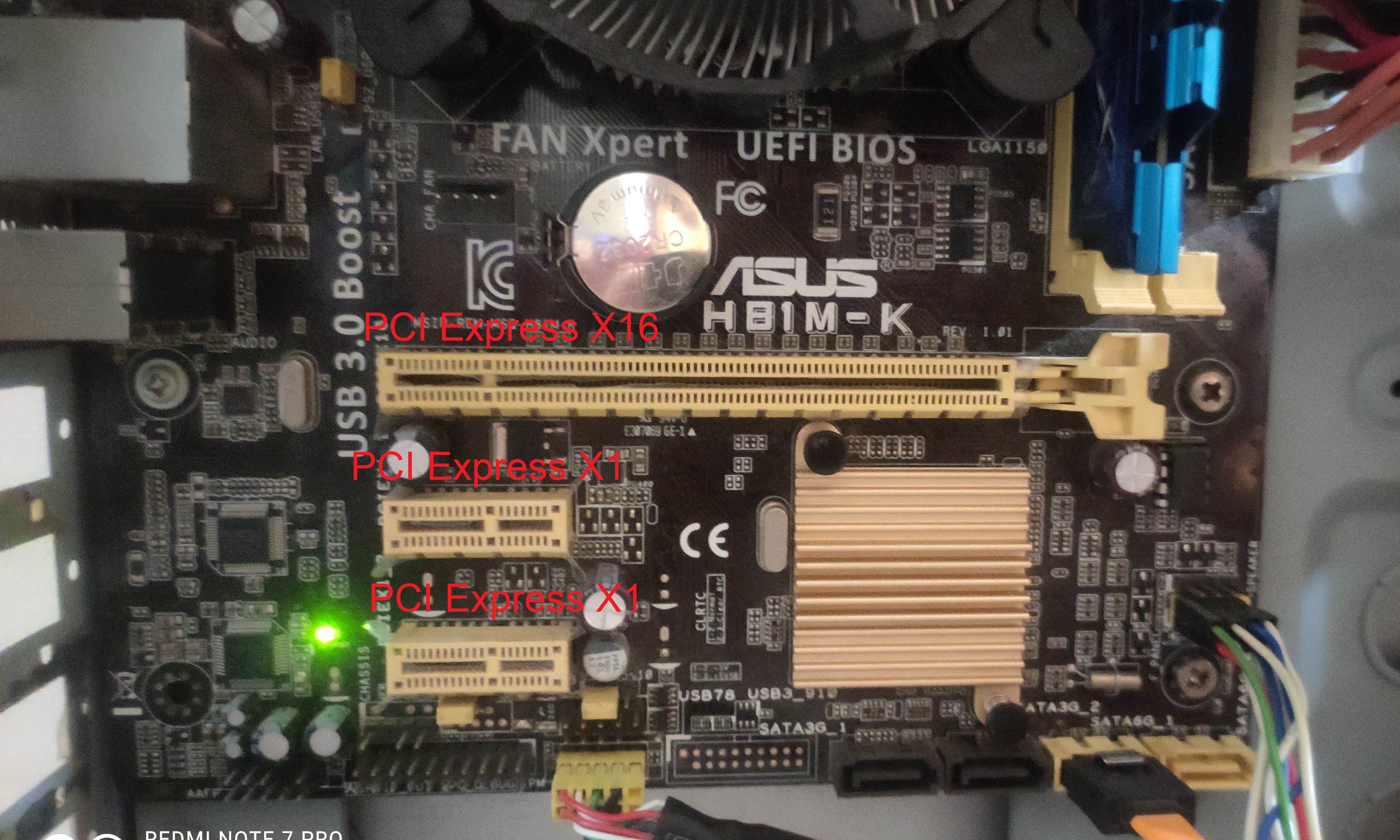
PCIe
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism (Advanced Error Reporting, AER), and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization. The PCI Express electrical interface is measured by the number of simultaneous lanes. (A lane is a single send/receive line of data. The analogy is a highway with traffic in both directions.) T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed video data and compressed or uncompressed digital audio data from an HDMI-compliant source device, such as a display controller, to a compatible computer monitor, video projector, digital television, or digital audio device. HDMI is a digital replacement for analog video standards. HDMI implements the EIA/CEA-861 standards, which define video formats and waveforms, transport of compressed and uncompressed LPCM audio, auxiliary data, and implementations of the VESA EDID. CEA-861 signals carried by HDMI are electrically compatible with the CEA-861 signals used by the Digital Visual Interface (DVI). No signal conversion is necessary, nor is there a loss of video quality when a DVI-to-HDMI adapter is used. The Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) capability allows HDMI devices to control each other when necessary and allows the user to operate multiple devices with on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spread Spectrum Clocking
In telecommunication and radio communication, spread-spectrum techniques are methods by which a signal (e.g., an electrical, electromagnetic, or acoustic signal) generated with a particular bandwidth is deliberately spread in the frequency domain, resulting in a signal with a wider bandwidth. These techniques are used for a variety of reasons, including the establishment of secure communications, increasing resistance to natural interference, noise, and jamming, to prevent detection, to limit power flux density (e.g., in satellite downlinks), and to enable multiple-access communications. Telecommunications Spread spectrum generally makes use of a sequential noise-like signal structure to spread the normally narrowband information signal over a relatively wideband (radio) band of frequencies. The receiver correlates the received signals to retrieve the original information signal. Originally there were two motivations: either to resist enemy efforts to jam the communications (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SATA
SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) standard to become the predominant interface for storage devices. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO) which are then promulgated by the INCITS Technical Committee T13, AT Attachment (INCITS T13). History SATA was announced in 2000 in order to provide several advantages over the earlier PATA interface such as reduced cable size and cost (seven conductors instead of 40 or 80), native hot swapping, faster data transfer through higher signaling rates, and more efficient transfer through an (optional) I/O queuing protocol. Revision 1.0 of the specification was released in January 2003. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA Internati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |