|
Definition Of Music
A definition of music endeavors to give an accurate and concise explanation of music's basic attributes or essential nature and it involves a process of defining what is meant by the term ''music''. Many authorities have suggested definitions, but defining music turns out to be more difficult than might first be imagined, and there is ongoing debate. A number of explanations start with the notion of music as ''organized sound,'' but they also highlight that this is perhaps too broad a definition and cite examples of organized sound that are not defined as music, such as human speech and sounds found in both natural and industrial environments . The problem of defining music is further complicated by the influence of culture in music cognition. The '' Concise Oxford Dictionary'' defines music as "the art of combining vocal or instrumental sounds (or both) to produce beauty of form, harmony, and expression of emotion". However, some music genres, such as noise music and musique c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Definition
A definition is a statement of the meaning of a term (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Definitions can be classified into two large categories: intensional definitions (which try to give the sense of a term), and extensional definitions (which try to list the objects that a term describes).Lyons, John. "Semantics, vol. I." Cambridge: Cambridge (1977). p.158 and on. Another important category of definitions is the class of ostensive definitions, which convey the meaning of a term by pointing out examples. A term may have many different senses and multiple meanings, and thus require multiple definitions. In mathematics, a definition is used to give a precise meaning to a new term, by describing a condition which unambiguously qualifies what the mathematical term is and is not. Definitions and axioms form the basis on which all of modern mathematics is to be constructed. Basic terminology In modern usage, a definition is something, typically expressed in words, that at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Indian
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of the Americas as such. These populations exhibit significant diversity; some Indigenous peoples were historically hunter-gatherers, while others practiced agriculture and aquaculture. Various Indigenous societies developed complex social structures, including pre-contact monumental architecture, organized city, cities, city-states, chiefdoms, state (polity), states, monarchy, kingdoms, republics, confederation, confederacies, and empires. These societies possessed varying levels of knowledge in fields such as Pre-Columbian engineering in the Americas, engineering, Pre-Columbian architecture, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, History of writing, writing, physics, medicine, Pre-Columbian agriculture, agriculture, irrigation, geology, minin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapuche
The Mapuche ( , ) also known as Araucanians are a group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who share a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their homelands once extended from Choapa River, Choapa Valley to the Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Pampas, Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the Indigenous peoples in Chile and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are concentrated in the Araucanía (historic region), Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities, more than 92% of the Mapuches are from Chile. The Mapuche traditional e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jarawa Language (Nigeria)
Jarawa (also known as Jhar, or in Hausa: ''Jaranci'') is the most populous of the Bantu languages of northern Nigeria Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, .... It is a dialect cluster consisting of many varieties. Phonology * /β/ only appears as a marginal phoneme. * �only appears in non-word-initial syllables. * Sounds /n, t, l, r/ can be heard as palatal or retroflex �, ʈ, ɭ, ɽin word-final position. /k/ can also be heard as uvular in the same position, and may also alternate with �or � * Sounds /k͡x, ɡ͡ɣ/ can be heard as fricatives , ɣor �, ʁin intervocalic position. * Sounds /ɛ, ɔ/ only appear after glides. Dialects Jarawa dialects are: * Zhár (Bankal) * Zugur (Duguri) * Gwak (Gingwak) * Ndaŋshi * Dòòrì * Mbat (Bada) * Mùùn * Kanta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eggon Language
Eggon (also Egon, Ero, or Mo Egon), erroneously referred to as Mada - formerly a Plateau language spoken in central Nigeria. It is one of the major language in Nasarawa State. Classification The exact classification of the Eggon language has been in dispute and it can be said that this issue remains unresolved. Eggon was first classified by Greenberg (1963) as a Plateau language in his group 5, together with Nungu and Yeskwa. In the revision prepared by Carl Hoffman published in Hansford et al. (1976) a Benue group was set up that combined Greenberg's Plateau 5 and 7 with Jukunoid. The new subgrouping classified Eggon together with Nungu, Ake and Jidda-Abu. This concept of a Benue grouping came from the lexicostatistical studies of Shimizu (1975) who argued against the unity of Greenberg's Plateau and proposed the Benue group. However, in 1983, Gerhardt published a convincing rebuttal of Shimizu's arguments. The latest version of classification of Plateau languages in Gerha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idoma Language
Idoma (Ìdɔ́mà) is the second official language spoken in Benue State in southeast-central Nigeria, by approximately one million people (2020 estimate). The Idoma language is made up of the dialects of Agatu, Edumoga, Otukpo, Otukpa, Orokam, Akpa Agila, Utonkon, Igede The Igede people are a Nigerian ethnic group in Benue State of Nigeria. They are native to the Oju and Obi local government areas of Benue State, Nigeria, where 2006 population figures stand at an estimated 267,198 people. However, many Igede pe ..., Etilo, Iyala. The Idoma people are predominantly hunters, farmers and fishermen. They are bordered to the north by Nasarawa, south by cross river, east by Taraba and west by Enugu and Kogi States. Animal names References Idomoid languages {{VoltaNiger-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
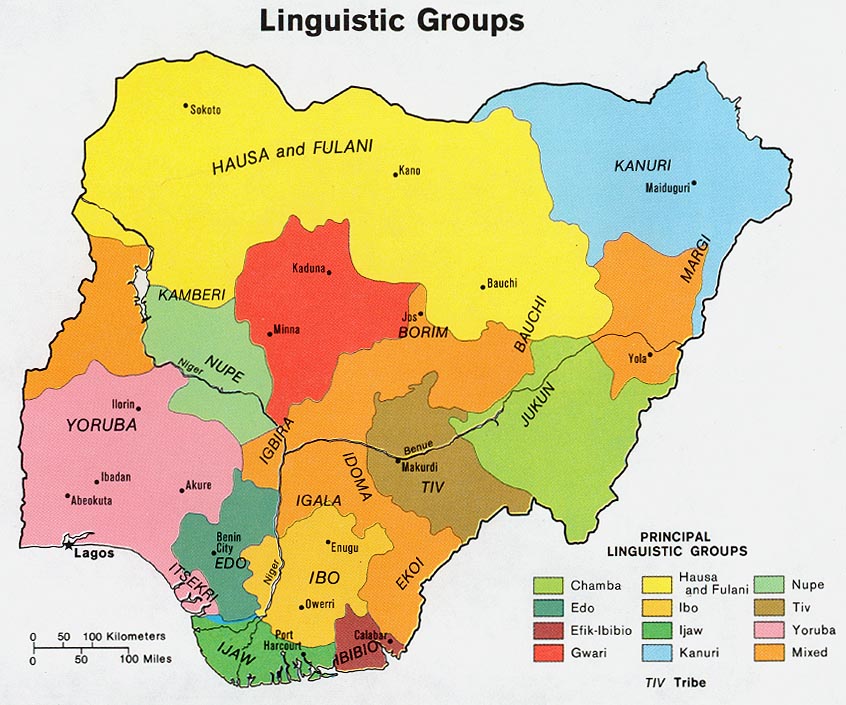
Hausa Language
Hausa (; / ; Hausa Ajami, Ajami: ) is a Chadic language spoken primarily by the Hausa people in the northern parts of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern parts of Niger, and Chad, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast. A small number of speakers also exist in Sudan. Hausa is a member of the Afroasiatic language family and is the most widely spoken language within the Chadic branch of that family. Despite originating from a non-tonal language family, Hausa utilizes differences in pitch to distinguish words and grammar. ''Ethnologue'' estimated that it was spoken as a first language by some 58 million people and as a second language by another 36 million, bringing the total number of Hausa speakers to an estimated 94 million. In Nigeria, the Hausa film industry is known as Kannywood. Classification Hausa belongs to the West Chadic languages subgroup of the Chadic languages group, which in turn is part of the Afroasiatic languages, Afro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berom Language
Berom or Birom () is the most widely spoken Plateau language in Nigeria. The language is locally numerically important and is consistently spoken by Berom of all ages in rural areas. However, the Berom are shifting to Hausa in cities. The small Cen and Nincut dialects may be separate languages. Approximately 1 million (2010) people speak in this language. Berom is spoken in a large area extending from some precolonial settlements embedded within the Jos metropolitan Metropolitan Area to the south of Jos city to Barkin Ladi and Riyom in Plateau State, Nigeria. The Berom population distribution culminates at the edge of the Jos plateau in Sopp chiefdom of Riyom Local Government Area. History The Berom have a link to the Nok culture, a civilization that existed between 200 BCE to 1,000 CE. Generally, the Berom speakers are identified to live in the core Jos Plateau and down the low plains of Kaduna State. Dialects The Berom dialect clusters are: *Gyel–Kuru–Vwang *Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efik Language
Efik (''Usem Efịk'') is the indigenous language of the Efik people, who are situated in the present-day Cross River State and Akwa Ibom State of Nigeria, as well as in the north-west of Cameroon. The Efik language is mutually intelligible with other lower Cross River languages such as Ibibio, Anaang, Oro and Ekid but the degree of intelligibility in the case of Oro and Ekid is unidirectional; in other words, speakers of these languages speak and understand Efik (and Ibibio) but not vice versa. The Efik vocabulary has been enriched and influenced by external contact with the British, Portuguese and other surrounding communities such as Balondo, Oron, Efut, Okoyong, Efiat and Ekoi (Qua). Classification The Efik Language has undergone several linguistic classifications since the 19th century. The first attempt at classifying the Efik language was by Dr. William Balfour Baikie in 1854. Baikie, p. 420 Dr Baikie had stated, "All the coast dialects from One to Old Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igbo Language
Igbo ( , ; Standard Igbo: ''Ásụ̀sụ́ Ìgbò'' ) is the principal native language cluster of the Igbo people, an ethnicity in the Southeastern part of Nigeria. Igbo languages are spoken by a total of 31 million people. The number of Igboid languages depends on how one classifies a language versus a dialect, so there could be around 35 different Igbo languages. The core Igbo cluster, or Igbo proper, is generally thought to be one language but there is limited mutual intelligibility between the different groupings (north, west, south and east). A standard literary language termed 'Igbo izugbe' (meaning "general igbo") was generically developed and later adopted around 1972, with its core foundation based on the Orlu, Imo, Orlu (Isu people, Isu dialects), Anambra (Awka dialects) and Umuahia (Ohuhu dialects), omitting the nasal vowel, nasalization and aspiration (phonetics), aspiration of those varieties. History The first book to publish Igbo terms was ''History of the Mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoruba Language
Yoruba (, ; Yor. ) is a Niger–Congo languages, Niger-Congo language that is spoken in West Africa, primarily in South West (Nigeria), Southwestern and Middle Belt, Central Nigeria, Benin, and parts of Togo. It is spoken by the Yoruba people. Yoruba speakers number roughly 50 million, including around 2 million second-language or L2 speakers. As a pluricentric language, it is primarily spoken in a dialectal area spanning Nigeria, Benin, and Togo with smaller migrated communities in Côte d'Ivoire, Sierra Leone and The Gambia. Yoruba vocabulary is also used in African diaspora religions such as the Afro-Brazilian religion of Candomblé, the Caribbean religion of Santería in the form of the liturgical Lucumí language, and various Afro-American religions of North America. Most modern practitioners of these religions in the Americas are not fluent in the Yoruba language, yet they still use Yoruba words and phrases for songs or chants—rooted in cultural traditions. For such pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiv Language
Tiv is a Tivoid language spoken in some states in North Central Nigeria, with some speakers in Cameroon. It had over 5.2 million speakers in 2024. The largest population of Tiv speakers are found in Benue state in Nigeria. The language is also widely spoken in some Nigerian states namely, Plateau, Taraba, Nasarawa, Cross River, Adamawa, Kaduna, and Abuja. It is by far the largest of the Tivoid languages, a group of languages belonging to the Southern Bantoid languages. History and classification The first reference to the Tiv language (''dzwa Tiv'') was made by Sigismund Koelle (1854) from liberated slaves from Sierra Leone. Johnston Harry H (1919) classified it as a peculiar language among the Semi-Bantu languages, and Talbot P. Amaury (1926) concurred. Roy Clive Abraham (1933), who has made the most complete linguistic study of Tiv, classifies it as Bantu, stating that its vocabulary is more similar to the East African Nyanza group of Bantu languages than to Eko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |