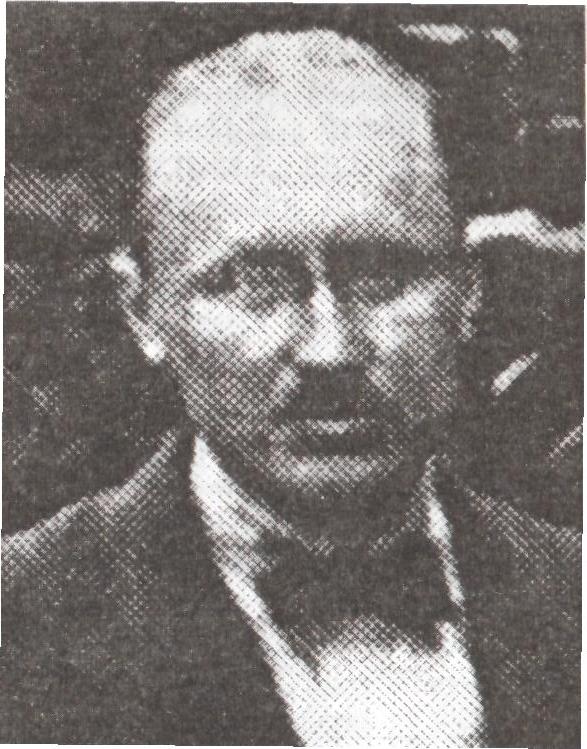|
Endgame Study
In the game of chess, an endgame study, or just study, is a type of chess problem that starts with a composed position—i.e. one that has been made up rather than played in an actual game—where the goal is to find the essentially unique way for one side (usually White) to win or draw, as stipulated, against any moves the other side plays. If the study does not end in the end of the game, then the game's eventual outcome should be obvious, and White can have a selection of various moves. There is no limit to the number of moves which are allowed to achieve the win; this distinguishes studies from the genre of direct mate problems (e.g. "mate in 2"). Such problems also differ qualitatively from the very common genre of tactical puzzles based around the middlegame, often based on an actual game, where a decisive tactic must be found. Composed studies Composed studies predate the modern form of chess. Shatranj studies exist in manuscripts from the 9th century, and the earliest trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves Perfect information, no hidden information and no elements of game of chance, chance. It is played on a square chessboard, board consisting of 64 squares arranged in an 8×8 grid. The players, referred to as White and Black in chess, "White" and "Black", each control sixteen Chess piece, pieces: one king (chess), king, one queen (chess), queen, two rook (chess), rooks, two bishop (chess), bishops, two knight (chess), knights, and eight pawn (chess), pawns, with each type of piece having a different pattern of movement. An enemy piece may be captured (removed from the board) by moving one's own piece onto the square it occupies. The object of the game is to "checkmate" (threaten with inescapable capture) the enemy king. There are also several ways a game can end in a draw (chess), draw. The recorded history of chess goes back to at least the emergence of chaturanga—also thought to be an ancesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Endgame
The endgame (or ending) is the final stage of a chess game which occurs after the middlegame. It begins when few pieces are left on the board. The line between the middlegame and the endgame is often not clear, and may occur gradually or with a quick exchange of pieces. The endgame, however, tends to have different characteristics from the middlegame, and the players have correspondingly different strategic concerns. In particular, pawns become more important as endgames often revolve around attempts to promote a pawn by advancing it to the eighth . The king, which normally is kept safe during the game, becomes active in the endgame, as it can help escort pawns to promotion, attack enemy pawns, protect other pieces, and restrict the movement of the enemy king. Not all chess games reach an endgame; some of them end earlier. All chess positions with up to seven pieces on the board have been solved by endgame tablebases, so the outcome (win, loss, or draw) of best play by bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambit Publications
Gambit Publications is a major publisher of chess books. The company's headquarters is in London. It has published more than 200 chess books. The company was founded by three chess players. Grandmaster (GM) John Nunn is the chess director, GM Murray Chandler is the managing director, and FIDE Master Graham Burgess is the editorial director. Some of the major books published by Gambit are ''Mastering the Chess Openings'' (four volumes) by John Watson, ''Secrets of Modern Chess Strategy'' also by Watson, ''Fundamental Chess Endings'' by Karsten Müller and Frank Lamprecht, ''Understanding the Chess Openings'' by Sam Collins, and the new ''Chess Explained'' series by various authors.{{Cite web , last=Peter Wells and 5 more , date=23 December 2013 , title=Chess Explained (8 books) , url=https://www.amazon.in/Chess-Explained/dp/B08P1K7185 , website=Amazon.com Amazon.com, Inc., doing business as Amazon, is an American multinational technology company engaged in e-com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saavedra Position
The Saavedra position is one of the best-known chess endgame studies. It is named after the Spanish priest Fernando Saavedra (1849–1922), who lived in Glasgow during the late 19th century. Though not a strong player, he spotted a win involving a dramatic underpromotion in a position previously thought to have been a draw. The Saavedra position has inspired many chess composers. There are only four pieces, yet there are both tricks and counter-tricks, challenging a composer's imagination as to just what might be achievable with a full set of pieces. It is among a minority of positions where a king and a pawn can win against a king and a rook. Solution The position as it is usually given today, with White to move and win, is shown in the diagram. The solution is: :1. c7 Rd6+ 2. Kb5 (If 2.Kc5 then Rd1 threatening a skewer via 3...Rc1; if instead 2.Kb7? then Rd7 pins the pawn, allowing Black to capture it to assure a draw.) :2... Rd5+ Or 2...Rd2 3.c8=Q Rb2+ 4.Ka4 Ra2+ 5.Kb3 R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chess Endgame Study Composers
This is a list of chess endgame study composers ordered alphabetically by surname. Russian names may be written with other spellings. *Yochanan Afek (born 1952). Israeli chess master and composer of endgame studies and problems. Grandmaster for chess compositions (2015). He published about 120 studies and won many awards, e.g. eleven first prizes. *Iuri Akobia (born 1937–2014). Georgian composer of over 300 studies and author of many books on endgame composition, among which 4332 Studies with Stalemate, 4492 Studies with Mate, 4324 Studies with Positional draw. By profession a radiotechnical engineer, he worked for many years in the Georgian National TV station. *Friedrich Amelung (1842–1909). Estonian composer of about 230 studies. *Ghamiet Amirjan (born 1934). Armenian composer of over 300 studies. *Yuri Averbakh (born 1922). Russian Grandmaster (winner of a USSR Chess Championship, Soviet Championship in 1954) and composer of over 200 studies, many of which give importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chessbase
ChessBase is a German company that develops and sells chess software, maintains a chess news site, and operates an internet chess server for online chess. Founded in 1986, it maintains and sells large-scale databases containing the moves of recorded chess games. The databases contain data from prior games and provide engine analyses of games. Endgame tablebases are also provided by the company. ChessBase's Indian YouTube channel ChessBase India has amassed more than 2.5 million YouTube subscribers and more than 2.5 billion total views as of December 2024. History Starting in 1983, Frederic Friedel and his colleagues put out a magazine ''Computer-schach und Spiele'' covering the emerging hobby of computer chess. In 1985, Friedel invited then world chess champion Garry Kasparov to his house. Kasparov mused about how a chess database would make it easier for him to prepare for specific opponents. Friedel began working with Bonn physicist Matthias Wüllenweber who created the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frédéric Lazard
Frédéric Lazard (20 February 1883, in Marseille – 18 November 1948, in Le Vésinet) was a French chess master, problemist and journalist. He lived in Paris, where he played in many local tournaments. He took twice 4th place in 1905, shared 3rd in 1908, took 3rd ( Arnold Aurbach won) in 1909, shared 2nd behind H. Weinstein in 1909, won ahead of Amédée Gibaud in 1910, tied for 1st with Aristide Gromer in 1912, took 4th in 1914, and shared 2nd, behind Alphonse Goetz, at Lyon 1914. In 1912, he drew a match with Gibaud (3–3), and lost to Edward Lasker (0.5–2.5). In 1913, he drew with Smirnov (1.5–1.5). After World War I, he won at Paris 1920, took 2nd at Paris 1922 (''Triangular'', André Muffang won), represented France in 1st unofficial Chess Olympiad at Paris 1924, took 9th at Strasbourg 1924 ( French Chess Championship, Robert Crépeaux won), tied for 2nd-3rd at Nice 1925 (FRA-ch, Crépeaux won), shared 1st with André Chéron at Biarritz 1926 (FRA-ch), took ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elo Ratings
The Elo rating system is a method for calculating the relative skill levels of players in zero-sum games such as chess or esports. It is named after its creator Arpad Elo, a Hungarian-American chess master and physics professor. The Elo system was invented as an improved chess-rating system over the previously used Harkness system, but is also used as a rating system in association football (soccer), American football, baseball, basketball, pool, various board games and esports, and, more recently, large language models. The difference in the ratings between two players serves as a predictor of the outcome of a match. Two players with equal ratings who play against each other are expected to score an equal number of wins. A player whose rating is 100 points greater than their opponent's is expected to score 64%; if the difference is 200 points, then the expected score for the stronger player is 76%. A player's Elo rating is a number that may change depending on the outcome o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rook (chess)
The rook (; ♖, ♜) is a piece in the game of chess. It may move any number of squares horizontally or vertically without jumping, and it may an enemy piece on its path; it may participate in castling. Each player starts the game with two rooks, one in each corner on their side of the board. Formerly, the rook (from ) was alternatively called the ''tower'', ''marquess'', ''rector'', and ''comes'' (''count'' or ''earl''). The term "castle" is considered to be informal or old-fashioned. Placement and movement The white rooks start on the squares a1 and h1, while the black rooks start on a8 and h8. The rook moves horizontally or vertically, through any number of unoccupied squares. The rook cannot jump over pieces. The rook may capture an enemy piece by moving to the square on which the enemy piece stands, removing it from play. The rook also participates with the king in a special move called castling, wherein it is transferred to the square crossed by the king after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King (chess)
The king (♔, ♚) is the most important chess piece, piece in the game of chess. It may move to any adjoining square; it may also perform, in tandem with the Rook (chess), rook, a special move called ''castling''. If a player's king is threatened with capture, it is said to be ''in Check (chess), check'', and the player must remove or evade the threat of immediately, such as by moving it away from the attacked square. If this cannot be done, the king is said to be in checkmate, resulting in a loss for that player. A player cannot make any move that places their own king in check. Despite this, the king can become a strong offensive piece in the Chess endgame, endgame or, rarely, the Chess middlegame, middlegame. In Algebraic notation (chess), algebraic notation, the king is abbreviated by the letter ''K'' among English speakers. The white king starts the game on e1; the black king starts on e8. Unlike all other pieces, each player can have only one king, and the kings are never ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexey Selezniev
Alexey (Alex) Sergeyevich Selezniev (, alternative transliterations: Selesniev, Selesniew, Selesnev, Selesnieff; pronounced "selezNYOFF"; 1888June 1967) was a Russian chess master and chess composer. Selezniev was born in Tambov, Russian Empire, into a wealthy merchant Russian family, and was a graduate from Moscow University's law faculty. He played in a number of pre-revolutionary tournaments at the Moscow Chess Club. He tied for 8-10th at Vilna 1912 (7th RUS-ch, B tourn, Karel Hromadka won). In 1913, he tied for 1st-2nd, tied for 4-5th, and tied for 5-6th in Moscow. In July–August 1914, he played in Mannheim (19th DSB Congress), and tied for 6-10th in interrupted tournament (''Hauptturnier A''). After the declaration of war against Russia, eleven “Russian players” (Alekhine, Bogoljubow, Bogatyrchuk, Flamberg, Koppelman, Maliutin, Rabinovich, Romanovsky, Saburov, Selezniev, Weinstein) from the Mannheim tournament were interned by Germany. In September 1914, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrifice (chess)
In chess, a sacrifice is a move that gives up a piece with the objective of gaining tactical or positional compensation in other forms. A sacrifice could also be a deliberate exchange of a chess piece of higher value for an opponent's piece of lower value. Any chess piece except the king may be sacrificed. Because players usually try to hold on to their own pieces, offering a sacrifice can come as an unpleasant surprise to one's opponent, putting them off balance and causing them to waste precious time trying to calculate whether the sacrifice is sound or not, and whether to accept it. Sacrificing one's queen (the most valuable piece), or a string of pieces, adds to the surprise, and such games can be awarded . Types of sacrifice Real versus sham Rudolf Spielmann proposed a division between sham and real sacrifices: * In a ''real sacrifice'', the sacrificing player will often have to play on with less than their opponent for quite some time. * In a ''sham sacrifice'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |