|
Diagonal Pliers
Diagonal pliers (also known as wire cutters or diagonal cutting pliers, or under many regional names) are pliers intended for the cutting of wire or small stock, rather than grabbing or turning. The plane defined by the cutting edges of the jaws intersects the joint rivet at an angle or "on a diagonal", giving pliers their name. They are also adapted for use in inaccessible places. Action Instead of using a shearing action as with scissors, diagonal pliers cut by indenting and wedging the wire apart. The jaw edges are ground to a symmetrical " V" shape, thus the two jaws can be visualized to form the letter " X", as seen end-on when closed. The blades are made of tempered steel, and inductive heating and quenching are often used to harden the jaws. Jargon In UK English and Irish English, diagonal pliers are commonly referred to as snips, nippers or side cutters. The term snips commonly refers to larger items, not to those used for cutting electrical wiring etc. In Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handle (grip)
A handle is a part of, or an attachment to, an object that allows it to be grasped and manipulated by hand. The design of each type of handle involves substantial ergonomic issues, even where these are dealt with intuitively or by following tradition. Handles for tools are an important part of their function, enabling the user to exploit the tools to maximum effect. Package handles allow for convenient carrying of packages. General design criteria The three nearly universal requirements of are: # Sufficient strength to support the object, or to otherwise transmit the force involved in the task the handle serves. # Sufficient length to permit the hand or hands gripping it to comfortably exert the force. # Sufficiently small circumference to permit the hand or hands to surround it far enough to grip it as solidly as needed to exert that force. Specific needs Other requirements may apply to specific handles: * A sheath or coating on the handle that provides friction aga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linesman's Pliers
Lineman's pliers (US English), Kleins (genericized trademark, US usage), linesman pliers (Canadian English), side cutting linesman pliers and combination pliers (UK / US English) are a type of pliers used by lineworkers, electricians, and other tradesmen primarily for gripping, twisting, bending and cutting wire, cable, and small metalwork components. They owe their effectiveness to their plier design, which multiplies force through leverage. Lineman's pliers are distinguished by a flat gripping surface at their snub nose. Combination pliers have a shorter flat surface plus a concave / curved gripping surface which is useful in light engineering to work with metal bar, etc. Both usually have a bevelled cutting edge similar to that on diagonal pliers in their craw, and each may include an additional gripping, crimping, or wire shearing (for a flat ended cut) device at the crux of the handle side of the pliers' joint. Designed for potentially heavy manual operation, these plier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apex (geometry)
In geometry, an apex (: apices) is the vertex which is in some sense the "highest" of the figure to which it belongs. The term is typically used to refer to the vertex opposite from some " base". The word is derived from the Latin for 'summit, peak, tip, top, extreme end'. The term apex may be used in different contexts: * In an isosceles triangle, the apex is the vertex where the two sides of equal length meet, opposite the unequal third side. * In a pyramid or cone In geometry, a cone is a three-dimensional figure that tapers smoothly from a flat base (typically a circle) to a point not contained in the base, called the '' apex'' or '' vertex''. A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines ..., the apex is the vertex at the "top" (opposite the base). In a pyramid, the vertex is the point that is part of all the lateral faces, or where all the lateral edges meet. References Parts of a triangle Polyhedra {{elementary-geometry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
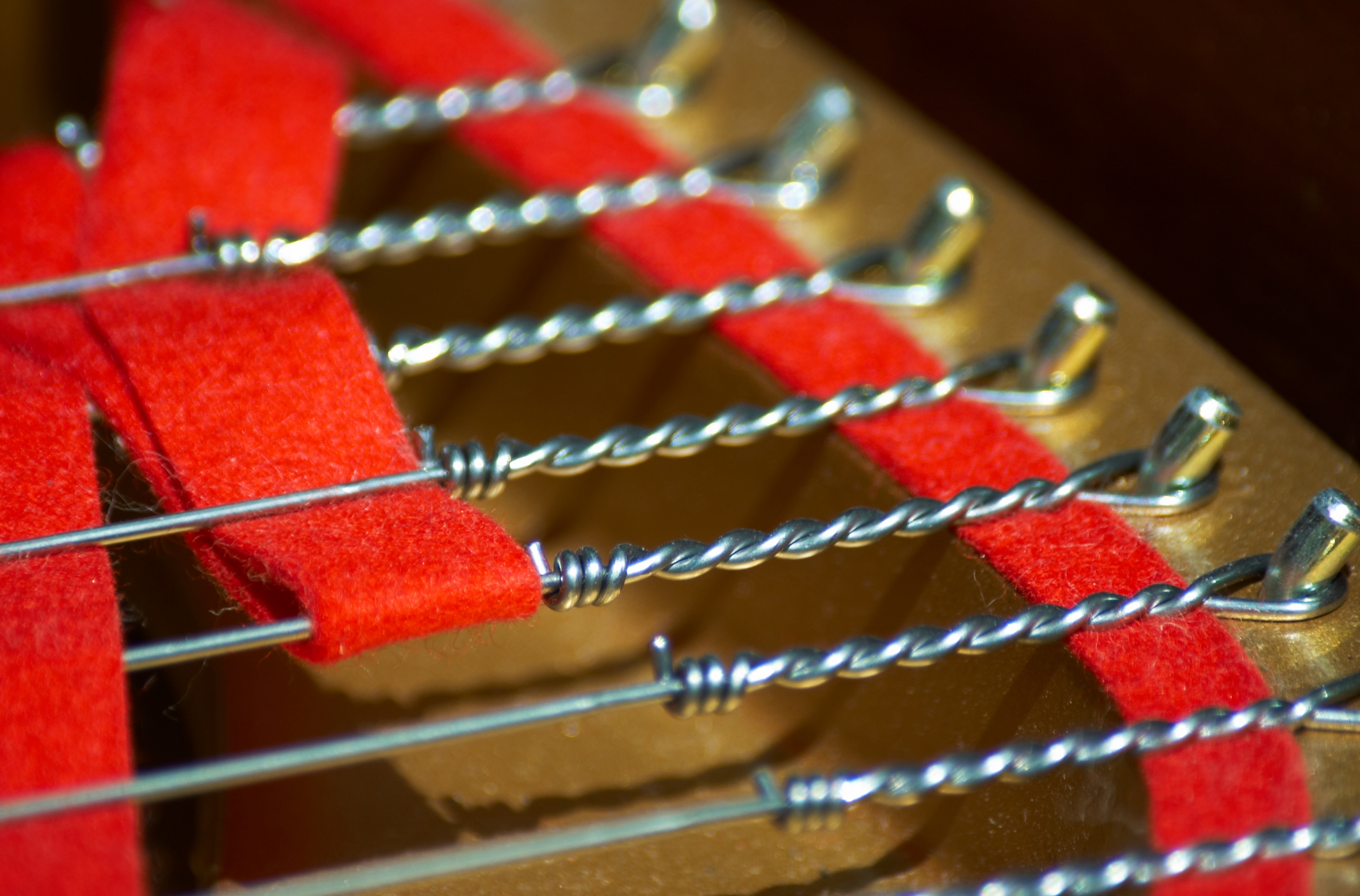
Piano Wire
Piano wire, or "music wire", is a specialized type of wire made for use in piano string (music), strings but also in other applications as Spring (device), springs. It is made from tempering (metallurgy), tempered high-carbon steel, also known as spring steel, which replaced iron as the material starting in 1834. Piano wire has a very high ultimate tensile strength, tensile strength to cope with the heavy demands placed upon piano strings; accordingly, piano wire is also used for a number of other purposes, including springs, surgical uses, and in special effects. History The oldest record of wire being made for musical instruments is from Augsburg in 1351.Dolge (1911, 124) Starting around 1800, the piano began to be built ever more ambitiously, with sturdier (eventually, iron) framing and greater string tension. This led to innovations in making tougher piano wire. In 1834, the Webster & Horsfal firm of Birmingham, United Kingdom brought out a form of piano wire made from c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength and low raw material cost, steel is one of the most commonly manufactured materials in the world. Steel is used in structures (as concrete Rebar, reinforcing rods), in Bridge, bridges, infrastructure, Tool, tools, Ship, ships, Train, trains, Car, cars, Bicycle, bicycles, Machine, machines, Home appliance, electrical appliances, furniture, and Weapon, weapons. Iron is always the main element in steel, but other elements are used to produce various grades of steel demonstrating altered material, mechanical, and microstructural properties. Stainless steels, for example, typically contain 18% chromium and exhibit improved corrosion and Redox, oxidation resistance versus its carbon steel counterpart. Under atmospheric pressures, steels generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has a great affinity towards oxygen, passivation (chemistry), forming a protective layer of aluminium oxide, oxide on the surface when exposed to air. It visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, magnetism, nonmagnetic, and ductility, ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the abundance of the chemical elements, 12th-most abundant element in the universe. The radioactive decay, radioactivity of aluminium-26, 26Al leads to it being used in radiometric dating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth's crust, being mainly deposited by meteorites in its metallic state. Extracting usable metal from iron ores requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching , about 500 °C (900 °F) higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BC and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys – in some regions, only around 1200 BC. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. In the modern world, iron alloys, such as steel, stainless steel, cast iron and special steels, are by far the most common industrial metals, due to their mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, in proportions which can be varied to achieve different colours and mechanical, electrical, acoustic and chemical properties, but copper typically has the larger proportion, generally copper and zinc. In use since prehistoric times, it is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other within the same crystal structure. Brass is similar to bronze, a copper alloy that contains tin instead of zinc. Both bronze and brass may include small proportions of a range of other Chemical element, elements including arsenic, lead, phosphorus, aluminium, manganese and silicon. Historically, the distinction between the two alloys has been less consistent and clear, and increasingly museums use the more general term "list of copper alloys, copper alloy". Brass has long been a popular material for its bright gold-like appearance and is still used for drawer pulls and door handle, doorknobs. It has also been widely used to ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulator (electrical)
An electrical insulator is a material in which electric current does not flow freely. The atoms of the insulator have tightly bound electrons which cannot readily move. Other materials—semiconductors and electrical conductor, conductors—conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. The most common examples are Nonmetal (chemistry), non-metals. A perfect insulator does not exist because even the materials used as insulators contain small numbers of mobile charges (charge carriers) which can carry current. In addition, all insulators become electrically conductive when a sufficiently large voltage is applied that the electric field tears electrons away from the atoms. This is known as electrical breakdown, and the voltage at which it occurs is called the breakdown voltage of an insulator. Some materials such as glass, Electrical insulation paper, paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrink Fit
Shrink-fitting is a technique in which an interference fit is achieved by a relative size change after assembly. This is usually achieved by heating or cooling one component before assembly and allowing it to return to the ambient temperature after assembly, employing the phenomenon of thermal expansion to make a joint. For example, the thermal expansion of a piece of a metallic drainpipe allows a builder to fit the cooler piece to it. As the adjoined pieces reach the same temperature, the joint becomes strained and stronger. Other examples are the fitting of a wrought iron tyre around the rim of a wooden cart wheel by a wheelwright, or of a steel tyre to the wheel of a railway engine or rolling stock. In both cases the tyre will be heated and expands to slightly greater than the wheel's diameter, and is fitted around it. After cooling, the tyre contracts, binding tightly in place. The bombard Mons Meg was assembled from longitudinal staves of iron held in place by shrink-fitted ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |