|
Expressionist Music
The term expressionism "was probably first applied to music in 1918, especially to Schoenberg", because like the painter Wassily Kandinsky (1866–1944) he avoided "traditional forms of beauty" to convey powerful feelings in his music. Theodor Adorno interprets the expressionist movement in music as seeking to "eliminate all of traditional music's conventional elements, everything formulaically rigid". This he sees as analogous "to the literary ideal of the 'scream' ". As well Adorno sees expressionist music as seeking "the truthfulness of subjective feeling without illusions, disguises or euphemisms". Adorno also describes it as concerned with the unconscious, and states that "the depiction of fear lies at the centre" of expressionist music, with dissonance predominating, so that the "harmonious, affirmative element of art is banished". Expressionist music would "thus reject the depictive, sensual qualities that had come to be associated with impressionist music. It would endeavor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Schoenberg La 1948
Arnold may refer to: People * Arnold (given name), a masculine given name * Arnold (surname), a German and English surname Places Australia * Arnold, Victoria, a small town in the Australian state of Victoria Canada * Arnold, Nova Scotia United Kingdom * Arnold, East Riding of Yorkshire * Arnold, Nottinghamshire United States * Arnold, California, in Calaveras County * Arnold, Carroll County, Illinois * Arnold, Morgan County, Illinois * Arnold, Iowa * Arnold, Kansas * Arnold, Maryland * Arnold, Mendocino County, California * Arnold, Michigan * Arnold, Minnesota * Arnold, Missouri * Arnold, Nebraska * Arnold, Ohio * Arnold, Pennsylvania * Arnold, Texas * Arnold, Brooke County, West Virginia * Arnold, Lewis County, West Virginia * Arnold, Wisconsin * Arnold Arboretum of Harvard University, Massachusetts * Arnold Township, Custer County, Nebraska Other uses * Arnold (automobile), a short-lived English car * Arnold of Manchester, a former English coachbuilder * Arnold (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Ruggles
Carl Ruggles (born Charles Sprague Ruggles; March 11, 1876 – October 24, 1971) was an American composer, painter and teacher. His pieces employed "dissonant counterpoint", a term coined by fellow composer and musicologist Charles Seeger to describe Ruggles' music. His method of atonal counterpoint was based on a non- serial technique of avoiding repeating a pitch class until a generally fixed number of eight pitch classes intervened. He is considered a founder of the ultramodernist movement of American composers that included Henry Cowell and Ruth Crawford Seeger, among others. He had no formal musical education, yet was an extreme perfectionist — writing music at a painstakingly slow rate and leaving behind a very small output. Famous for his prickly personality, Ruggles was nonetheless close friends with Cowell, Seeger, Edgard Varèse, Charles Ives, and the painter Thomas Hart Benton. His students include the experimental composers James Tenney and Merton Brown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libretto
A libretto (Italian for "booklet") is the text used in, or intended for, an extended musical work such as an opera, operetta, masque, oratorio, cantata or musical. The term ''libretto'' is also sometimes used to refer to the text of major liturgical works, such as the Mass, requiem and sacred cantata, or the story line of a ballet. ''Libretto'' (; plural ''libretti'' ), from Italian, is the diminutive of the word '' libro'' ("book"). Sometimes other-language equivalents are used for libretti in that language, ''livret'' for French works, ''Textbuch'' for German and ''libreto'' for Spanish. A libretto is distinct from a synopsis or scenario of the plot, in that the libretto contains all the words and stage directions, while a synopsis summarizes the plot. Some ballet historians also use the word ''libretto'' to refer to the 15 to 40 page books which were on sale to 19th century ballet audiences in Paris and contained a very detailed description of the ballet's story, scene by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erwartung
' (''Expectation''), Op. 17, is a one-act monodrama in four scenes by Arnold Schoenberg to a libretto by . Composed in 1909, it was not premiered until 6 June 1924 in Prague conducted by Alexander Zemlinsky with Marie Gutheil-Schoder as the soprano. The opera takes the unusual form of a monologue for solo soprano accompanied by a large orchestra. In performance, it lasts for about half an hour. It is sometimes paired with BĂ©la BartĂłk's opera '' Bluebeard's Castle'' (1911), as the two works were roughly contemporary and share similar psychological themes. Schoenberg described ''Erwartung'', saying "the aim is to represent in slow motion everything that occurs during a single second of maximum spiritual excitement, stretching it out to half an hour." Philip Friedheim has described ' as Schoenberg's "only lengthy work in an athematic style", where no musical material returns once stated over the course of 426 measures. In his analysis of the structure, one indication of the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefan George
Stefan Anton George (; 12 July 18684 December 1933) was a German symbolist poet and a translator of Dante Alighieri, William Shakespeare, Hesiod, and Charles Baudelaire. He is also known for his role as leader of the highly influential literary circle called the George-Kreis and for founding the literary magazine ' ("Journal for the Arts"). From the inception of his circle, George and his followers represented a literary and cultural revolt against the literary realism trend in German literature during the last decades of the German Empire. Biography Early life George was born in 1868 in Büdesheim (now part of Bingen on the river Rhine) in the Grand Duchy of Hesse. His father, also named Stefan George, was an inn keeper and wine merchant and his mother Eva (née Schmitt) was a homemaker. When Stefan was five years old, the family moved to Bingen am Rhein.Michael and Erika Metzger (1972), ''Stefan George'', Twayne's World Authors Series. Page 13. According to Michael and Er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Quartets (Schoenberg)
The Austrian composer Arnold Schoenberg published four string quartets, distributed over his lifetime: String Quartet No. 1 in D minor, Op. 7 (1905), String Quartet No. 2 in F minor, Op. 10 (1908), String Quartet No. 3, Op. 30 (1927), and the String Quartet No. 4, Op. 37 (1936). In addition to these, he wrote several other works for string quartet which were not published. The most notable was his early String Quartet in D major (1897). There was also a Presto in C major (c. 1895), a Scherzo in F major (1897), and later a Four-part Mirror Canon in A major (c. 1933). Finally, several string quartets exist in fragmentary form. These include String Quartet in F major (before 1897), String Quartet in D minor (1904), String Quartet in C major (after 1904), String Quartet Movement (1926), String Quartet (1926), String Quartet in C major (after 1927) and String Quartet No. 5 (1949). Schoenberg also wrote a Concerto for String Quartet and Orchestra in B major (1933): a recomposition of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelve-tone Technique
The twelve-tone technique—also known as dodecaphony, twelve-tone serialism, and (in British usage) twelve-note composition—is a method of musical composition first devised by Austrian composer Josef Matthias Hauer, who published his "law of the twelve tones" in 1919. In 1923, Arnold Schoenberg (1874–1951) developed his own, better-known version of 12-tone technique, which became associated with the "Second Viennese School" composers, who were the primary users of the technique in the first decades of its existence. The technique is a means of ensuring that all 12 notes of the chromatic scale are sounded as often as one another in a piece of music while preventing the emphasis of any one notePerle 1977, 2. through the use of tone rows, orderings of the 12 pitch classes. All 12 notes are thus given more or less equal importance, and the music avoids being in a key. Over time, the technique increased greatly in popularity and eventually became widely influential on 20th-cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinz Holliger
Heinz Robert Holliger (born 21 May 1939) is a Swiss virtuoso oboist, composer and conductor. Celebrated for his versatility and technique, Holliger is among the most prominent oboists of his generation. His repertoire includes Baroque and Classical pieces, but he has regularly engaged in lesser known pieces of Romantic music, as well as his own compositions. He often performed contemporary works with his wife, the harpist Ursula Holliger; composers such as Berio, Carter, Henze, Krenek, Lutosławski, Martin, Penderecki, Stockhausen and Yun have written works for him. Holliger is a noted composer himself, writing works such as the opera '' Schneewittchen'' (1998). Biography Holliger was born in Langenthal, Switzerland. He began playing the oboe at age eleven, and studied at the conservatory of Bern before taking first prize for oboe in the Geneva International Music Competition in 1959. He studied composition with Sándor Veress and Pierre Boulez. He has become one of the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Maxwell Davies
Sir Peter Maxwell Davies (8 September 1934 – 14 March 2016) was an English composer and conductor, who in 2004 was made Master of the Queen's Music. As a student at both the University of Manchester and the Royal Manchester College of Music, Davies formed a group dedicated to contemporary music called the New Music Manchester with fellow students Harrison Birtwistle, Alexander Goehr, Elgar Howarth and John Ogdon. Davies’s compositions include eight works for the stage—from the monodrama '' Eight Songs for a Mad King'', which shocked the audience in 1969, to '' Kommilitonen!'', first performed in 2011—and ten symphonies, written between 1973 and 2013. As a conductor, Davies was artistic director of the Dartington International Summer School from 1979 to 1984 and associate conductor/composer with the Royal Philharmonic Orchestra from 1992 to 2002, holding the latter position with the BBC Philharmonic Orchestra as well. Early life and education Davies was born in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Strauss
Richard Georg Strauss (; 11 June 1864 – 8 September 1949) was a German composer, conductor, pianist, and violinist. Considered a leading composer of the late Romantic and early modern eras, he has been described as a successor of Richard Wagner and Franz Liszt. Along with Gustav Mahler, he represents the late flowering of German Romanticism, in which pioneering subtleties of orchestration are combined with an advanced harmonic style. Strauss's compositional output began in 1870 when he was just six years old and lasted until his death nearly eighty years later. While his output of works encompasses nearly every type of classical compositional form, Strauss achieved his greatest success with tone poems and operas. His first tone poem to achieve wide acclaim was '' Don Juan'', and this was followed by other lauded works of this kind, including '' Death and Transfiguration'', '' Till Eulenspiegel's Merry Pranks'', '' Also sprach Zarathustra'', '' Don Quixote'', ''Ein Heldenl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
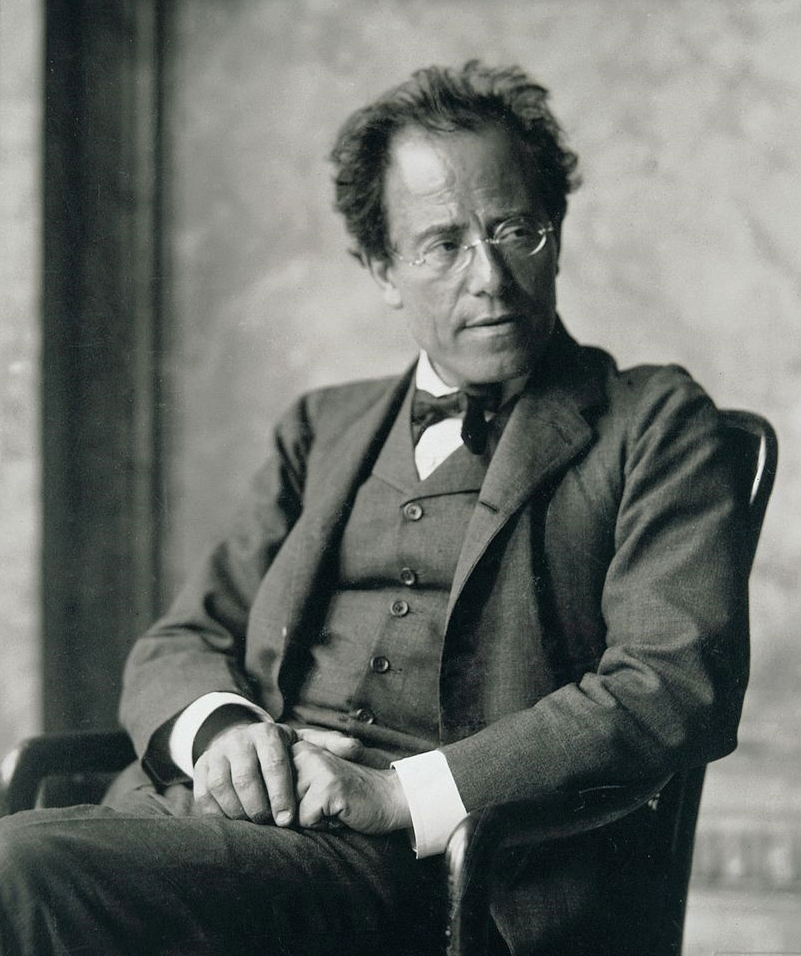
Gustav Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 – 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism of the early 20th century. While in his lifetime his status as a conductor was established beyond question, his own music gained wide popularity only after periods of relative neglect, which included a ban on its performance in much of Europe during the Nazi era. After 1945 his compositions were rediscovered by a new generation of listeners; Mahler then became one of the most frequently performed and recorded of all composers, a position he has sustained into the 21st century. Born in Bohemia (then part of the Austrian Empire) to Jewish parents of humble origins, the German-speaking Mahler displayed his musical gifts at an early age. After graduating from the Vienna Conservatory in 1878, he held a succession of conducting posts of rising ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |