|
Diplopia
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often voluntary. However, when occurring involuntarily, it results from impaired function of the extraocular muscles, where both eyes are still functional, but they cannot turn to target the desired object. Problems with these muscles may be due to mechanical problems, disorders of the neuromuscular junction, disorders of the cranial nerves ( III, IV, and VI) that innervate the muscles, and occasionally disorders involving the supranuclear oculomotor pathways or ingestion of toxins. Diplopia can be one of the first signs of a systemic disease, particularly to a muscular or neurological process, and it may disrupt a person's balance, movement, or reading abilities. Causes Diplopia has a diverse range of ophthalmologic, infectious, autoimmune, neurological, and neoplasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trochlear Nerve
The trochlear nerve (), ( lit. ''pulley-like'' nerve) also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates a single muscle - the superior oblique muscle of the eye (which operates through the pulley-like trochlea). Unlike most other cranial nerves, the trochlear nerve is exclusively a motor nerve ( somatic efferent nerve). The trochlear nerve is unique among the cranial nerves in several respects: * It is the ''smallest'' nerve in terms of the number of axons it contains. * It has the greatest intracranial length. * It is the only cranial nerve that exits from the dorsal (rear) aspect of the brainstem. * It innervates a muscle, the superior oblique muscle, on the opposite side (contralateral) from its nucleus. The trochlear nerve decussates within the brainstem before emerging on the contralateral side of the brainstem (at the level of the inferior colliculus). An injury to the trochlear nucleus in the brainstem will result i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abducens Nerve
The abducens nerve or abducent nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VI, or simply CN VI, is a cranial nerve in humans and various other animals that controls the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, one of the extraocular muscles responsible for outward Gaze (physiology), gaze. It is a Somatic (biology), somatic efferent nerve fiber, efferent nerve. Structure Nucleus The abducens nucleus is located in the pons, on the floor of the fourth ventricle, at the level of the facial colliculus. Axons from the facial nerve loop around the abducens nucleus, creating a slight bulge (the facial colliculus) that is visible on the dorsal surface of the floor of the fourth ventricle. The abducens nucleus is close to the midline, like the other motor nuclei that control eye movements (the Oculomotor nucleus, oculomotor and Trochlear nucleus, trochlear nuclei). Motor axons leaving the abducens nucleus run ventrally and caudally through the pons. They pass lateral to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniseikonia
Aniseikonia is an ocular condition where there is a significant difference in the perceived size of images. It can occur as an overall difference between the two eyes, or as a difference in a particular meridian. If the ocular image size in both eyes are equal, the condition is known as ''iseikonia''. Symptoms and signs Up to 7% difference in image size is well tolerated. If magnification difference becomes excessive the effect can cause diplopia, suppression, disorientation, eyestrain, headache, and dizziness and balance disorders. Asthenopic symptoms alone may occur even if image size difference is less than 7%. Causes Retinal image size is determined by many factors. The size and position of the object being viewed affects the characteristics of the light entering the system. Corrective lenses affect these characteristics and are used commonly to correct refractive error. The optics of the eye including its refractive power and axial length also play a major role in retinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graves Disease
Graves' disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter or Basedow's disease, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in and is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It also often results in an enlarged thyroid. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea and unintentional weight loss. Other symptoms may include thickening of the skin on the shins, known as pretibial myxedema, and eye bulging, a condition caused by Graves' ophthalmopathy. About 25 to 30% of people with the condition develop eye problems. The exact cause of the disease is unclear, but symptoms are a result of antibodies binding to receptors on the thyroid causing over-expression of thyroid hormone. Persons are more likely to be affected if they have a family member with the disease. If one monozygotic twin is affected, a 30% chance exists that the other twin will also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a late-onset neurodegenerative disease involving the gradual deterioration and death of specific volumes of the brain, linked to 4-repeat tau pathology. The condition leads to symptoms including Balance disorder, loss of balance, Hypokinesia, slowing of movement, Ophthalmoparesis, difficulty moving the eyes, and cognitive impairment. PSP may be mistaken for other types of neurodegeneration such as Parkinson's disease, frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's disease. It is the second most common tauopathy behind Alzheimer's disease. The cause of the condition is uncertain, but involves the accumulation of tau protein within the brain. Medications such as L-DOPA, levodopa and amantadine may be useful in some cases. PSP was first officially described by Richardson, Steele, and Olszewski in 1963 as a form of progressive parkinsonism. However, the earliest known case presenting clinical features consistent with PSP, along with pathological co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple System Atrophy
Multiple system atrophy (MSA) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder characterized by tremors, slow movement, muscle rigidity, postural instability (collectively known as parkinsonism), autonomic dysfunction and ataxia. This is caused by progressive degeneration of neurons in several parts of the brain including the basal ganglia, inferior olivary nucleus, and cerebellum. MSA was first described in 1960 by Milton Shy and Glen Drager and was then known as Shy–Drager syndrome. Many people affected by MSA experience dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, which commonly manifests as orthostatic hypotension, impotence, loss of sweating, dry mouth and urinary retention and incontinence. Palsy of the vocal cords is an important and sometimes initial clinical manifestation of the disorder. A prion of the alpha-synuclein protein within affected neurons may cause MSA. About 55% of MSA cases occur in men, with those affected first showing symptoms at the age of 50–60 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Nerves
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of Visual perception, vision, taste, Olfaction, smell, and hearing. The cranial nerves emerge from the central nervous system above the level of the Atlas (anatomy), first vertebra of the vertebral column. Each cranial nerve is paired and is present on both sides. There are conventionally twelve pairs of cranial nerves, which are described with Roman numerals I–XII. Some considered there to be thirteen pairs of cranial nerves, including the non-paired cranial nerve zero. The numbering of the cranial nerves is based on the order in which they emerge from the brain and brainstem, from front to back. The terminal nerves (0), olfactory nerves (I) and optic nerves (II) emerge f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraocular Muscles
The extraocular muscles, or extrinsic ocular muscles, are the seven extrinsic muscles of the eye in human eye, humans and other animals. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior oblique muscle, superior and inferior oblique muscles, control Eye movement, movement of the eye. The other muscle, the Levator palpebrae superioris muscle, levator palpebrae superioris, controls eyelid elevation and depression, elevation. The actions of the six muscles responsible for eye movement depend on the position of the eye at the time of muscle contraction. The ciliary muscle, pupillary sphincter muscle and pupillary dilator muscle sometimes are called intrinsic ocular muscles or intraocular muscles. Structure Since only a small part of the eye called the Fovea centralis, fovea provides sharp vision, the eye must move to follow a target. Eye movements must be precise and fast. This is seen in scenarios like reading, where the reader must shift gaze constantly. Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to insulin's effects. Classic symptoms include polydipsia (excessive thirst), polyuria (excessive urination), polyphagia (excessive hunger), weight loss, and blurred vision. If left untreated, the disease can lead to various health complications, including disorders of the cardiovascular system, eye, kidney, and nerves. Diabetes accounts for approximately 4.2 million deaths every year, with an estimated 1.5 million caused by either untreated or poorly treated diabetes. The major types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2. The most common treatment for type 1 is insulin replacement therapy (insulin injections), while anti-diabetic medications (such as metformin and semaglutide) and lifestyle modificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drunkenness
Alcohol intoxication, commonly described in higher doses as drunkenness or inebriation, and known in overdose as alcohol poisoning, is the behavior and physical effects caused by recent consumption of alcohol. The technical term ''intoxication'' in common speech may suggest that a large amount of alcohol has been consumed, leading to accompanying physical symptoms and deleterious health effects. Mild intoxication is mostly referred to by slang terms such as ''tipsy'' or ''buzzed''. In addition to the toxicity of ethanol, the main psychoactive component of alcoholic beverages, other physiological symptoms may arise from the activity of acetaldehyde, a metabolite of alcohol. These effects may not arise until hours after ingestion and may contribute to a condition colloquially known as a hangover. Symptoms of intoxication at lower doses may include mild sedation and poor coordination. At higher doses, there may be slurred speech, trouble walking, impaired vision, mood swing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism is a clinical syndrome characterized by tremor, bradykinesia (slowed movements), Rigidity (neurology), rigidity, and balance disorder, postural instability. Both hypokinetic features (bradykinesia and akinesia) and hyperkinetic features (cogwheel rigidity and tremors at rest) are displayed in parkinsonism. These are the four Parkinson's disease#Motor, motor signs that are found in Parkinson's disease (PD)after which Parkinsonism is namedand in dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD), and many other conditions. This set of signs occurs in a wide range of conditions and may have many causes, including neurodegenerative conditions, drugs, toxins, metabolic diseases, and neurological conditions other than Parkinson's disease. Signs and symptoms Parkinsonism is a clinical syndrome characterized by the four Parkinson's disease#Motor, motor signs that are found in Parkinson's disease: tremor, bradykinesia (slowed movements), Rigidity (neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
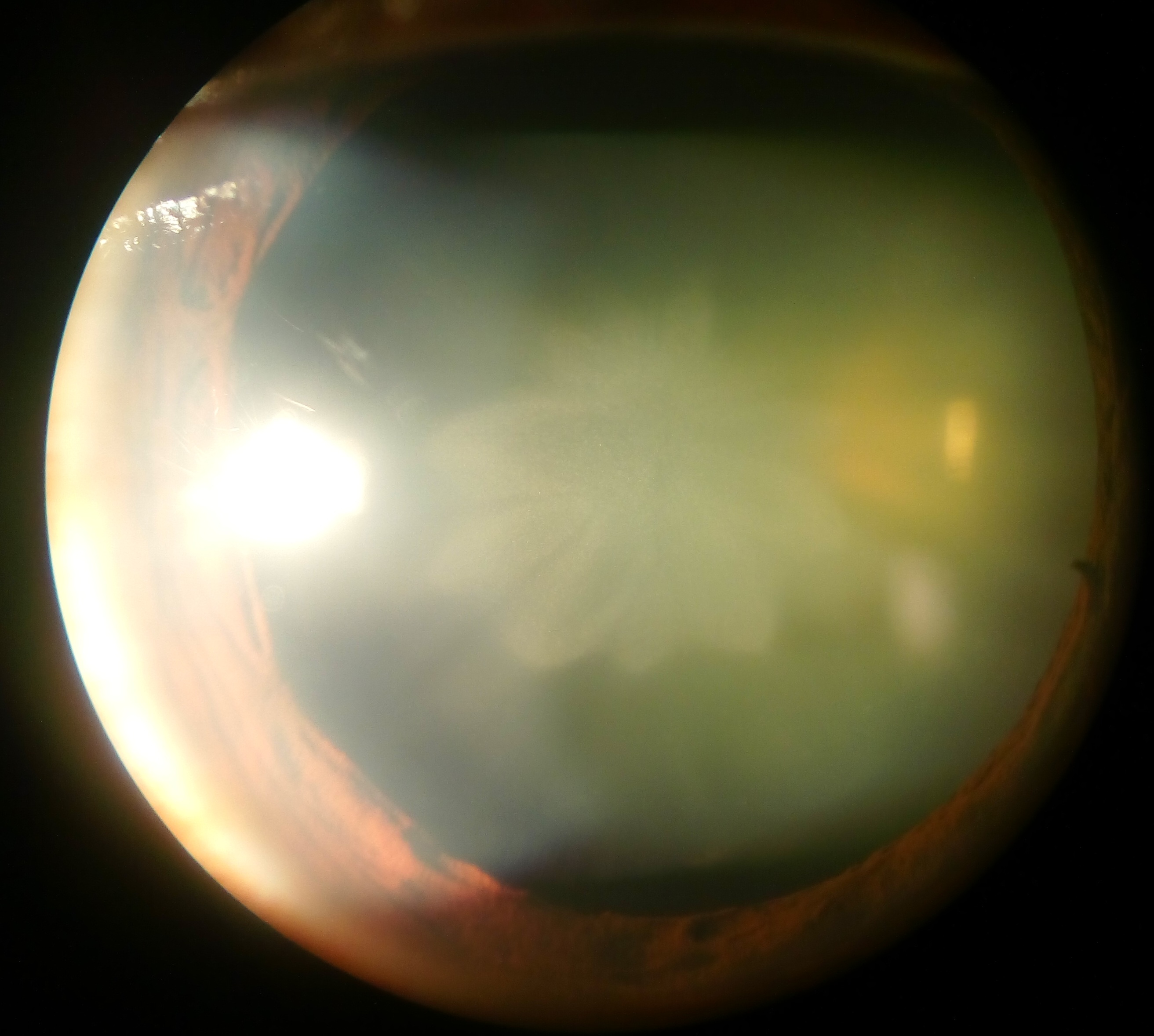
Cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens (anatomy), lens of the eye that leads to a visual impairment, decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and Nyctalopia, difficulty seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of Falling (accident), falling and Depression (mood), depression. Cataracts cause 51% of all cases of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide. Cataracts are most commonly due to senescence, aging but may also occur due to Trauma (medicine), trauma or radiation exposure, be congenital cataract, present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes mellitus, diabetes, longstanding use of corticosteroid medication, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |