|
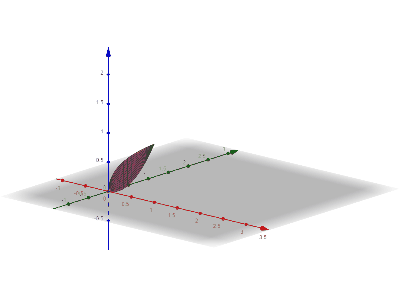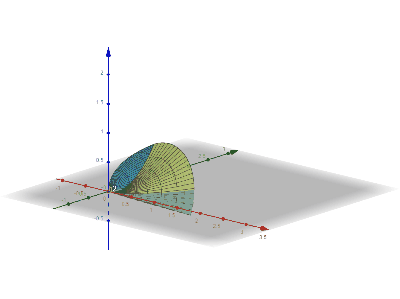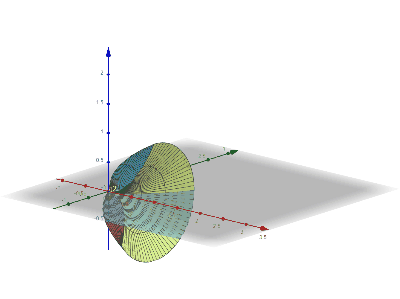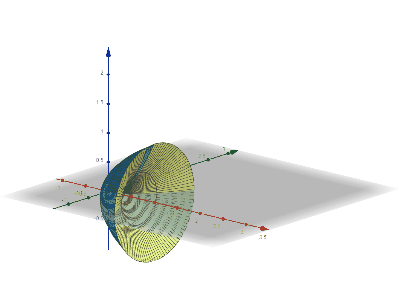
Disk Integration
Disc integration, also known in integral calculus as the disc method, is a method for calculating the volume of a solid of revolution of a solid-state material when integrating along an axis "parallel" to the axis of revolution. This method models the resulting three-dimensional shape as a stack of an infinite number of discs of varying radius and infinitesimal thickness. It is also possible to use the same principles with rings instead of discs (the "washer method") to obtain hollow solids of revolutions. This is in contrast to shell integration, which integrates along an axis ''perpendicular'' to the axis of revolution. Definition Function of If the function to be revolved is a function of , the following integral represents the volume of the solid of revolution: :\pi\int_a^b R(x)^2\,dx where is the distance between the function and the axis of rotation. This works only if the axis of rotation is horizontal (example: or some other constant). Function of If the function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disc Integration
Disc integration, also known in integral calculus as the disc method, is a method for calculating the volume of a solid of revolution of a solid-state material when integrating along an axis "parallel" to the axis of revolution. This method models the resulting three-dimensional shape as a stack of an infinite number of discs of varying radius and infinitesimal thickness. It is also possible to use the same principles with rings instead of discs (the "washer method") to obtain hollow solids of revolutions. This is in contrast to shell integration, which integrates along an axis ''perpendicular'' to the axis of revolution. Definition Function of If the function to be revolved is a function of , the following integral represents the volume of the solid of revolution: :\pi\int_a^b R(x)^2\,dx where is the distance between the function and the axis of rotation. This works only if the axis of rotation is horizontal (example: or some other constant). Function of If the function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral Calculus
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to Function (mathematics), functions in a way that describes Displacement (geometry), displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with Derivative, differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential operation of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. and serves as a tool to solve problems in mathematics and physics involving the area of an arbitrary shape, the length of a curve, and the volume of a solid, among others. The integrals enumerated here are those termed definite integrals, which can be interpreted as the signed area of the region in the plane that is bounded by the Graph of a function, graph of a given function between two points in the real line. Conventionally, areas above the horizontal axis of the plane are posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). The definition of length (cubed) is interrelated with volume. The volume of a container is generally understood to be the capacity of the container; i.e., the amount of fluid (gas or liquid) that the container could hold, rather than the amount of space the container itself displaces. In ancient times, volume is measured using similar-shaped natural containers and later on, standardized containers. Some simple three-dimensional shapes can have its volume easily calculated using arithmetic formulas. Volumes of more complicated shapes can be calculated with integral calculus if a formula exists for the shape's boundary. Zero-, one- and two-dimensional objects have no volume; in fourth and higher dimensions, an analogous concept to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Of Revolution
In geometry, a solid of revolution is a solid figure obtained by rotating a plane figure around some straight line (the '' axis of revolution'') that lies on the same plane. The surface created by this revolution and which bounds the solid is the surface of revolution. Assuming that the curve does not cross the axis, the solid's volume is equal to the length of the circle described by the figure's centroid multiplied by the figure's area ( Pappus's second centroid theorem). A representative disc is a three-dimensional volume element of a solid of revolution. The element is created by rotating a line segment (of length ) around some axis (located units away), so that a cylindrical volume Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). ... of units is enclosed. Finding the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential operation of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. and serves as a tool to solve problems in mathematics and physics involving the area of an arbitrary shape, the length of a curve, and the volume of a solid, among others. The integrals enumerated here are those termed definite integrals, which can be interpreted as the signed area of the region in the plane that is bounded by the graph of a given function between two points in the real line. Conventionally, areas above the horizontal axis of the plane are positive while areas below are negative. Integrals also refer to the concept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Of Revolution
In geometry, a solid of revolution is a solid figure obtained by rotating a plane figure around some straight line (the '' axis of revolution'') that lies on the same plane. The surface created by this revolution and which bounds the solid is the surface of revolution. Assuming that the curve does not cross the axis, the solid's volume is equal to the length of the circle described by the figure's centroid multiplied by the figure's area ( Pappus's second centroid theorem). A representative disc is a three-dimensional volume element of a solid of revolution. The element is created by rotating a line segment (of length ) around some axis (located units away), so that a cylindrical volume of units is enclosed. Finding the volume Two common methods for finding the volume of a solid of revolution are the disc method and the shell method of integration. To apply these methods, it is easiest to draw the graph in question; identify the area that is to be revolved about the axis o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shell Integration
Shell integration (the shell method in integral calculus) is a method for calculating the volume of a solid of revolution, when integrating along an axis ''perpendicular to'' the axis of revolution. This is in contrast to disc integration which integrates along the axis ''parallel'' to the axis of revolution. Definition The shell method goes as follows: Consider a volume in three dimensions obtained by rotating a cross-section in the -plane around the -axis. Suppose the cross-section is defined by the graph of the positive function on the interval . Then the formula for the volume will be: :2 \pi \int_a^b x f(x)\, dx If the function is of the coordinate and the axis of rotation is the -axis then the formula becomes: :2 \pi \int_a^b y f(y)\, dy If the function is rotating around the line then the formula becomes: :\begin \displaystyle 2 \pi \int_a^b (x-h) f(x)\,dx, & \text\ h \le a < b\\ \displaystyle 2 \pi \int_a^b (h-x) f(x)\,dx, & \text\ a < b \le h, \end an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Of Rotation
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed- axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's rotation theorem, simultaneous rotation along a number of stationary axes at the same time is impossible; if two rotations are forced at the same time, a new axis of rotation will appear. This article assumes that the rotation is also stable, such that no torque is required to keep it going. The kinematics and dynamics of rotation around a fixed axis of a rigid body are mathematically much simpler than those for free rotation of a rigid body; they are entirely analogous to those of linear motion along a single fixed direction, which is not true for ''free rotation of a rigid body''. The expressions for the kinetic energy of the object, and for the forces on the parts of the object, are also simpler for rotation around a fixed axis, than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Of Revolution
In geometry, a solid of revolution is a solid figure obtained by rotating a plane figure around some straight line (the '' axis of revolution'') that lies on the same plane. The surface created by this revolution and which bounds the solid is the surface of revolution. Assuming that the curve does not cross the axis, the solid's volume is equal to the length of the circle described by the figure's centroid multiplied by the figure's area ( Pappus's second centroid theorem). A representative disc is a three-dimensional volume element of a solid of revolution. The element is created by rotating a line segment (of length ) around some axis (located units away), so that a cylindrical volume Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). ... of units is enclosed. Finding the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shell Integration
Shell integration (the shell method in integral calculus) is a method for calculating the volume of a solid of revolution, when integrating along an axis ''perpendicular to'' the axis of revolution. This is in contrast to disc integration which integrates along the axis ''parallel'' to the axis of revolution. Definition The shell method goes as follows: Consider a volume in three dimensions obtained by rotating a cross-section in the -plane around the -axis. Suppose the cross-section is defined by the graph of the positive function on the interval . Then the formula for the volume will be: :2 \pi \int_a^b x f(x)\, dx If the function is of the coordinate and the axis of rotation is the -axis then the formula becomes: :2 \pi \int_a^b y f(y)\, dy If the function is rotating around the line then the formula becomes: :\begin \displaystyle 2 \pi \int_a^b (x-h) f(x)\,dx, & \text\ h \le a < b\\ \displaystyle 2 \pi \int_a^b (h-x) f(x)\,dx, & \text\ a < b \le h, \end an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank J
Frank or Franks may refer to: People * Frank (given name) * Frank (surname) * Franks (surname) * Franks, a medieval Germanic people * Frank, a term in the Muslim world for all western Europeans, particularly during the Crusades - see Farang Currency * Liechtenstein franc or frank, the currency of Liechtenstein since 1920 * Swiss franc or frank, the currency of Switzerland since 1850 * Westphalian frank, currency of the Kingdom of Westphalia between 1808 and 1813 * The currencies of the German-speaking cantons of Switzerland (1803–1814): ** Appenzell frank ** Argovia frank ** Basel frank ** Berne frank ** Fribourg frank ** Glarus frank ** Graubünden frank ** Luzern frank ** Schaffhausen frank ** Schwyz frank ** Solothurn frank ** St. Gallen frank ** Thurgau frank ** Unterwalden frank ** Uri frank ** Zürich frank Places * Frank, Alberta, Canada, an urban community, formerly a village * Franks, Illinois, United States, an unincorporated community * Franks, Missour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliott Mendelson
Elliott Mendelson (May 24, 1931 – May 7, 2020) was an American logician. He was a professor of mathematics at Queens College of the City University of New York, and the Graduate Center, CUNY. He was Jr. Fellow, Society of Fellows, Harvard University, 1956–58. Career Mendelson earned his BA from Columbia University and PhD from Cornell University. Mendelson taught mathematics at the college level for more than 30 years, and is the author of books on logic, philosophy of mathematics, calculus, game theory and mathematical analysis. His ''Introduction to Mathematical Logic'', first published in 1964, was reviewed by Dirk van Dalen who noted that it included "a large variety of subjects that should be part of the education of any mathematics student with an interest in foundational matters." Dirk van Dalen (1969Review: Introduction to Mathematical Logic Journal of Symbolic Logic 34(1): 110,1 via JSTOR Books Sole author * * * * * * * Co-author * * * * Editor * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |