|
Dorsal Carpometacarpal Ligaments
The dorsal carpometacarpal ligaments, the strongest and most distinct carpometacarpal ligaments, connect the carpal and metacarpal bones on their dorsal surfaces. * The second metacarpal bone receives two fasciculi, one from the greater, the other from the lesser multangular. * The third metacarpal receives two, one each from the lesser multangular and capitate. * The fourth two, one each from the capitate and hamate The hamate bone (from Latin hamatus, "hooked"), or unciform bone (from Latin ''uncus'', "hook"), Latin os hamatum and occasionally abbreviated as just hamatum, is a bone in the human wrist readily distinguishable by its wedge shape and a hook-l .... * The fifth receives a single fasciculus from the hamate, and this is continuous with a similar ligament on the volar surface, forming an incomplete capsule. References External links * Ligaments of the upper limb {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpal Bones
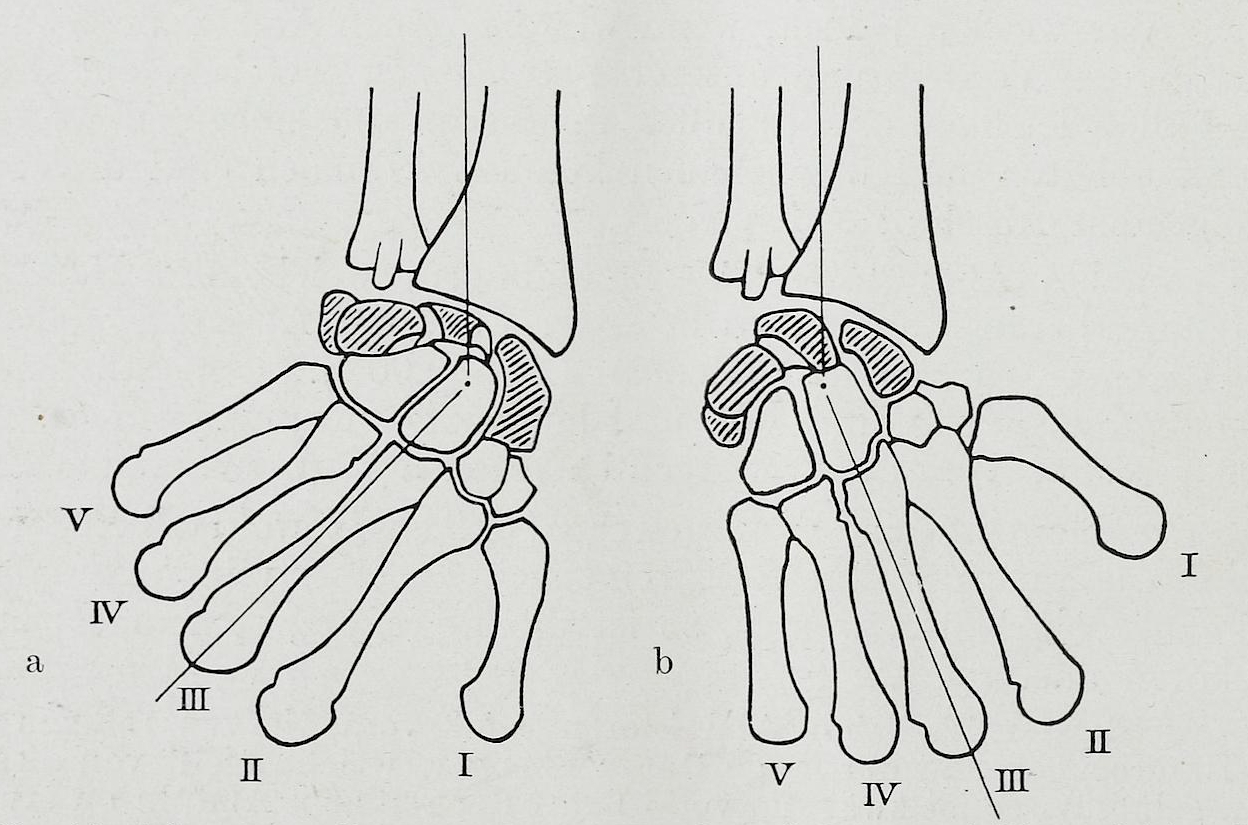
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (or carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the wrist is to facilitate effective positioning of the hand and powerful use of the extensors and flexors of the forearm, and the mobility of individual carpal bones increase the freedom of movements at the wrist.Kingston 2000, pp 126-127 In tetrapods, the carpus is the sole cluster of bones in the wrist between the radius and ulna and the metacarpus. The bones of the carpus do not belong to individual fingers (or toes in quadrupeds), whereas those of the metacarpus do. The corresponding part of the foot is the tarsus. The carpal bones allow the wrist to move and rotate vertically. Structure Bones The eight carpal bones may be conceptually organized as either two transverse rows, or three longitudinal columns. When c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacarpus
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist, which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones are analogous to the metatarsal bones in the foot. Structure The metacarpals form a transverse arch to which the rigid row of distal carpal bones are fixed. The peripheral metacarpals (those of the thumb and little finger) form the sides of the cup of the palmar gutter and as they are brought together they deepen this concavity. The index metacarpal is the most firmly fixed, while the thumb metacarpal articulates with the trapezium and acts independently from the others. The middle metacarpals are tightly united to the carpus by intrinsic interlocking bone elements at their bases. The ring metacarpal is somewhat more mobile while the fifth metacarpal is semi-independent.Tubiana ''et al'' 1998, p 11 Each metacarpal bone consists of a bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpal
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (or carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the wrist is to facilitate effective positioning of the hand and powerful use of the extensors and flexors of the forearm, and the mobility of individual carpal bones increase the freedom of movements at the wrist.Kingston 2000, pp 126-127 In tetrapods, the carpus is the sole cluster of bones in the wrist between the radius and ulna and the metacarpus. The bones of the carpus do not belong to individual fingers (or toes in quadrupeds), whereas those of the metacarpus do. The corresponding part of the foot is the tarsus. The carpal bones allow the wrist to move and rotate vertically. Structure Bones The eight carpal bones may be conceptually organized as either two transverse rows, or three longitudinal columns. When c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacarpal
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist, which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones are analogous to the metatarsal bones in the foot. Structure The metacarpals form a transverse arch to which the rigid row of distal carpal bones are fixed. The peripheral metacarpals (those of the thumb and little finger) form the sides of the cup of the palmar gutter and as they are brought together they deepen this concavity. The index metacarpal is the most firmly fixed, while the thumb metacarpal articulates with the trapezium and acts independently from the others. The middle metacarpals are tightly united to the carpus by intrinsic interlocking bone elements at their bases. The ring metacarpal is somewhat more mobile while the fifth metacarpal is semi-independent.Tubiana ''et al'' 1998, p 11 Each metacarpal bone consists of a bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Metacarpal
The second metacarpal bone (metacarpal bone of the index finger) is the longest, and its base the largest, of all the metacarpal bones.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918). See infobox. Human anatomy Its base is prolonged upward and medialward, forming a prominent ridge. It presents four articular facets, three on the upper surface and one on the ulnar side: * Of the facets on the upper surface: ** the ''intermediate'' is the largest and is concave from side to side, convex from before backward for articulation with the lesser multangular; ** the ''lateral'' is small, flat and oval for articulation with the greater multangular; ** the ''medial'', on the summit of the ridge, is long and narrow for articulation with the capitate. * The facet on the ulnar side articulates with the third metacarpal. The extensor carpi radialis longus muscle is inserted on the dorsal surface and the flexor carpi radialis muscle on the volar surface of the base. The shaft gives origin to the first palmar in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciculus
''Fasciculus vesanus'' is an extinct species of stem-group ctenophores known from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. It is dated to and belongs to middle Cambrian strata. The species is remarkable for its two sets of long and short comb rows, not seen in similar form elsewhere in the fossil record or among modern species. See also *''Ctenorhabdotus capulus'' *''Xanioascus canadensis'' Maotianshan shales ctenophores **''Maotianoascus octonarius'' **''Sinoascus paillatus'' **''Stromatoveris psygmoglena ''Stromatoveris psygmoglena'' is a genus of basal petalonam from the Chengjiang deposits of Yunnan that was originally aligned with the fossil ''Charnia'' (strictly, the Charniomorpha) from the Ediacara biota. However, such an affinity is devel ...'' References External links * Prehistoric ctenophore genera Burgess Shale animals Monotypic ctenophore genera Fossil taxa described in 1978 Cambrian genus extinctions {{Ctenophore-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Multangular
The trapezoid bone (lesser multangular bone) is a carpal bone in tetrapods, including humans. It is the smallest bone in the distal row of carpal bones that give structure to the palm of the hand. It may be known by its wedge-shaped form, the broad end of the wedge constituting the dorsal, the narrow end the palmar surface; and by its having four articular facets touching each other, and separated by sharp edges. It is homologous with the "second distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians. Structure The trapezoid is a four-sided carpal bone found within the hand. The trapezoid is found within the distal row of carpal bones. Surfaces The '' superior surface'', quadrilateral, smooth, and slightly concave, articulates with the scaphoid. The '' inferior surface'' articulates with the proximal end of the second metacarpal bone; it is convex from side to side, concave from before backward and subdivided by an elevated ridge into two unequal facets. The ''dorsal'' and '' palmar surfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Metacarpal
The third metacarpal bone (metacarpal bone of the middle finger) is a little smaller than the second. The dorsal aspect of its base presents on its radial side a pyramidal eminence, the styloid process, which extends upward behind the capitate; immediately distal to this is a rough surface for the attachment of the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle. The carpal articular facet is concave behind, flat in front, and articulates with the capitate. On the radial side is a smooth, concave facet for articulation with the second metacarpal, and on the ulnar side two small oval facets for the fourth metacarpal. Ossification The ossification process begins in the shaft during prenatal life, and in the head between 11th and 27th months. Additional images File:Third metacarpal bone (left hand) - animation01.gif, Third metacarpal bone of the left hand (shown in red). Animation. File:Third metacarpal bone (left hand) - animation02.gif, Third metacarpal bone of the left hand. Close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitate
The capitate bone is a bone in the human wrist found in the center of the carpal bone region, located at the distal end of the radius and ulna bones. It articulates with the third metacarpal bone (the middle finger) and forms the third carpometacarpal joint. The capitate bone is the largest of the carpal bones in the human hand. It presents, above, a rounded portion or head, which is received into the concavity formed by the scaphoid and lunate bones; a constricted portion or neck; and below this, the body.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918). See infobox. The bone is also found in many other mammals, and is homologous with the "third distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians. Structure The capitate is the largest carpal bone found within the hand. The capitate is found within the distal row of carpal bones. The capitate lies directly adjacent to the metacarpal of the ring finger on its distal surface, has the hamate on its ulnar surface and trapezoid on its radial surface, and abuts the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamate
The hamate bone (from Latin hamatus, "hooked"), or unciform bone (from Latin ''uncus'', "hook"), Latin os hamatum and occasionally abbreviated as just hamatum, is a bone in the human wrist readily distinguishable by its wedge shape and a hook-like process ("hamulus") projecting from its palmar surface. Structure The hamate is an irregularly shaped carpal bone found within the hand. The hamate is found within the distal row of carpal bones, and abuts the metacarpals of the little finger and ring finger. Adjacent to the hamate on the ulnar side, and slightly above it, is the pisiform bone. Adjacent on the radial side is the capitate, and proximal is the lunate bone. Surfaces The hamate bone has six surfaces: * The ''superior'', the apex of the wedge, is narrow, convex, smooth, and articulates with the lunate. * The ''inferior'' articulates with the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones, by concave facets which are separated by a ridge. * The ''dorsal'' is triangular and rough for l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_dorsal_view.png)
_-_animation02.gif)