|
Energy–momentum Relation
In physics, the energy–momentum relation, or relativistic dispersion relation, is the relativistic equation relating total energy (which is also called relativistic energy) to invariant mass (which is also called rest mass) and momentum. It is the extension of mass–energy equivalence for bodies or systems with non-zero momentum. It can be formulated as: This equation holds for a body or system, such as one or more particles, with total energy , invariant mass , and momentum of magnitude ; the constant is the speed of light. It assumes the special relativity case of flat spacetime and that the particles are free. Total energy is the sum of rest energy E_0 = m_0 c^2 and relativistic kinetic energy: E_K = E - E_0 = \sqrt- m_c^2 Invariant mass is mass measured in a center-of-momentum frame. For bodies or systems with zero momentum, it simplifies to the mass–energy equation E_0 = m_0 c^2, where total energy in this case is equal to rest energy. The Dirac sea mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion. In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating object of mass ''m'' traveling at a speed ''v'' is \fracmv^2.Resnick, Robert and Halliday, David (1960) ''Physics'', Section 7-5, Wiley International Edition The kinetic energy of an object is equal to the work, or force ( F) in the direction of motion times its displacement ( s), needed to accelerate the object from rest to its given speed. The same amount of work is done by the object when decelerating from its current speed to a state of rest. The SI unit of energy is the joule, while the English unit of energy is the foot-pound. In relativistic mechanics, \fracmv^2 is a good approximation of kinetic energy only when ''v'' is much less than the speed of light. History and etymology The adjective ''kinetic'' has its roots in the Greek word κίνησις ''kinesis'', meaning "motion". The dichoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirac Sea
The Dirac sea is a theoretical model of the electron vacuum as an infinite sea of electrons with negative energy, now called '' positrons''. It was first postulated by the British physicist Paul Dirac in 1930 to explain the anomalous negative-energy quantum states predicted by the relativistically-correct Dirac equation for electrons. The positron, the antimatter counterpart of the electron, was originally conceived of as a hole in the Dirac sea, before its experimental discovery in 1932.This was not the original intent of Dirac though, as the title of his 1930 paper (''A Theory of Electrons and Protons'') indicates. But it soon afterwards became clear that the mass of holes must be that of the electron. In hole theory, the solutions with negative time evolution factors are reinterpreted as representing the positron, discovered by Carl Anderson. The interpretation of this result requires a Dirac sea, showing that the Dirac equation is not merely a combination of special relativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Frame
In classical physics and special relativity, an inertial frame of reference (also called an inertial space or a Galilean reference frame) is a frame of reference in which objects exhibit inertia: they remain at rest or in uniform motion relative to the frame until acted upon by external forces. In such a frame, the laws of nature can be observed without the need to correct for acceleration. All frames of reference with zero acceleration are in a state of constant rectilinear motion (straight-line motion) with respect to one another. In such a frame, an object with zero net force acting on it, is perceived to move with a constant velocity, or, equivalently, Newton's first law of motion holds. Such frames are known as inertial. Some physicists, like Isaac Newton, originally thought that one of these frames was absolute — the one approximated by the fixed stars. However, this is not required for the definition, and it is now known that those stars are in fact moving, relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frame Of Reference
In physics and astronomy, a frame of reference (or reference frame) is an abstract coordinate system, whose origin (mathematics), origin, orientation (geometry), orientation, and scale (geometry), scale have been specified in physical space. It is based on a set of reference points, defined as point (geometry), geometric points whose position (geometry), position is identified both mathematically (with numerical coordinate values) and physically (signaled by conventional markers). An important special case is that of ''inertial reference frames'', a stationary or uniformly moving frame. For ''n'' dimensions, reference points are sufficient to fully define a reference frame. Using Cartesian coordinate system, rectangular Cartesian coordinates, a reference frame may be defined with a reference point at the origin and a reference point at one unit distance along each of the ''n'' coordinate Cartesian coordinate system, axes. In Theory of relativity, Einsteinian relativity, referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity, and as Einstein's theory of gravity, is the differential geometry, geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General theory of relativity, relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time in physics, time, or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ''curvature of spacetime'' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever is present, including matter and radiation. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second-order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes gravity in classical mechanics, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiant Energy
In physics, and in particular as measured by radiometry, radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic and gravitational radiation. As energy, its SI unit is the joule (J). The quantity of radiant energy may be calculated by Integral, integrating radiant flux (or radiant flux, power) with respect to time. The symbol ''Q''e is often used throughout literature to denote radiant energy ("e" for "energetic", to avoid confusion with photometric quantities). In branches of physics other than radiometry, electromagnetic energy is referred to using ''E'' or ''W''. The term is used particularly when electromagnetic radiation is emitted by a source into the surrounding environment. This radiation may be visible or invisible to the human eye. Terminology use and history The term "radiant energy" is most commonly used in the fields of radiometry, solar energy, heating and lighting, but is also sometimes used in other fields (such as telecommunications). In modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
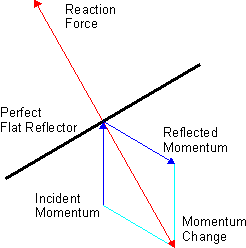
Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure (also known as light pressure) is mechanical pressure exerted upon a surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbed, Reflection (physics), reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Electromagnetism
Classical electromagnetism or classical electrodynamics is a branch of physics focused on the study of interactions between electric charges and electrical current, currents using an extension of the classical Newtonian model. It is, therefore, a classical field theory. The theory provides a description of electromagnetic phenomena whenever the relevant length scales and field strengths are large enough that quantum mechanical effects are negligible. For small distances and low field strengths, such interactions are better described by quantum electrodynamics which is a quantum field theory. History The physical phenomena that electromagnetism describes have been studied as separate fields since antiquity. For example, there were many advances in the field of History of optics, optics centuries before light was understood to be an electromagnetic wave. However, the theory of electromagnetism, as it is currently understood, grew out of Michael Faraday's experiments suggesting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can move no faster than the speed of light measured in vacuum. The photon belongs to the class of boson particles. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While Planck was trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, he proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |