|
Digital Micromirror Device
The digital micromirror device, or DMD, is the microoptoelectromechanical system (MOEMS) that is the core of the trademarked Digital Light Processing (DLP) projection technology from Texas Instruments (TI). The device is used in digital projectors and consists of an array of millions of microscopic mirrors which can be individually tilted many thousand times per second, thereby creating the pixels of the projected images. History The technology goes back to 1973 with Harvey C. Nathanson's (inventor of MEMS c. 1965) use of millions of microscopically small moving mirrors to create a video display of the type now found in digital projectors. The project at Texas Instrument's began as the deformable mirror device in 1977 using micromechanical analog light modulators. The DMD was invented by solid-state physicist and TI Fellow Emeritus Dr. Larry Hornbeck in 1987. The first analog DMD product was the TI DMD2000 airline ticket printer that went to market in 1990 and used a DM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DLP CINEMA
DLP may refer to: Politics * Democratic Left Party (Turkey), a political party from Turkey * Democratic Labour Party (Australia), an Australian political party * Democratic Labour Party (Barbados), a major political party in Barbados * Democratic Labour Party (New Zealand), a former New Zealand political party * Democratic Labour Party (Trinidad and Tobago), a political party in Trinidad and Tobago * Dominica Labour Party, a social democratic political party in Dominica * Dominion Labor Party (Alberta) * Dominion Labour Party (Manitoba) * Dutch Labour Party, in the Netherlands * Jammu Kashmir Democratic Liberation Party, a political party in Jammu Kashmir Science and technology * Data level parallelism, a form of data parallelism in computer science * Data loss prevention, a field of computer security; See Data loss prevention software * Digital Light Processing, a display device based on optical micro-electro-mechanical technology * Discrete logarithm problem, a mathematical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static RAM
Static random-access memory (static RAM or SRAM) is a type of random-access memory (RAM) that uses latching circuitry (flip-flop) to store each bit. SRAM is volatile memory; data is lost when power is removed. The ''static'' qualifier differentiates SRAM from ''dynamic'' random-access memory (DRAM): * SRAM will hold its data permanently in the presence of power, while data in DRAM decays in seconds and thus must be periodically refreshed. * SRAM is faster than DRAM but it is more expensive in terms of silicon area and cost. * Typically, SRAM is used for the cache and internal registers of a CPU while DRAM is used for a computer's main memory. History Semiconductor bipolar SRAM was invented in 1963 by Robert Norman at Fairchild Semiconductor. Metal–oxide–semiconductor SRAM (MOS-SRAM) was invented in 1964 by John Schmidt at Fairchild Semiconductor. The first device was a 64-bit MOS p-channel SRAM. SRAM was the main driver behind any new CMOS-based technology fabrica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optogenetics
Optogenetics is a biological technique to control the activity of neurons or other cell types with light. This is achieved by Gene expression, expression of Channelrhodopsin, light-sensitive ion channels, Halorhodopsin, pumps or Photoactivated adenylyl cyclase, enzymes specifically in the target cells. On the level of individual Cell (biology), cells, Photoactivated adenylyl cyclase, light-activated enzymes and transcription factors allow precise control of biochemical signaling pathways. In Neuroscience, systems neuroscience, the ability to control the activity of a genetically defined set of neurons has been used to understand their contribution to decision making, learning, fear memory, mating, addiction, feeding, and locomotion. In a first medical application of optogenetic technology, vision was partially restored in a blind patient with Retinitis pigmentosa. Optogenetic techniques have also been introduced to map the Brain connectivity estimators, functional connectivity of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotomography
Holotomography (HT) is a laser technique to measure the three-dimensional refractive index (RI) tomogram of a microscopic sample such as biological cells and tissues. Because the RI can serve as an intrinsic imaging contrast for transparent or phase objects, measurements of RI tomograms can provide label-free quantitative imaging of microscopic phase objects. In order to measure 3-D RI tomogram of samples, HT employs the principle of holographic imaging and inverse scattering. Typically, multiple 2D holographic images of a sample are measured at various illumination angles, employing the principle of interferometric imaging. Then, a 3D RI tomogram of the sample is reconstructed from these multiple 2D holographic images by inversely solving light scattering in the sample. History The first theoretical proposal was presented by Emil Wolf, and the first experimental demonstration was shown by Fercher et al. From 2000s, HT techniques had been extensively studied and applied to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multivariate Optical Computing
Multivariate optical computing, also known as molecular factor computing, is an approach to the development of compressed sensing spectroscopic instruments, particularly for industrial applications such as process analytical support. "Conventional" spectroscopic methods often employ multivariate and chemometric methods, such as multivariate calibration, pattern recognition, and classification, to extract analytical information (including concentration) from data collected at many different wavelengths. Multivariate optical computing uses an optical computer to analyze the data as it is collected. The goal of this approach is to produce instruments which are simple and rugged, yet retain the benefits of multivariate techniques for the accuracy and precision of the result. An instrument which implements this approach may be described as a multivariate optical computer. Since it describes an approach, rather than any specific wavelength range, multivariate optical computers ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Light Modulator
A spatial light modulator (SLM) is a device that can control the intensity, phase, or polarization of light in a spatially varying manner. A simple example is an overhead projector transparency. Usually when the term SLM is used, it means that the transparency can be controlled by a computer. SLMs are primarily marketed for image projection, displays devices, and maskless lithography. SLMs are also used in optical computing and holographic optical tweezers. Usually, an SLM modulates the intensity of the light beam. However, it is also possible to produce devices that modulate the phase of the beam or both the intensity and the phase simultaneously. It is also possible to produce devices that modulate the polarization of the beam, and modulate the polarization, phase, and intensity simultaneously. SLMs are used extensively in holographic data storage setups to encode information into a laser beam similarly to the way a transparency does for an overhead projector. They can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Space Measurement With Forward Modeling
Phase space measurement with forward modeling is one approach to address the scattering issue in biomedical imaging. Scattering is one of the biggest problems in biomedical imaging, given that scattered light is eventually defocused, thus resulting in diffused images.Elizabeth M. C. Hillman et al., (2007"Optical brain imaging in vivo: techniques and applications from animal to man"/ref> Instead of removing the scattered light, this approach uses the information of scattered light to reconstruct the original light signals. This approach requires the phase space data of light in imaging system and a forward model to describe scattering events in a turbid medium. Phase space of light can be obtained by using digital micromirror device (DMD)Liu et al., 201"3D imaging in volumetric scattering media using phase-space measurements"/ref> or light field microscopy.Pegard et al., 201"Compressive light-field microscopy for 3D neural activity recording"/ref> Phase space measurement with forwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
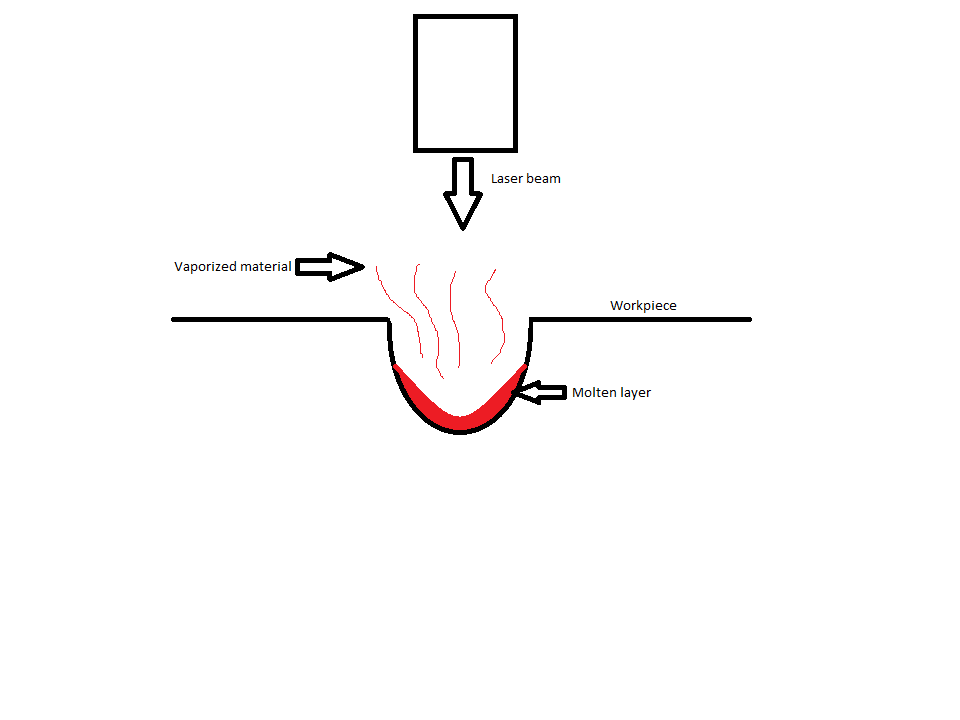
Laser Beam Machining
Laser beam machining (LBM) is a form of machining that uses heat directed from a laser beam. This process uses thermal energy to remove material from metallic or nonmetallic surfaces. The high frequency of monochromatic light will fall on the surface, thus heating, melting and vaporizing the material due to the impinge of photons (see Coulomb explosion). Laser beam machining is best suited for brittle materials with low conductivity, but can be used on most materials. Laser beam machining can be done on glass without melting the surface. With photosensitive glass, the laser alters the chemical structure of the glass allowing it to be selectively etched. The glass is also referred to as photomachinable glass. The advantage of photomachinable glass is that it can produce precisely vertical walls and the native glass is suitable for many biological applications such as substrates for genetic analysis. Types of lasers There are many different types of lasers including gas, solid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference (wave propagation), interference'' of Superposition principle, superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, Optical fiber, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, Nuclear physics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, interactome, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms. Interferometers are devices that extract information from interference. They are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of microscopic displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In the case with most interferometers, light from a single source is split into two beams that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Cinema
Digital cinema is the digital technology used within the film industry to distribute or project motion pictures as opposed to the historical use of reels of motion picture film, such as 35 mm film. Whereas film reels have to be shipped to movie theaters, a digital movie can be distributed to cinemas in a number of ways: over the Internet or dedicated satellite links, or by sending hard drives or optical discs such as Blu-ray discs, then projected using a digital video projector instead of a film projector. Typically, digital movies are shot using digital movie cameras or in animation transferred from a file and are edited using a non-linear editing system (NLE). The NLE is often a video editing application installed in one or more computers that may be networked to access the original footage from a remote server, share or gain access to computing resources for rendering the final video, and allow several editors to work on the same timeline or project. Alternatively a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
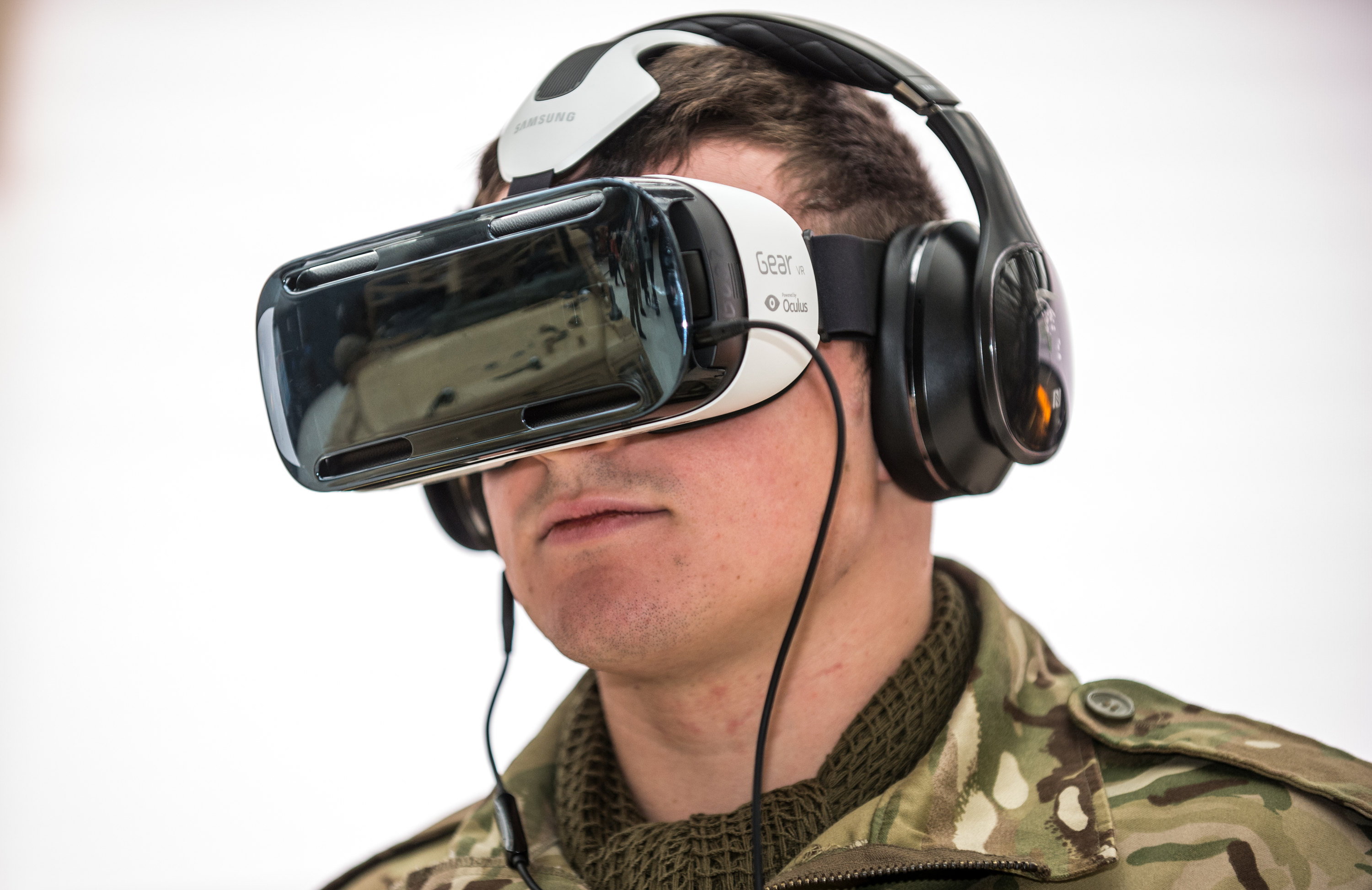
Head-mounted Display
A head-mounted display (HMD) is a display device, worn on the head or as part of a helmet (see helmet-mounted display for aviation applications), that has a small display optic in front of one (monocular HMD) or each eye (binocular vision, binocular HMD). HMDs have many uses including gaming, aviation, engineering, and medicine. Virtual reality headsets are a type of HMD that track 3D position and rotation to provide a virtual environment to the user. 3DOF VR headsets typically use an Inertial measurement unit, IMU for tracking. 6DOF VR headsets typically use sensor fusion from multiple data sources including at least one IMU. An optical head-mounted display (OHMD) is a wearable display that can reflect projected images and allows a user to see through it. Overview A typical HMD has one or two small displays, with lenses and semi-transparent mirrors embedded in eyeglasses (also termed data glasses), a visor, or a helmet. The display units are miniaturized and may include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holographic Versatile Disc
The Holographic Versatile Disc (HVD) is an optical disc technology that was expected to store up to several terabytes of data on an optical disc 10 cm or 12 cm in diameter. Its development commenced in April 2004. The technology was abandoned due to funding issues. One of the responsible companies went bankrupt in 2010. The reduced radius was meant to reduce costs and materials used. It employs a technique known as Collinear Holography, whereby a blue-green and red laser beam are collimated in a single beam. The blue-green laser reads data encoded as laser interference fringes from a holographic layer near the top of the disc. A red laser is used as the reference beam to read servoinformation from a regular CD-style aluminium layer near the bottom. Servoinformation is used to monitor the position of the read head over the disc, similar to the head, track, and sector information on a conventional hard disk drive. On a CD or DVD this servoinformation is interspersed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |