|
Dental Lamina
The dental lamina is a band of epithelial tissue seen in histologic sections of a developing tooth. The dental lamina is first evidence of tooth development and begins (in humans) at the sixth week in utero or three weeks after the rupture of the buccopharyngeal membrane. It is formed when cells of the oral ectoderm proliferate faster than cells of other areas. Best described as an in-growth of oral ectoderm, the dental lamina is frequently distinguished from the vestibular lamina, which develops concurrently. This dividing tissue is surrounded by and, some would argue, stimulated by ectomesenchymal growth. When it is present, the dental lamina connects the developing tooth bud to the epithelium of the oral cavity. Eventually, the dental lamina disintegrates into small clusters of epithelium and is resorbed. In situations when the clusters are not resorbed, (this remnant of the dental lamina is sometimes known as the glands of Serres) eruption cysts are formed over the developi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many other animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. Calcium hardens the tooth enamel. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface. Features Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and contains the highest percentage of minerals (at 96%),Ross ''et al.'', p. 485 with water and organic material composing the rest.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nancy, Elsevier, pp. 70–94 The primary mineral is hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. Enamel is formed on the tooth while the tooth develops withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphyodont
A diphyodont is any animal with two ss of teeth, initially the '' deciduous'' set and consecutively the '' permanent'' set. Most mammals are diphyodonts—as to chew their food they need a strong, durable and complete set of teeth. Diphyodonts contrast with ''polyphyodonts'', whose teeth are constantly replaced. Diphyodonts also differ from ''monophyodonts'', which are animals who have only one set of teeth that do not change over a long period of growth. In diphyodonts, the number of teeth that are replaced varies from species to species. In humans, a set of twenty deciduous teeth, or "milk teeth", are replaced by a completely new set of thirty-two adult teeth. In some cases hypodontia or hyperdontia occurs, the latter in cleidocranial dysostosis and Gardner's syndrome. In the hare the anterior incisors are not replaced but the posterior smaller incisors are replaced. Not much is known about the developmental mechanisms regulating diphyodont replacement. The house shrew, ''Sun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gardner's Syndrome
Gardner's syndrome (also known as Gardner syndrome, familial polyposis of the colon, or familial colorectal polyposis) is a subtype of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Gardner syndrome is an autosomal dominant form of polyposis characterized by the presence of multiple polyps in the colon together with tumors outside the colon. The extracolonic tumors may include osteomas of the skull, thyroid cancer, epidermoid cysts, fibromas, as well as the occurrence of desmoid tumors in approximately 15% of affected individuals. Desmoid tumors are fibrous tumors that usually occur in the tissue covering the intestines and may be provoked by surgery to remove the colon. The countless polyps in the colon predispose to the development of colon cancer; if the colon is not removed, the chance of colon cancer is considered to be very significant. Polyps may also grow in the stomach, duodenum, spleen, kidneys, liver, mesentery, and small bowel. In a small number of cases, polyps have als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atavism
In biology, an atavism is a modification of a biological structure whereby an ancestral genetic trait reappears after having been lost through evolutionary change in previous generations. Atavisms can occur in several ways; one of which is when genes for previously existing phenotypic features are preserved in DNA, and these become expressed through a mutation that either knocks out the dominant genes for the new traits or makes the old traits dominate the new one. A number of traits can vary as a result of shortening of the fetal development of a trait ( neoteny) or by prolongation of the same. In such a case, a shift in the time a trait is allowed to develop before it is fixed can bring forth an ancestral phenotype. Atavisms are often seen as evidence of evolution. In social sciences, atavism is the tendency of reversion. For example, people in the modern era reverting to the ways of thinking and acting of a former time. The word ''atavism'' is derived from the Latin ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperdontia
Hyperdontia is the condition of having supernumerary teeth, or teeth that appear in addition to the regular number of teeth (32 in the average adult). They can appear in any area of the dental arch and can affect any dental organ. The opposite of hyperdontia is hypodontia, where there is a congenital lack of teeth, which is a condition seen more commonly than hyperdontia.Pathology of the Hard Dental Tissues The scientific definition of hyperdontia is "any tooth or odontogenic structure that is formed from tooth germ in excess of usual number for any given region of the dental arch."R. S. Omer, R. P. Anthonappa, and N. M. King, "Determination of the optimum time for surgical removal of unerupted anterior supernumerary teeth," Pediatric Dentistry, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 14–20, 2010. The additional teeth, which may be few or many, can occur on any place in the dental arch. Their arrangement may be symmetrical or non-symmetrical. Signs and symptoms The presence of a supernumerary t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every organ in the developing embryo. Vertebrates Structure Mesenchyme is characterized morphologically by a prominent ground substance matrix containing a loose aggregate of reticular fibers and unspecialized mesenchymal stem cells. Mesenchymal cells can migrate easily (in contrast to epithelial cells, which lack mobility), are organized into closely adherent sheets, and are polarized in an apical-basal orientation. Development The mesenchyme originates from the mesoderm. From the mesoderm, the mesenchyme appears as an embryologically primitive "soup". This "soup" exists as a combination of the mesenchymal cells plus serous fluid plus the many different tissue proteins. Serous fluid is typically stocked with the many serous elements, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odontoblasts
In vertebrates, an odontoblast is a cell of neural crest origin that is part of the outer surface of the dental pulp, and whose biological function is dentinogenesis, which is the formation of dentin, the substance beneath the tooth enamel on the crown and the cementum on the root. Structure Odontoblasts are large columnar cells, whose cell bodies are arranged along the interface between dentin and pulp, from the crown to cervix to the root apex in a mature tooth. The cell is rich in endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex, especially during primary dentin formation, which allows it to have a high secretory capacity; it first forms the collagenous matrix to form predentin, then mineral levels to form the mature dentin. Odontoblasts form approximately 4 μm of predentin daily during tooth development.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nanci, Elsevier, 2013, page 170 During secretion after differentiation from the outer cells of the dental papilla, it is noted that it is polarized so i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Papilla
In embryology and prenatal development, the dental papilla is a condensation of ectomesenchymal cells called odontoblasts, seen in histologic sections of a developing tooth. It lies below a cellular aggregation known as the enamel organ. The dental papilla appears after 8–10 weeks intra uteral life. The dental papilla gives rise to the dentin and pulp of a tooth. The enamel organ, dental papilla, and dental follicle together forms one unit, called the tooth germ. This is of importance because all the tissues of a tooth and its supporting structures form from these distinct cellular aggregations. Similar to dental follicle, the dental papilla has a very rich blood supply and provides nutrition to the enamel organ. Embryology Formation of dental papilla occurs in the Cap stage of Odontogenesis. The cap stage The cap stage is the second stage of tooth development and occurs during the ninth or tenth week of prenatal development. Unequal proliferation of the tooth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectomesenchyme
Ectomesenchyme has properties similar to mesenchyme. The origin of the ectomesenchyme is disputed. It is either like the mesenchyme, arising from mesodermic cells, or conversely arising from neural crest cells. The neural crest is a critical group of cells that form in the cranial region during early vertebrate development. Ectomesenchyme plays a critical role in the formation of the hard and soft tissues of the head and neck such as bones, muscles, teeth and, notably, the pharyngeal arches The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arche .... References Developmental biology {{developmental-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ameloblasts
Ameloblasts are cells present only during tooth development that deposit tooth enamel, which is the hard outermost layer of the tooth forming the surface of the crown. Structure Each ameloblast is a columnar cell approximately 4 micrometers in diameter, 40 micrometers in length and is hexagonal in cross section. The secretory end of the ameloblast ends in a six-sided pyramid-like projection known as the Tomes' process. The angulation of the Tomes' process is significant in the orientation of enamel rods, the basic unit of tooth enamel. Distal terminal bars are junctional complexes that separate the Tomes' processes from ameloblast proper. Development Ameloblasts are derived from oral epithelium tissue of ectodermal origin. Their differentiation from preameloblasts (whose origin is from inner enamel epithelium) is a result of signaling from the ectomesenchymal cells of the dental papilla. Initially the preameloblasts will differentiate into presecretory ameloblasts and then int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
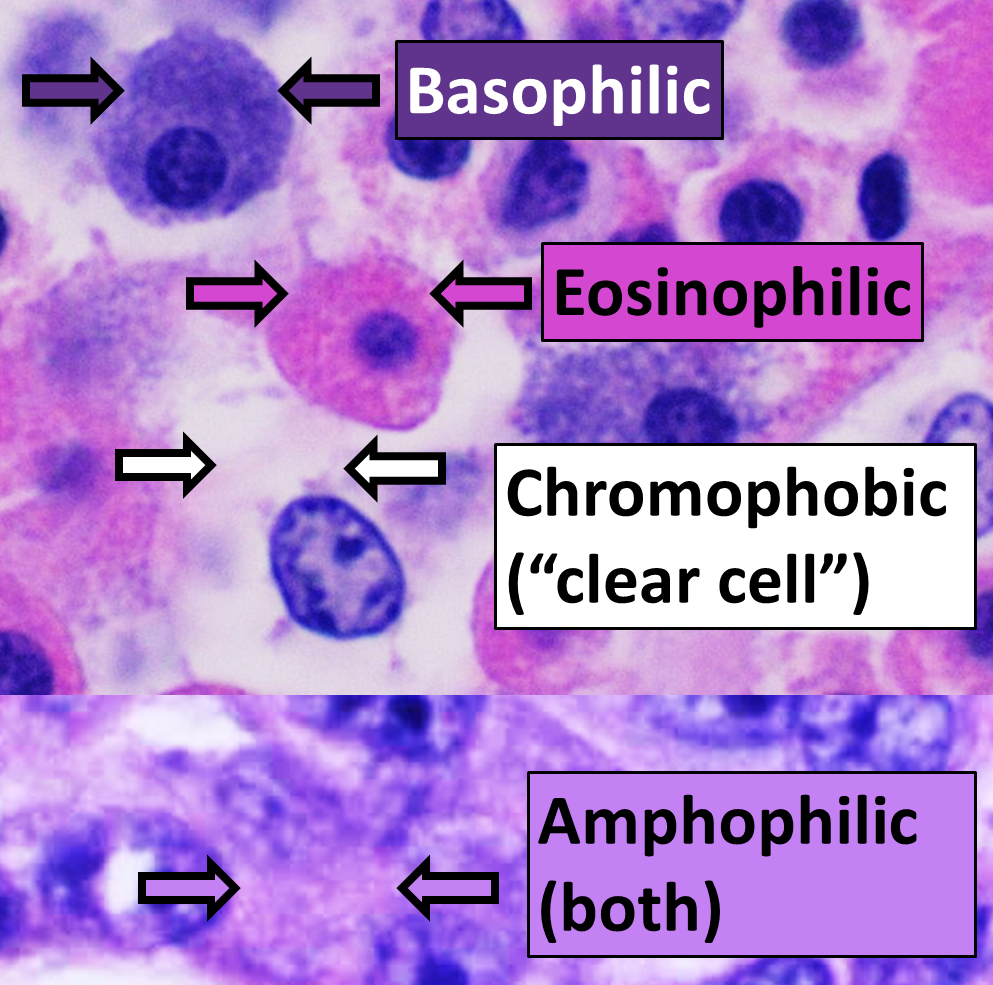
H&E Stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E. H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin. The hematoxylin stains cell nuclei a purplish blue, and eosin stains the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm pink, with other structures taking on different shades, hues, and combinations of these colors. Hence a pathologist can easily differentiate between the nuclear and cytoplasmic parts of a cell, and additionally, the overall patterns of coloration from the stain show the general layout and distribution of cells and provides a general overview of a tissue sample's structure. Thus, pattern r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |