|
Eschatology Of Jehovah's Witnesses
The eschatology of Jehovah's Witnesses is central to their religious beliefs. They believe that Jesus Christ has been ruling in heaven as king since 1914, a date they believe was prophesied in Scripture, and that after that time a period of cleansing occurred, resulting in God's selection of the Bible Students associated with Charles Taze Russell to be his people in 1919. They believe the destruction of those who reject their message and thus willfully refuse to obey God will shortly take place at Armageddon, ensuring that the beginning of the new earthly society will be composed of willing subjects of that kingdom. The group's doctrines surrounding 1914 are the legacy of a series of emphatic claims regarding the years 1799, 1874, 1878, 1914, 1918 and 1925 made in the Watch Tower Society's publications between 1879 and 1924. Claims about the significance of those years, including the presence of Jesus Christ, the beginning of the " last days", the destruction of worldly governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eschatology
Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of Contemporary era, present age, human history, or the world itself. The end of the world or end times is predicted by several world religions (both Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic and non-Abrahamic), which teach that negative world events will reach a climax. Briefly: the eschaton is the all-inclusive term evoking this predicted climax of a particular theological or political worldview. The scope of expected consequence is global and not local. Eschatology denotes the theory, discussion, techniques, behaviors and orientation toward the eschaton. Theories of afterlife may also be a dimension of eschatology in certain contexts—in these contexts the afterlife of an individual is a kind of hologram or particular microcosm of the overall eschaton. The Eschaton is, furthermore, related to telos: a Greek word simultaneously denoting purpose, climax and end (ie. death, terminus etc. but also perfection, completion etc.). Eschaton is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God's Kingdom
The concept of the kingship of God appears in all Abrahamic religions, where in some cases the terms kingdom of God and kingdom of Heaven are also used. The notion of God's kingship goes back to the Hebrew Bible, which refers to "his kingdom" but does not include the term "Kingdom of God". The "Kingdom of God" and its equivalent form "Kingdom of Heaven" in the Gospel of Matthew is one of the key elements of the teachings of Jesus in the New Testament. The Gospel of Mark indicates that the gospel is the good news about the Kingdom of God. The term pertains to the kingship of Christ over all creation. The phrase "Kingdom of heaven" appears in Matthew's gospel due primarily to Jewish sensibilities about uttering the "name" (God). Jesus did not teach the kingdom of God ''per se'' so much as the ''return'' of that kingdom. The notion of God's kingdom (as it had been under Moses) returning became an agitation in Roman Palestine 60 years before Jesus was born, and continued to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern English Bible Translations
Modern English Bible translations consists of English Bible translations developed and published throughout the late modern period () to the present (). A multitude of recent attempts have been made to translate the Bible into English. Most modern translations published since are based on recently published critical editions of the original Hebrew and Greek texts. These translations typically rely on the '' Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia'' / ''Biblia Hebraica Quinta'', counterparted by the '' Novum Testamentum Graece'' (and the ''Greek New Testament'', published by the United Bible Societies, which contains the same text). With regard to the use of Bible translations among biblical scholarship, the New Revised Standard Version is used broadly, but the English Standard Version is emerging as a primary text of choice among biblical scholars and theologians inclined toward theological conservatism. Development of Modern English Bible versions The Wessex Gospels were the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jehovah
Jehovah () is a Romanization, Latinization of the Hebrew language, Hebrew , one Tiberian vocalization, vocalization of the Tetragrammaton (YHWH), the proper name of the God in Judaism, God of Israel in the Hebrew BibleOld Testament. The Tetragrammaton is considered one of the Names of God in Judaism#Seven names of God, seven names of God in Judaism and a form of names of God in Christianity, God's name in Christianity. The Scholarly consensus, consensus among scholars is that the historical vocalization of the Tetragrammaton at the time of the redaction of the Torah (6th century BCE) is most likely Yahweh. The historical vocalization was lost because in Second Temple Judaism, during the 3rd to 2nd centuries BCE, the pronunciation of the Tetragrammaton came to be avoided, being substituted with ('my Lord'). The Hebrew vowel points of were added to the Tetragrammaton by the Masoretes, and the resulting form was transliterated around the 12th century CE as ''Yehowah' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labashi-Marduk
Labashi-Marduk ( or , meaning "O Marduk, may I not come to shame") was the fifth and penultimate king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling in 556 BC. He was the son and successor of Neriglissar. Though classical authors such as Berossus wrote that Labashi-Marduk was just a child when he became king, Babylonian documents indicate that he had been in charge of his own affairs before his rise to the throne, suggesting he was an adult, though possibly still relatively young. Labashi-Marduk's reign was very short, lasting only one to three months, with the last evidence of Neriglissar's life dating in April 556 BC and documents dated to Labashi-Marduk's successor, Nabonidus, appearing in May that same year and becoming widespread in Babylonia by the end of June. Nabonidus's son Belshazzar led a coup against the king, deposing and killing Labashi-Marduk and proclaiming Nabonidus as king. The reason for Labashi-Marduk's deposition is unknown, Berossus simply describes the justificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neriglissar
Neriglissar ( Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nergal-šar-uṣur'' or ''Nergal-šarra-uṣur'', meaning "Nergal, protect the king") was the fourth king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from his usurpation of the throne in 560 BC to his death in 556 BC. Though unrelated to previous Babylonian kings, possibly being of Aramean ancestry, Neriglissar was a prominent official and general in the reign of Nebuchadnezzar II (605–562 BC) and became even more influential through marrying one of Nebuchadnezzar's daughters, possibly Kashshaya. Nebuchadnezzar was initially succeeded by his son, Amel-Marduk, but Amel-Marduk's reign only lasted for two years before Neriglissar usurped the Babylonian throne and put him to death. Through his marriage to Nebuchadnezzar's daughter, possibly significantly older than any of the old king's sons, Neriglissar might have represented a less legitimate but more wealthy and well-established faction of the royal family, even if he himself was not part of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabonidus
Nabonidus (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-naʾid'', meaning "May Nabu be exalted" or "Nabu is praised") was the last king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from 556 BC to the fall of Babylon to the Achaemenian Empire under Cyrus the Great in 539 BC. Nabonidus was the last native ruler of ancient Mesopotamia, the end of his reign marking the end of thousands of years of Sumero-Akkadian language, Akkadian states, Monarchy, kingdoms and empires. He was also the last independent king of Babylon. Regarded as one of the most vibrant and individualistic rulers of his time, Nabonidus is characterised by some scholars as an unorthodox religious reformer and as the first archaeologist. The origins of Nabonidus, his connection to previous royalty, and subsequently what claim he had to the throne remain unclear, given that Nabonidus made no genealogical claims of kinship to previous kings. This suggests that he was neither related nor connected to the Chaldean dynasty of Babylonian rulers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amel-Marduk
Amel-Marduk ( Babylonian cuneiform: ''Amēl-Marduk'', meaning "man of Marduk"), also known as Awil-Marduk, or in the biblical rendition of his name, Evil-Merodach (), was the third emperor of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from 562 BCE until his overthrow and murder in 560 BCE. He was the successor of Nebuchadnezzar II (605–562 BCE). On account of the small number of surviving cuneiform sources, little is known of Amel-Marduk's reign and actions as king. Amel-Marduk, originally named Nabu-shum-ukin, was not Nebuchadnezzar's eldest son nor the oldest living son at his appointment as crown prince and heir. It is not clear why Amel-Marduk was appointed by his father as successor, mainly since there appear to have been altercations between the two, possibly involving an attempt by Amel-Marduk to take the throne while his father was still alive. After the conspiracy, Amel-Marduk was imprisoned, possibly together with Jeconiah, the captured king of Judah. Nabu-shum-ukin changed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
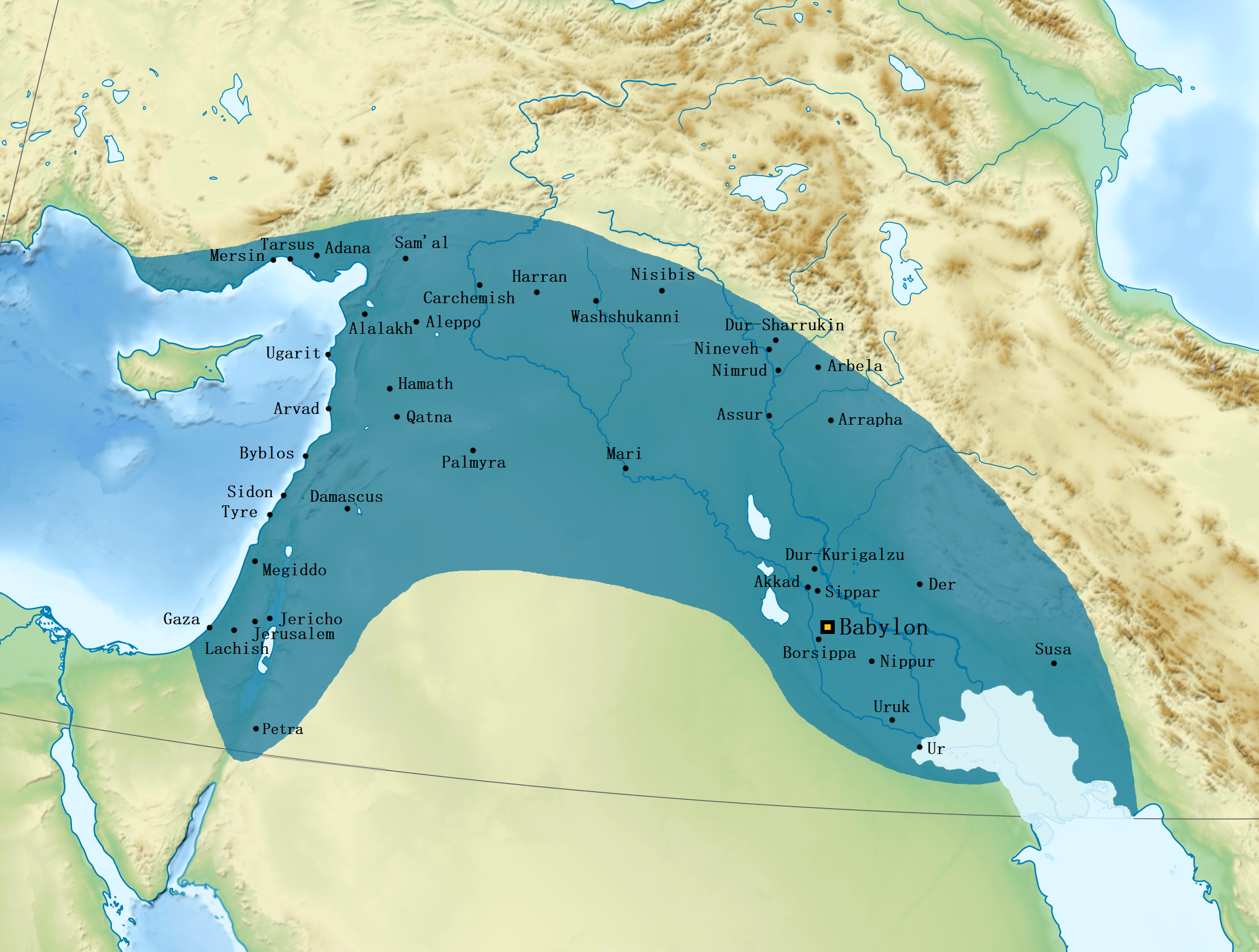
Neo-Babylonian
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to ancient Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC and being firmly established through the fall of the Assyrian Empire in 612 BC, the Neo-Babylonian Empire was conquered by the Achaemenid Persian Empire in 539 BC, marking the collapse of the Chaldean dynasty less than a century after its founding. The defeat of the Assyrian Empire and subsequent return of power to Babylon marked the first time that the city, and southern Mesopotamia in general, had risen to dominate the ancient Near East since the collapse of the Old Babylonian Empire (under Hammurabi) nearly a thousand years earlier. The period of Neo-Babylonian rule thus saw unprecedented economic and population growth throughout Babylonia, as well as a renaissance of culture and artwork as Neo-Babylonian kings conducted massive buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonian Captivity
The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile was the period in Jewish history during which a large number of Judeans from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were forcibly relocated to Babylonia by the Neo-Babylonian Empire. The deportations occurred in multiple waves: After the Siege of Jerusalem (597 BC), siege of Jerusalem in 597 BCE, around 7,000 individuals were deported to Mesopotamia. Further deportations followed the destruction of Jerusalem and Solomon's Temple in 587 BCE. Although the dates, numbers of deportations, and numbers of deportees vary in the several biblical accounts, the following is a general outline of what occurred. After the Battle of Carchemish in 605 BCE, the Babylonian king Nebuchadnezzar II besieged Jerusalem, which resulted in tribute being paid by the Judean king Jehoiakim. In 602 BCE, Jehoiakim refused to pay further tribute, which led in 598/597 BCE to Siege of Jerusalem (597 BC), another siege of the city by Nebuchadnezzar II and culminated in the dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Coming
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is the Christianity, Christian and Islam, Islamic belief that Jesus, Jesus Christ will return to Earth after his Ascension of Jesus, ascension to Heaven (Christianity), Heaven (which is said to have occurred about two thousand years ago). The idea is based on Jesus and messianic prophecy, messianic prophecies and is part of most Christian eschatologies. In Islamic eschatology, Jesus in Islam, Jesus (''ʿĪsā ibn Maryam'') is also believed to return in the end times. According to Islamic belief, he will descend from Heaven to defeat the Al-Masih ad-Dajjal, false messiah (''al-Masih ad-Dajjal''), restore justice, and reaffirm monotheism. His return is regarded as one of the Judgement Day in Islam, major signs of the Day of Judgment, and he is viewed as a revered prophet, not divine, in Islamic theology. Other faiths have various interpretations of it. Terminology Several different terms are used to refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millenarianism
Millenarianism or millenarism () is the belief by a religious, social, or political group or movement in a coming fundamental transformation of society, after which "all things will be changed". Millenarianism exists in various cultures and religions worldwide, with various interpretations of what constitutes a transformation. These movements believe in radical changes to society after a major cataclysm or transformative event.''Millenarianism'' . In James Crossley and Alastair Lockhart (eds.) ''Critical Dictionary of Apocalyptic and Millenarian Movements''. 2021 Millenarianist movements can be secular (not espousing a particular religion) or religious in nature,Gordon Marshall, "millenarianism", ''The Concise Oxford Dictionary of Sociology'' (1994), p. 333. and are therefore not necessarily linked to < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |