|
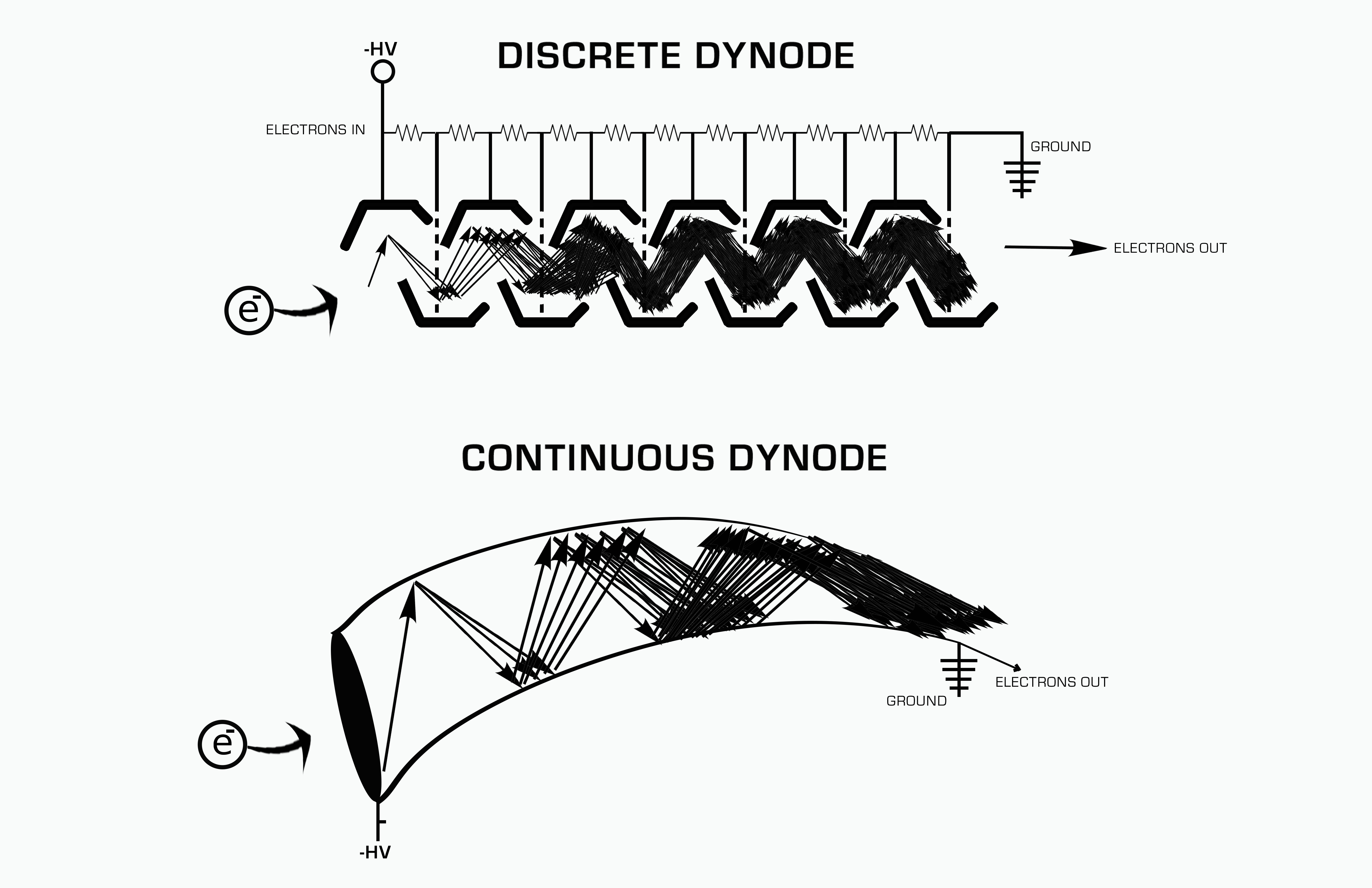
Dynode
A dynode is an electrode in a vacuum tube that serves as an electron multiplier through secondary emission. The first tube to incorporate a dynode was the Dynatron oscillator, dynatron, an ancestor of the magnetron, which used a single dynode.Albert W. Hull, E. F. Hennelly and F. R. Elder, The Dynatron Detector -- a new heterodyne receiver for continuous and modulated wavesProceedings of the Institute of Radio EngineersVol. 10, No. 5 (Oct. 1922), pages 320-343 Photomultiplier and video camera tubes generally include a series of dynodes, each at a more positive electrical potential than its predecessor. Secondary emission occurs at the surface of each dynode. Such an arrangement is able to amplify the tiny current emitted by the photocathode, typically by a factor of one million. Operation The electrons emitted from the cathode are accelerated toward the first dynode, which is maintained 90 to 100 V positive concerning the cathode. Each accelerated photoelectron that strikes the dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Multiplier
An electron multiplier is a vacuum-tube structure that multiplies incident charges. In a process called secondary emission, a single electron can, when bombarded on secondary-emissive material, induce emission of roughly 1 to 3 electrons. If an electric potential is applied between this metal plate and yet another, the emitted electrons will accelerate to the next metal plate and induce secondary emission of still more electrons. This can be repeated a number of times, resulting in a large shower of electrons all collected by a metal anode, all having been triggered by just one. History In 1930, Russian physicist Leonid Aleksandrovitch Kubetsky proposed a device which used photocathodes combined with dynodes, or secondary electron emitters, in a single tube to remove secondary electrons by increasing the electric potential through the device. The electron multiplier can use any number of dynodes in total, which use a coefficient, σ, and created a gain of σn where n is the number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Emission
In particle physics, secondary emission is a phenomenon where primary incident particles of sufficient energy, when hitting a surface or passing through some material, induce the emission of secondary particles. The term often refers to the emission of electrons when charged particles like electrons or ions in a vacuum tube strike a metal surface; these are called secondary electrons. In this case, the number of secondary electrons emitted per incident particle is called secondary emission yield. If the secondary particles are ions, the effect is termed ''secondary ion emission''. Secondary electron emission is used in photomultiplier tubes and image intensifier tubes to amplify the small number of photoelectrons produced by photoemission, making the tube more sensitive. It also occurs as an undesirable side effect in electronic vacuum tubes when electrons from the cathode strike the anode, and can cause parasitic oscillation. Applications Secondary emissive materials Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It takes the form of an evacuated tubular envelope of glass or sometimes metal containing electrodes connected to external connection pins. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental Electronics, electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current Rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as vacuum phototubes achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light and measurement of its intensity. In both types the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The first, and simplest, vacuum tube, the diode or Flem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Camera Tube
Video camera tubes are devices based on the cathode-ray tube that were used in television cameras to capture television images, prior to the introduction of charge-coupled device (CCD) image sensors in the 1980s. Several different types of tubes were in use from the early 1930s, and as late as the 1990s. In these tubes, an cathode ray, electron beam is scanned across an image of the scene to be broadcast focused on a target. This generated a current that is dependent on the brightness of the image on the target at the scan point. The size of the striking ray is tiny compared to the size of the target, allowing 480–486 horizontal scan lines per image in the NTSC format, 576 lines in PAL, and as many as 1035 lines in Multiple sub-Nyquist sampling encoding, Hi-Vision. Cathode-ray tube Any vacuum tube which operates using a focused beam of electrons, originally called cathode rays, is known as a cathode-ray tube (CRT). These are usually seen as display devices as used in older (i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are devices that detect light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. They are essential in a wide range of applications, from digital imaging and optical communication to scientific research and industrial automation. Photodetectors can be classified by their mechanism of detection, such as the photoelectric effect, photochemical reactions, or thermal effects, or by performance metrics like spectral response. Common types include photodiodes, phototransistors, and photomultiplier tubes, each suited to specific uses. Solar cells, which convert light into electricity, are also a type of photodetector. This article explores the principles behind photodetectors, their various types, applications, and recent advancements in the field. History The development of photodetectors began with the discovery of the photoelectric effect by Heinrich Hertz in 1887, later explained by Albert Einst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectric Effect
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons from a material caused by electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, solid state, and quantum chemistry to draw inferences about the properties of atoms, molecules and solids. The effect has found use in electronic devices specialized for light detection and precisely timed electron emission. The experimental results disagree with classical electromagnetism, which predicts that continuous light waves transfer energy to electrons, which would then be emitted when they accumulate enough energy. An alteration in the intensity of light would theoretically change the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons, with sufficiently dim light resulting in a delayed emission. The experimental results instead show that electrons are dislodged only when the light exceeds a certain frequency—regardless of the ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microchannel Plate Detector
A microchannel plate (MCP) is used to detect single particles (electrons, ions and neutrons) and photons (ultraviolet radiation and X-rays). It is closely related to an electron multiplier, as both intensify single particles or photons by the multiplication of electrons via secondary emission. Because a microchannel plate detector has many separate channels, it can provide spatial resolution. Basic design A microchannel plate is a slab made from resistive material (most often glass) 0.5 to 2mm thick with a regular array of tiny tubes (microchannels) leading from one face to the other. The microchannels are typically 5-20 micrometers in diameter, parallel to each other and enter the plate at a small angle to the surface (8-13° from normal). Plates are often round disks, but can be cut to any shape from sizes 10mm up to 200mm. They may also be curved. Operating mode At non-relativistic energies, single particles generally produce effects too small to enable their direct det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectron
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons from a material caused by electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, solid state, and quantum chemistry to draw inferences about the properties of atoms, molecules and solids. The effect has found use in electronic devices specialized for light detection and precisely timed electron emission. The experimental results disagree with classical electromagnetism, which predicts that continuous light waves transfer energy to electrons, which would then be emitted when they accumulate enough energy. An alteration in the intensity of light would theoretically change the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons, with sufficiently dim light resulting in a delayed emission. The experimental results instead show that electrons are dislodged only when the light exceeds a certain frequency—regardless of the ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device such as a lead-acid battery. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. Conventional current describes the direction in which positive charges move. Electrons, which are the carriers of current in most electrical systems, have a negative electrical charge, so the movement of electrons is ''opposite'' to that of the conventional current flow: this means that electrons flow ''into'' the device's cathode from the external circuit. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a + (plus) is the cathode. The electrode through which conventional current flows the other way, into the device, is termed an anode. Charge flow Conventional current flows from cathode to anode outside the cell or device (with electrons moving in the opposite direction), regardless of the cell or device type and operating mode. Cathode polarity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
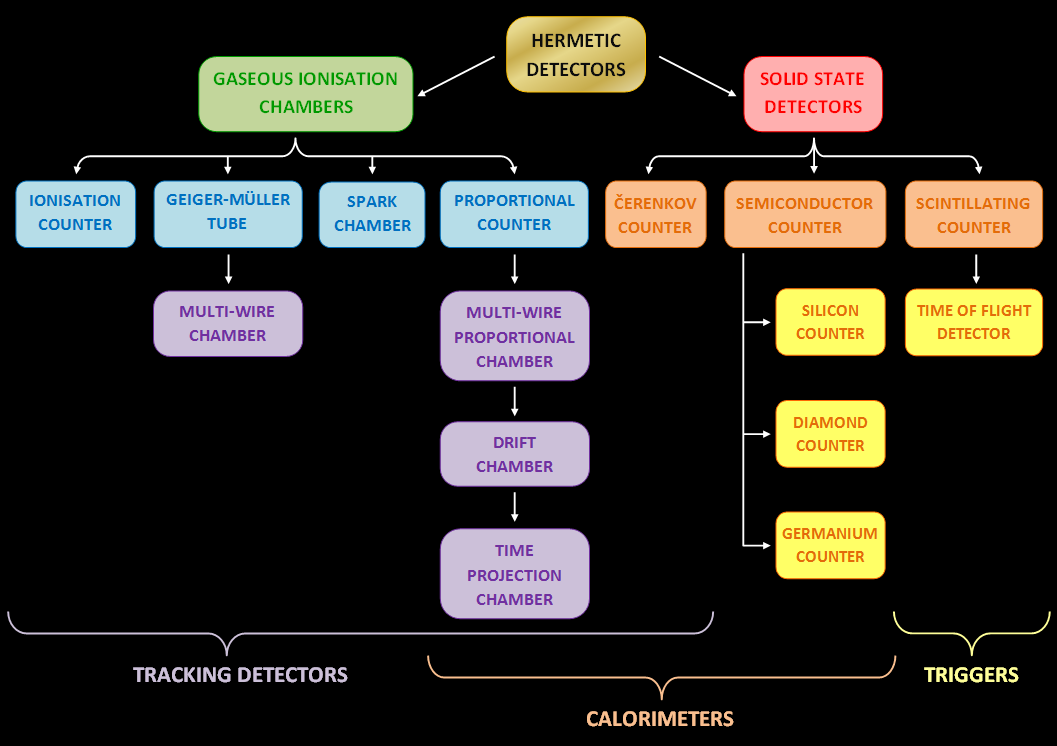
Particle Detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing elementary particle, particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle. The operating of a nuclear radiation detector The operating principle of a nuclear radiation detector can be summarized as follows: The detector identifies high-energy particles or photons—such as alpha, beta, gamma radiation, or neutrons—through their interactions with the atoms of the detector material. These interactions generate a primary signal, which may involve ionization of gas, the creation of electron-hole pairs in semiconductors, or the emission of light in scint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Hull
Albert Wallace Hull (19 April 1880 – 22 January 1966) was an American physicist and electrical engineer who made contributions to the development of vacuum tubes, and invented the magnetron. He was a member of the National Academy of Sciences. Biography He was born on 19 April 1880 in Southington, Connecticut. He majored in Greek and after taking one undergraduate course in physics, graduated from Yale University. He taught languages at The Albany Academy before returning to Yale, to take a doctorate in physics. He then undertook research on photoelectricity whilst teaching physics for five years at the Worcester Polytechnic Institute. In 1914 Hull joined the General Electric Research Laboratory (GERL) in Schenectady, New York and remained there until his retirement in 1949. During 1916, Hull began investigation into the use of magnetic control of thermionic valves (vacuum tubes) as an alternative to grid or electrostatic control and he had tested successfully mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |