|
Dramaturgy
Dramaturgy is the study of dramatic composition and the representation of the main elements of drama on the stage. The role of a dramaturg in the field of modern dramaturgy is to help realize the multifaceted world of the play for a production using information from the script, playwright, and the context in which the play was written. It is a dramaturg's job to assist the director and sometimes the playwright, especially if the culture of the play is not fully experience by these people. The term first appears in the eponymous work '' Hamburg Dramaturgy'' (1767–69) by Gotthold Ephraim Lessing. Lessing composed this collection of essays on the principles of drama while working as the world's first dramaturge at the Hamburg National Theatre of Abel Seyler. Dramaturgy is distinct from play writing and directing, although the three may be practiced by one individual. Some dramatists combine writing and dramaturgy when creating a drama. Others work with a specialist, called a drama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg Dramaturgy
The ''Hamburg Dramaturgy'' () is a highly influential work on drama by Gotthold Ephraim Lessing, written between 1767 and 1769 when he worked as a dramaturg for Abel Seyler's Hamburg National Theatre. It was not originally conceived as a unified and systematical book, but rather as series of essays on the theater, which Lessing wrote as commentary on the plays of the short-lived Hamburg National Theater. This collection of 101 short essays represents one of the first sustained critical engagements with the potential of theater as a vehicle for the advancement of humanistic discourse. In many ways, the ''Hamburg Dramaturgy'' defined the new field of dramaturgy, and also introduced the term. During the time Lessing wrote the ''Hamburg Dramaturgy,'' there was a new movement of German theatre, based on self-reflection. Actors were beginning to perform the inner and outer lives of their characters at the same time. One of Lessing's most famous and renowned quotes from the compilation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natya Shastra (1898)
The ''Nāṭya Shāstra'' (, ''Nāṭyaśāstra'') is a Sanskrit treatise on the performing arts. The text is attributed to sage Bharata, and its first complete compilation is dated to between 200 BCE and 200 CE, but estimates vary between 500 BCE and 500 CE. The text consists of 36 chapters with a cumulative total of 6,000 poetic verses describing performance arts. The subjects covered by the treatise include dramatic composition, structure of a play and the construction of a stage to host it, genres of acting, body movements, make up and costumes, role and goals of an art director, the musical scales, musical instruments and the integration of music with art performance. The ''Nāṭya Śāstra'' is notable as an ancient encyclopedic treatise on the arts, one which has influenced dance, music and literary traditions in India. It is also notable for its aesthetic "Rasa" theory, which asserts that entertainment is a desired effect of performance arts but not t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dramaturge
A dramaturge or dramaturg (from Ancient Greek δραματουργός – dramatourgós) is a literary adviser or editor in a theatre, opera, or film company who researches, selects, adapts, edits, and interprets scripts, libretti, texts, and printed programmes (or helps others with these tasks), consults authors, and does public relations work. Its modern-day function was originated by the innovations of Gotthold Ephraim Lessing, an 18th-century German playwright, philosopher, and dramatic theory, theatre theorist. Responsibilities One of the dramaturge's contributions is to categorise and discuss the various types of plays or operas, their interconnectedness and their styles. The responsibilities of a dramaturge vary from one theatre or opera company to the next. They might include the hiring of actors, the development of a season of plays or operas with a sense of coherence among them, assistance with and editing of new plays or operas by resident or guest playwrights or compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
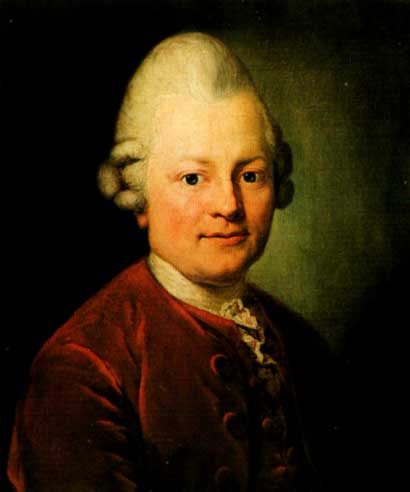
Gotthold Ephraim Lessing
Gotthold Ephraim Lessing (; ; 22 January 1729 – 15 February 1781) was a German philosopher, dramatist, publicist and art critic, and a representative of the Enlightenment era. His plays and theoretical writings substantially influenced the development of German literature. He is widely considered by theatre historians to be the first dramaturg in his role at Abel Seyler's Hamburgische Entreprise, Hamburg National Theatre. The word Dramaturgy first appears in his work ''Hamburg Dramaturgy.'' Life Lessing was born in Kamenz, a small town in Electorate of Saxony, Saxony, to pastor and theologian (1693–1770) and his wife Justine Salome Feller (1703–1777), daughter of pastor of Kamenz, Gottfried Feller (1674–1733). His father was a Lutheran minister and wrote on theology. Young Lessing studied at the Latin School in Kamenz from 1737 to 1741. With a father who wanted his son to follow in his footsteps, Lessing next attended the Sächsisches Landesgymnasium Sankt Afra zu Mei� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dramaturge
A dramaturge or dramaturg (from Ancient Greek δραματουργός – dramatourgós) is a literary adviser or editor in a theatre, opera, or film company who researches, selects, adapts, edits, and interprets scripts, libretti, texts, and printed programmes (or helps others with these tasks), consults authors, and does public relations work. Its modern-day function was originated by the innovations of Gotthold Ephraim Lessing, an 18th-century German playwright, philosopher, and dramatic theory, theatre theorist. Responsibilities One of the dramaturge's contributions is to categorise and discuss the various types of plays or operas, their interconnectedness and their styles. The responsibilities of a dramaturge vary from one theatre or opera company to the next. They might include the hiring of actors, the development of a season of plays or operas with a sense of coherence among them, assistance with and editing of new plays or operas by resident or guest playwrights or compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dramatist
A playwright or dramatist is a person who writes plays, which are a form of drama that primarily consists of dialogue between characters and is intended for theatrical performance rather than just reading. Ben Jonson coined the term "playwright" and is the first person in English literature to refer to playwrights as separate from poets. The earliest playwrights in Western literature with surviving works are the Ancient Greeks. William Shakespeare is amongst the most famous playwrights in literature, both in England and across the world. Etymology The word "play" is from Middle English , from Old English ("play, exercise; sport, game; drama, applause"). The word '' wright'' is an archaic English term for a craftsperson or builder (as in a wheelwright or cartwright). The words combine to indicate a person who has "wrought" words, themes, and other elements into a dramatic form — a play. (The homophone with "write" is coincidental.) The first recorded use of the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catharsis
Catharsis is from the Ancient Greek word , , meaning "purification" or "cleansing", commonly used to refer to the purification and purgation of thoughts and emotions by way of expressing them. The desired result is an emotional state of renewal and restoration. In dramaturgy, the term usually refers to arousing negative emotion in an audience, who subsequently expels it, making them feel happier. In Greek the term originally had only a physical meaning, describing purification practices. In medicine, it can still refer to the evacuation of the '' catamenia'' ("monthlies", menstrual fluid). Similarly, a cathartic is a substance that accelerates the defecation of faeces. The first recorded uses of the term in a mental sense were by Aristotle in the ''Politics'' and '' Poetics'', comparing the effects of music and tragedy on the mind of a spectator to the effect of catharsis on the body.Aristotle, ''Poetics''1449b/ref> The term is also used in Greek to refer to the spiritual p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drama
Drama is the specific Mode (literature), mode of fiction Mimesis, represented in performance: a Play (theatre), play, opera, mime, ballet, etc., performed in a theatre, or on Radio drama, radio or television.Elam (1980, 98). Considered as a genre of poetry in general, the dramatic mode has been contrasted with the Epic poetry, epic and the Lyric poetry, lyrical modes ever since Aristotle's ''Poetics (Aristotle), Poetics'' ()—the earliest work of dramatic theory. The term "drama" comes from a Ancient Greek, Greek word meaning "deed" or "Action (philosophy), act" (Classical Greek: , ''drâma''), which is derived from "I do" (Classical Greek: , ''dráō''). The two masks associated with drama represent the traditional Genre, generic division between Comedy (drama), comedy and tragedy. In English (as was the analogous case in many other European languages), the word ''Play (theatre), play'' or ''game'' (translating the Old English, Anglo-Saxon ''pleġan'' or Latin ''ludus'') wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abel Seyler
Abel Seyler (23 August 1730, Liestal – 25 April 1800, Rellingen) was a Swiss-born theatre director and former merchant banker, who was regarded as one of the great theatre principals of 18th century Europe. He played a pivotal role in the development of German theatre and opera, and was considered "the leading patron of German theatre" in his lifetime.Wilhelm Kosch, "Seyler, Abel", in '' Dictionary of German Biography'', eds. Walther Killy and Rudolf Vierhaus, Vol. 9, Walter de Gruyter, 2005, , p. 308 He supported the development of new works and experimental productions, helping to establish Hamburg as a center of theatrical innovation and to establish a publicly funded theater system in Germany. Working with some of Germany's foremost actors and playwrights of his era, he is credited with pioneering a new more realist style of acting, introducing Shakespeare to a German language audience, and with promoting the concept of a national theatre in the tradition of Ludvig Holber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg National Theatre
The Hamburg Enterprise (), commonly known as the Hamburg National Theatre, was a theatre company in Hamburg (now Germany), that existed 1767–1769 at the Gänsemarkt square, and that was led by Abel Seyler. It was the first attempt to establish a national theatre in Germany. It was modelled after Det Kongelige Teater, founded by Ludvig Holberg in Denmark in 1748. Its leading actor was Konrad Ekhof and the theatre employed Gotthold Ephraim Lessing as the world's first dramaturg; Lessing's influential ''Hamburg Dramaturgy'', based on his work at the Hamburg National Theatre, defined the new field of dramaturgy and also introduced the term.Luckhurst, Mary (2006). ''Dramaturgy: A Revolution in Theatre''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 24. The theatre premiered Lessing's '' Minna von Barnhelm'' on 30 September 1767. The Hamburg National Theatre was mainly owned and led by the former banker Abel Seyler Abel Seyler (23 August 1730, Liestal – 25 April 1800, Rellingen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
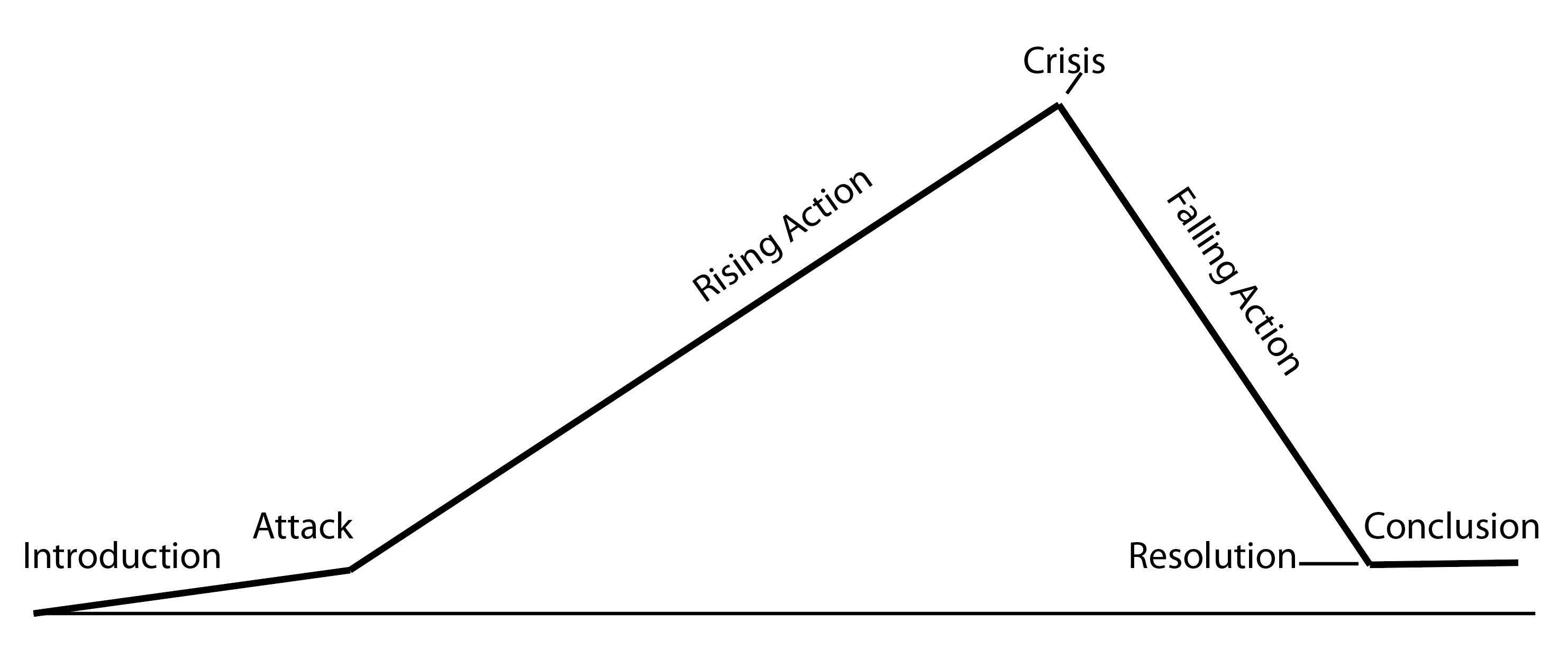
Freytag's Pyramid
A story structure, narrative structure, or dramatic structure (also known as a dramaturgical structure) is the structure of a dramatic work such as a book, play, or film. There are different kinds of narrative structures worldwide, which have been hypothesized by critics, writers, and scholars over time. This article covers the range of dramatic structures from around the world: how the acts are structured and what the center of the story is supposed to be about widely varies by region and time period. Africa and African diaspora Caribbean Kwik Kwak The Kwik Kwak (also called as crick crack) structure involves three elements: the narrator, the protagonist, and the audience. The story itself is considered a performance so there is a synergy among the aforementioned elements. In the story, the narrator may draw attention to the narrative or to himself as storyteller. The structure often includes the following: #Tell riddles to test the audience. #Audience becomes a chorus and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anagnorisis
Anagnorisis (; ) is a moment in a play or other work when a character makes a critical discovery. Anagnorisis originally meant recognition in its Greek context, not only of a person but also of what that person stood for. Anagnorisis was the hero's sudden awareness of a real situation, the realization of things as they stood, and finally, the hero's insight into a relationship with an often antagonistic character in Aristotelian tragedy. Tragedy In his '' Poetics,'' Aristotle discussed peripeteia. In this work, he defined anagnorisis as "a change from ignorance to knowledge, producing love or hate between the persons destined by the poet for good or bad fortune" (1452a). Anagnorisis is often discussed along with Aristotle's concept of catharsis. In the Aristotelian definition of tragedy, it was the discovery of one's own identity or true character (e.g. Cordelia, Edgar, Edmund, etc. in Shakespeare's ''King Lear'') or of someone else's identity or true nature (e.g. Lear's chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |