|
Entropy Monitoring
Entropy monitoring is a method of assessing the effect of certain anaesthetic drugs on the brain's EEG. It was commercially developed by Datex-Ohmeda, which is now part of GE Healthcare. Entropy is a quantitative EEG device which captures a single-lead frontal EEG via a 3-electrode sensor applied to the patient's forehead. The system calculates the "spectral entropy" of the electroencephalogram (EEG) signals, which is a measure of the degree that the power spectrum is uniform. Increasing brain levels of anaesthetic drugs causes the predominant frequencies in the EEG to be lower than when awake, and this is reflected in a decrease in the spectral entropy. Entropy monitors generate two numbers that are derived from different frequency bands used. The State Entropy (SE) is calculated from the 0.8 Hz to 32 Hz range, whereas the Response Entropy (RE) uses frequencies up to 47 Hz. Electromyogram activity is more predominant in those higher frequencies, and so the Response ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GE Healthcare
GE HealthCare is a subsidiary of American multinational conglomerate General Electric incorporated in New York and headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. As of 2017, it is a manufacturer and distributor of diagnostic imaging agents and radiopharmaceuticals for imaging modalities used in medical imaging procedures. It offers dyes used in magnetic-resonance-imaging procedures; manufactures medical diagnostic equipment, including CT image machines; MRI, XRAY; Ultrasound; Cath Labs; Mamogram; Nuclear Medicine Cameres; and develops Health technology for medical imaging and information technologies, medical diagnostics, patient monitoring systems, disease research, drug discovery, and biopharmaceutical manufacturing. It was incorporated in 1994 and operates in more than 100 countries. On November 9, 2021, General Electric announced it would demerge into three investment-grade public companies, GE HealthCare being one of the three planned divestitures. The spin-off of GE HealthCare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalogram
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the International 10-20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying brain tissue, the recordings made by the electrodes on the surface of the scalp vary in accordance with their orientation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two broad classes: general anesthetics, which result in a reversible loss of consciousness, and local anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of sensation for a limited region of the body without necessarily affecting consciousness. A wide variety of drugs are used in modern anesthetic practice. Many are rarely used outside anesthesiology, but others are used commonly in various fields of healthcare. Combinations of anesthetics are sometimes used for their synergistic and additive therapeutic effects. Adverse effects, however, may also be increased. Anesthetics are distinct from analgesics, which block only sensation of painful stimuli. Local anesthetics Local anesthetic agents prevent the transmission of nerve impulses without causi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has a slightly sweet scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful oxidiser similar to molecular oxygen. Nitrous oxide has significant medical uses, especially in surgery and dentistry, for its anaesthetic and pain-reducing effects. Its colloquial name, "laughing gas", coined by Humphry Davy, is due to the euphoric effects upon inhaling it, a property that has led to its recreational use as a dissociative anaesthetic. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is also used as an oxidiser in rocket propellants, and in motor racing to increase the power output of engines. Nitrous oxide's atmospheric concentration reached 333 parts per billion (ppb) in 2020, increasing at a rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vital Signs
Vital signs (also known as vitals) are a group of the four to six most crucial medical signs that indicate the status of the body's vital (life-sustaining) functions. These measurements are taken to help assess the general physical health of a person, give clues to possible diseases, and show progress toward recovery. The normal ranges for a person's vital signs vary with age, weight, gender, and overall health. There are four primary vital signs: body temperature, blood pressure, pulse ( heart rate), and breathing rate ( respiratory rate), often notated as BT, BP, HR, and RR. However, depending on the clinical setting, the vital signs may include other measurements called the "fifth vital sign" or "sixth vital sign". Vital signs are recorded using the LOINC internationally accepted standard coding system. Early warning scores have been proposed that combine the individual values of vital signs into a single score. This was done in recognition that deteriorating vital signs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the neck (carotid artery), wrist (radial artery), at the groin (femoral artery), behind the knee ( popliteal artery), near the ankle joint (posterior tibial artery), and on foot ( dorsalis pedis artery). Pulse (or the count of arterial pulse per minute) is equivalent to measuring the heart rate. The heart rate can also be measured by listening to the heart beat by auscultation, traditionally using a stethoscope and counting it for a minute. The radial pulse is commonly measured using three fingers. This has a reason: the finger closest to the heart is used to occlude the pulse pressure, the middle finger is used get a crude estimate of the blood pressure, and the finger most distal to the heart (usually the ring finger) is used to nullify the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide, but is also modulated by numerous factors, including, but not limited to, genetics, physical fitness, stress or psychological status, diet, drugs, hormonal status, environment, and disease/illness as well as the interaction between and among these factors. It is usually equal or close to the pulse measured at any peripheral point. The American Heart Association states the normal resting adult human heart rate is 60–100 bpm. Tachycardia is a high heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. Bradycardia is a low heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. When a human sleeps, a heartbeat with rates around 40–50 bpm is common and is considered normal. When the heart is not beating in a regular pattern, this is refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature—that healthcare professionals use in evaluating a patient's health. Normal resting blood pressure, in an adult is approximately systolic over diastolic, denoted as "120/80 mmHg". Globally, the average blood pressure, age standardized, has remained about the same sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scientists. Opinions differ about what exactly needs to be studied or even considered consciousness. In some explanations, it is synonymous with the mind, and at other times, an aspect of mind. In the past, it was one's "inner life", the world of introspection, of private thought, imagination and volition. Today, it often includes any kind of cognition, experience, feeling or perception. It may be awareness, awareness of awareness, or self-awareness either continuously changing or not. The disparate range of research, notions and speculations raises a curiosity about whether the right questions are being asked. Examples of the range of descriptions, definitions or explanations are: simple wakefulness, one's sense of selfhood or sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
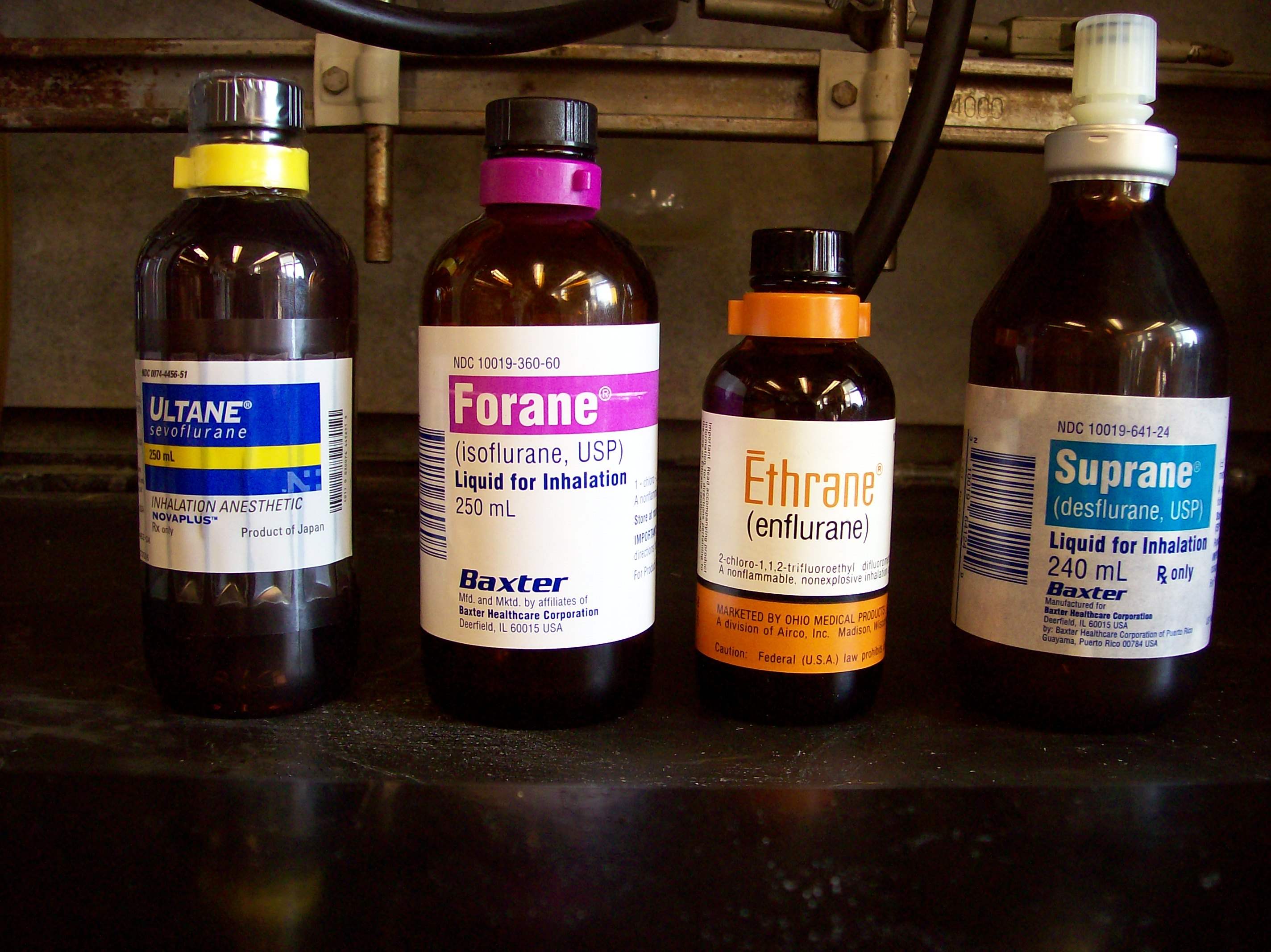
Inhalational Anaesthetic
An inhalational anesthetic is a chemical compound possessing general anesthetic properties that can be delivered via inhalation. They are administered through a face mask, laryngeal mask airway or tracheal tube connected to an anesthetic vaporiser and an anesthetic delivery system. Agents of significant contemporary clinical interest include volatile anesthetic agents such as isoflurane, sevoflurane and desflurane, as well as certain anesthetic gases such as nitrous oxide and xenon. List of inhalational anaesthetic agents Currently-used agents * Desflurane * Isoflurane * Nitrous oxide * Sevoflurane * Xenon Previously-used agents Although some of these are still used in clinical practice and in research, the following anaesthetic agents are primarily of historical interest in developed countries: * Acetylene * Chloroethane (ethyl chloride) * Chloroform * Cryofluorane * Cyclopropane * Diethyl ether * Divinyl ether * Enflurane * Ethylene * Fluroxene * Halothane (still wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaesthetist
Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology, or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critical emergency medicine, and pain medicine. A physician specialized in anesthesiology is called an anesthesiologist, anaesthesiologist, or anaesthetist, depending on the country. In some countries, the terms are synonymous, while in other countries they refer to different positions, and ''anesthetist'' is only used for non-physicians, such as nurse anesthetists. The core element of the specialty is the study and use of anesthesia to safely support a patient's vital functions through the perioperative period. Since the 19th century, anesthesiology has developed from an experimental area with non-specialist practitioners using novel, untested drugs and techniques into what is now a highly refined, safe and effective field of medicine. In some countries anesthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalograph
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the International 10-20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying brain tissue, the recordings made by the electrodes on the surface of the scalp vary in accordance with their orientation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.png)