|
Echolocation (animal)
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological active sonar used by several animal groups, both in the air and underwater. Echolocating animals emit calls and listen to the echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects. Echolocation is used for navigation, foraging, and hunting prey. Echolocation calls can be frequency modulated (FM, varying in pitch during the call) or constant frequency (CF). FM offers precise range discrimination to localize the prey, at the cost of reduced operational range. CF allows both the prey's velocity and its movements to be detected by means of the Doppler effect. FM may be best for close, cluttered environments, while CF may be better in open environments or for hunting while perched. Echolocating animals include mammals, especially odontocetes (toothed whales) and some bat species, and, using simpler forms, species in other groups such as shrews. A few bird speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Echolocation
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological active sonar used by several animal groups, both in the air and underwater. Echolocating animals emit calls and listen to the Echo (phenomenon) , echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects. Echolocation is used for animal navigation , navigation, foraging, and predation, hunting prey. Echolocation calls can be Frequency modulation, frequency modulated (FM, varying in pitch during the call) or constant frequency (CF). FM offers precise range discrimination to localize the prey, at the cost of reduced operational range. CF allows both the prey's velocity and its movements to be detected by means of the Doppler effect. FM may be best for close, cluttered environments, while CF may be better in open environments or for hunting while perched. Echolocating animals include mammals, especially odontocetes (toothed whales) and some bat species, and, using s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
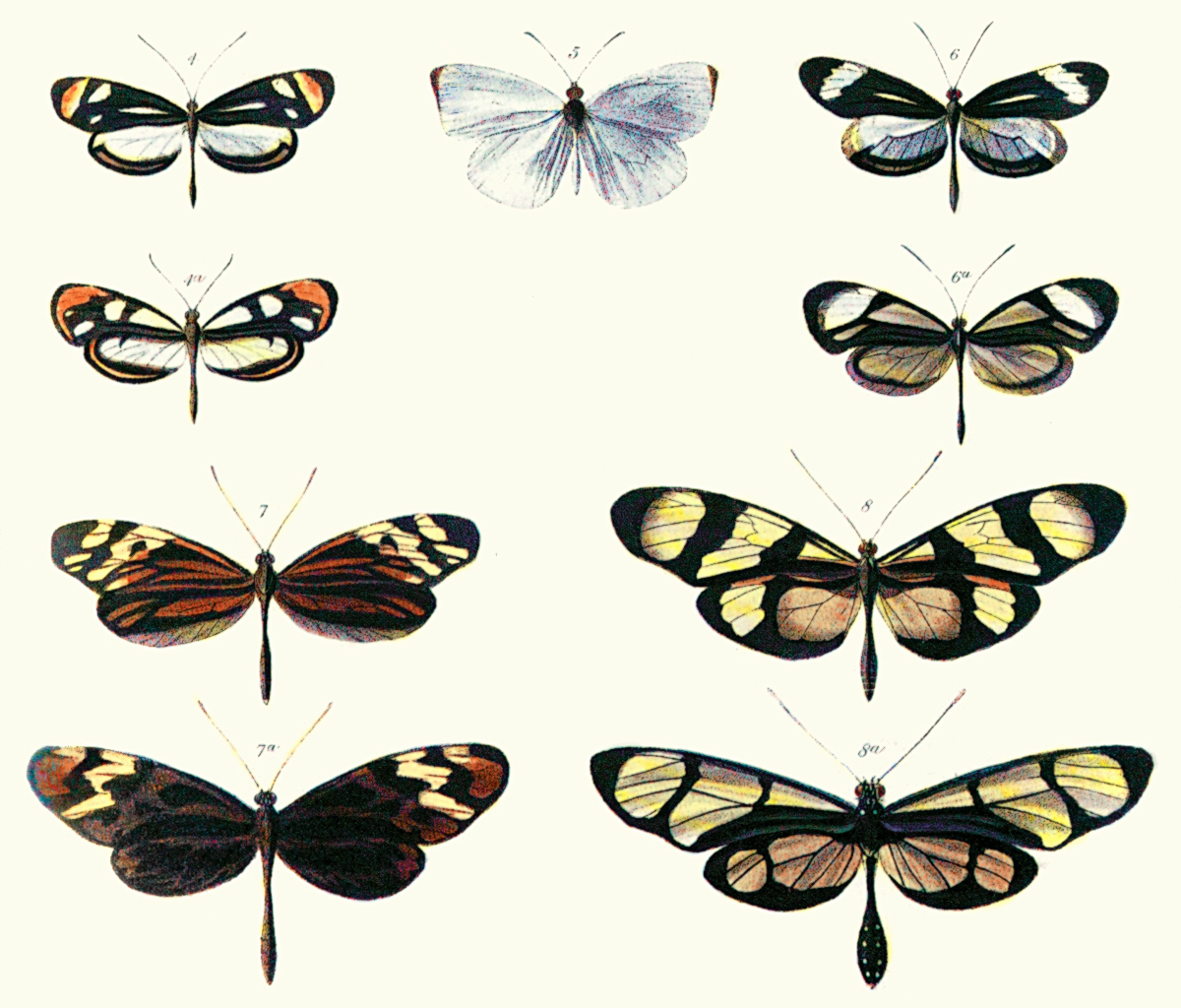
Batesian Mimicry
Batesian mimicry is a form of mimicry where a harmless species has evolved to imitate the warning signals of a harmful species directed at a predator of them both. It is named after the English naturalist Henry Walter Bates, who worked on butterflies in the rainforests of Brazil. Batesian mimicry is the most commonly known and widely studied of mimicry complexes, such that the word mimicry is often treated as synonymous with Batesian mimicry. There are many other forms however, some very similar in principle, others far separated. It is often contrasted with Müllerian mimicry, a form of mutually beneficial convergence between two or more harmful species. However, because the mimic may have a degree of protection itself, the distinction is not absolute. It can also be contrasted with functionally different forms of mimicry. Perhaps the sharpest contrast here is with aggressive mimicry where a predator or parasite mimics a harmless species, avoiding detection and improving its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Story Of Undersea Discovery And Adventure
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is '' a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, '' a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest known ancestor of A is ''aleph''—the first letter of the Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Yves Cousteau
Jacques-Yves Cousteau, (, also , ; 11 June 191025 June 1997) was a French naval officer, oceanographer, filmmaker and author. He co-invented the first successful open-circuit self-contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA), called the Aqua-Lung, which assisted him in producing some of the first underwater documentaries. Cousteau wrote many books describing his undersea explorations. In his first book, '' The Silent World: A Story of Undersea Discovery and Adventure'', Cousteau surmised the existence of the echolocation abilities of porpoises. The book was adapted into an underwater documentary called ''The Silent World''. Co-directed by Cousteau and Louis Malle, it was one of the first films to use underwater cinematography to document the ocean depths in color. The film won the 1956 at the Cannes Film Festival and remained the only documentary to do so until 2004 (when '' Fahrenheit 9/11'' received the award). It was also awarded the Academy Award for Best Docume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William E
William is a masculine given name of Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will or Wil, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, Billie, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie). Female forms include Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germanic name is a compound of *''wiljô'' "will, wish, desire" and *''helmaz'' "helm, helmet".Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply to any frequency range, including ultrasound. Ultrasonic devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who wrote on the mathematical properties of String instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamilton Hartridge
Hamilton Hartridge (7 May 1886 – 13 January 1976) was a British eye physiologist and medical writer.'Obituary: H. Hartridge', ''British Medical Journal'', 20 March 1976, p.716 Known for his ingenious experimentation and instrument construction abilities, he designed what is called the Hartridge Reversion Spectrometer. This was used for pioneering studies on haemoglobin oxygen-binding studies. Education and early career Hartridge was educated at Harrow and King's College, Cambridge, where he became a fellow from 1912 to 1926. He graduated in medicine from St George's Hospital in 1914, serving during the war as an experimental officer at RNAS Kingsnorth. In 1916 he married Kathleen Wilson, and they later had four children together. After the war he stayed in Cambridge University as lecturer in special senses and senior demonstrator in physiology. He gained a reputation as an ingenious experimenter, constructing, for example, the continuous-flow apparatus for measuring the rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrasound
Infrasound, sometimes referred to as low frequency sound or incorrectly subsonic (subsonic being a descriptor for "less than the speed of sound"), describes sound waves with a frequency below the lower limit of human audibility (generally 20 Hz, as defined by the ANSI/ASA S1.1-2013 standard). Hearing becomes gradually less sensitive as frequency decreases, so for humans to perceive infrasound, the sound pressure must be sufficiently high. Although the ear is the primary organ for sensing low sound, at higher intensities it is possible to feel infrasound vibrations in various parts of the body. The study of such sound waves is sometimes referred to as infrasonics, covering sounds beneath 20 Hz down to 0.1 Hz (and rarely to 0.001 Hz). People use this frequency range for monitoring earthquakes and volcanoes, charting rock and petroleum formations below the earth, and also in ballistocardiography and seismocardiography to study the mechanics of the human cardiovascul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiram Maxim
Sir Hiram Stevens Maxim (5 February 1840 – 24 November 1916) was an American-born British inventor best known as the creator of the first automatic machine gun, the Maxim gun. Maxim held patents on numerous mechanical devices such as hair-curling irons, a mousetrap, and steam pumps. Maxim laid claim to inventing the lightbulb. Maxim experimented with powered flight; his large aircraft designs were never successful. Circa 1904 he designed a highly successful amusement ride called the "Captive Flying Machine" to fund his research while generating public interest in flight. Maxim moved from the United States to the United Kingdom at the age of 41, and remained an American citizen until he became a naturalised British citizen in 1899, and received a knighthood in 1901. Birth and early life Maxim was born in Sangerville, Maine on 5 February 1840, into a family of French Huguenot origin. He became an apprentice Coach (vehicle), coachbuilder at the age of 14 and ten yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Magazine
The ''Philosophical Magazine'' is one of the oldest scientific journals published in English. It was established by Alexander Tilloch in 1798;John Burnett"Tilloch, Alexander (1759–1825)" Dictionary of National Biography#Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, Sept 2004; online edn, May 2006, accessed 17 Feb 2010 in 1822 Richard Taylor (editor), Richard Taylor became joint editor and it has been published continuously by Taylor & Francis ever since. Early history The name of the journal dates from a period when "natural philosophy" embraced all aspects of science. The very first paper published in the journal carried the title "Account of Mr Cartwright's Patent Steam Engine". Other articles in the first volume include "Methods of discovering whether Wine has been adulterated with any Metals prejudicial to Health" and "Description of the Apparatus used by Lavoisier to produce Water from its component Parts, Oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Jurine
Louis Jurine (; 6 February 1751 – 20 October 1819) was a Swiss physician, surgeon and naturalist mainly interested in entomology. He lived in Geneva. Surgeon He studied surgery in Paris and quickly acquired a great reputation for his expertise in medicine and natural history beyond that which he had in Geneva. He taught courses in anatomy and surgery at the Société des Arts in Geneva and was made honorary professor of zoology at the Academy (today: University of Geneva). He also founded a maternity hospice in 1807 and was awarded prizes for his work on the gasses of the human body, artificial feeding of infants, and pectoral angina. Naturalist Upon learning of Spallanzani's experiments with bats, in which Spallanzani showed that bats do not rely on sight when navigating in darkness, Jurine conducted a series of experiments from which he concluded that bats use sound to navigate in darkness.See: * Peschier (1798 "Extraits des expériences de Jurine sur les chauve-souris qu'o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazzaro Spallanzani
Lazzaro Spallanzani (; 12 January 1729 – 11 February 1799) was an Italian Catholic priest (for which he was nicknamed Abbé Spallanzani), biologist and physiologist who made important contributions to the experimental study of bodily functions, animal reproduction, and animal echolocation. His research on biogenesis paved the way for the downfall of the theory of spontaneous generation, a prevailing idea at the time that organisms develop from inanimate matters, though the final death blow to the idea was dealt by French scientist Louis Pasteur a century later. His most important works were summed up in his book ''Expériences pour servir a l'histoire de la génération des animaux et des plantes'' (''Experiences to Serve to the History of the Generation of Animals and Plants''), published in 1785. Among his contributions were experimental demonstrations of fertilisation between ova and spermatozoa, and ''in vitro'' fertilisation''.'' Biography Spallanzani was born in Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |