|
Detector (radio)
In radio, a detector is a device or circuit that extracts information from a modulated radio frequency current or voltage. The term dates from the first three decades of radio (1888–1918). Unlike modern radio stations which transmit sound (an audio signal) on an uninterrupted carrier wave, early radio stations transmitted information by ''radiotelegraphy''. The transmitter was switched On-off keying, on and off to produce long or short periods of radio waves, spelling out text messages in Morse code. Therefore, early radio receivers in order to receive the message, merely had to reproduce the Morse code "dots" and "dashes" by simply distinguishing between the presence or absence of a radio signal. The device that performed this function in the receiver circuit was called a ''detector''. A variety of different detector devices, such as the coherer, electrolytic detector, magnetic detector and the crystal detector, were used during the wireless telegraphy era until superseded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tapping Coherer
Tapping is a playing technique that can be used on any stringed instrument, but which is most commonly used on guitar. The technique involves a string being fretted and set into vibration as part of a single motion. This is in contrast to standard techniques that involve fretting with one hand and picking with the other. Tapping is the primary technique intended for instruments such as the Chapman Stick. Description Tapping is an extended technique, executed by using either hand to 'tap' the strings against the fingerboard, thus producing legato notes. Tapping generally incorporates pull-offs or hammer-ons. For example, a right-handed guitarist might press down abruptly ("hammer") onto fret twelve with the index finger of the right hand and, in the motion of removing that finger, pluck ("pull") the same string already fretted at the eighth fret by the little finger of their left hand. This finger would be removed in the same way, pulling off to the fifth fret. Thus the three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Demodulator
Demodulation is the process of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a carrier wave. A demodulator is an electronic circuit (or computer program in a software-defined radio) that is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave. There are many types of modulation, and there are many types of demodulators. The signal output from a demodulator may represent sound (an analog audio signal), images (an analog video signal) or binary data (a digital signal). These terms are traditionally used in connection with radio receivers, but many other systems use many kinds of demodulators. For example, in a modem, which is a contraction of the terms modulator/demodulator, a demodulator is used to extract a serial digital data stream from a carrier signal which is used to carry it through a telephone line, coaxial cable, or optical fiber. History Demodulation was first used in radio receivers. In the wireless telegraphy radio systems used d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Envelope Detection
An envelope detector (sometimes called a peak detector) is an electronic circuit that takes a (relatively) high-frequency signal as input and outputs the ''envelope'' of the original signal. Diode detector A simple form of envelope detector used in detectors for early radios is the diode detector. Its output approximates a voltage-shifted version of the input's upper envelope. Between the circuit's input and output is a diode that performs half-wave rectification, allowing substantial current flow only when the input voltage is around a diode drop higher than the output terminal. The output is connected to a capacitor of value C and resistor of value R in parallel to ground. The capacitor is charged as the input voltage approaches its positive peaks. At other times, the capacitor is gradually discharged through the resistor. The resistor and capacitor form a 1st-order low pass filter, which attenuates higher frequencies at a rate of -6 dB per octave above its cutoff fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Envelope (waves)
In physics and engineering, the envelope of an oscillating signal is a smooth curve outlining its extremes. The envelope thus generalizes the concept of a constant amplitude into an instantaneous amplitude. The figure illustrates a modulated sine wave varying between an ''upper envelope'' and a ''lower envelope''. The envelope function may be a function of time, space, angle, or indeed of any variable. In beating waves A common situation resulting in an envelope function in both space ''x'' and time ''t'' is the superposition of two waves of almost the same wavelength and frequency: : \begin F(x, \ t) & = \sin \left[ 2 \pi \left( \frac - ( f + \Delta f )t \right) \right] + \sin \left[ 2 \pi \left( \frac - ( f - \Delta f )t \right) \right] \\[6pt] & \approx 2\cos \left[ 2 \pi \left( \frac - \Delta f \ t \right) \right] \ \sin \left[ 2 \pi \left( \frac - f \ t \right) \right] \end which uses the trigonometric formula for the Trigonometric identity#Product-to-sum an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the '' condenser microphone''. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The utility of a capacitor depends on its capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed specifically to add capacitance to some part of the circuit. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors, often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconductin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in One-way traffic, one direction (asymmetric electrical conductance, conductance). It has low (ideally zero) Electrical resistance and conductance, resistance in one direction and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a Crystallinity, crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. It has an Exponential function, exponential current–voltage characteristic. Semiconductor diodes were the first Semiconductor device, semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a Crystal, crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Half-wave Rectification
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The process is known as ''rectification'', since it "straightens" the direction of current. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including Vacuum tube#Diodes, vacuum tube diodes, wet chemical cells, mercury-arc valves, stacks of copper and selenium rectifier, selenium oxide plates, Diode#Semiconductor diodes, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motor-generator sets have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a "Crystal detector#Cat whisker detector, cat's whisker" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or "crystal detector". Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Standing Wave Ratio
In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the transmission line, and SWR is defined as the ratio of the partial standing wave's amplitude at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at a node (minimum) along the line. Voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR) (pronounced "vizwar" ) is the ratio of maximum to minimum voltage on a transmission line . For example, a VSWR of 1.2 means a peak voltage 1.2 times the minimum voltage along that line, if the line is at least one half wavelength long. A SWR can be also defined as the ratio of the maximum amplitude to minimum amplitude of the transmission line's currents, electric field strength, or the magnetic field strength. Neglecting transmission line loss, these ratios are identical. The power standing wave ratio (PSWR) is defined as the square o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intermediate Frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency (IF) is a frequency to which a carrier wave is shifted as an intermediate step in Transmission (telecommunications), transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is created by mixing the carrier signal with a local oscillator signal in a process called heterodyning, resulting in a signal at the difference or beat frequency. Intermediate frequencies are used in Superheterodyne receiver, superheterodyne radio receivers, in which an incoming signal is shifted to an IF for Amplifier, amplification before final Detector (radio), detection is done. Conversion to an intermediate frequency is useful for several reasons. When several stages of filters are used, they can all be set to a fixed frequency, which makes them easier to build and to tune. Lower frequency transistors generally have higher gains so fewer stages are required. It's easier to make sharply selective filters at lower fixed frequencies. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
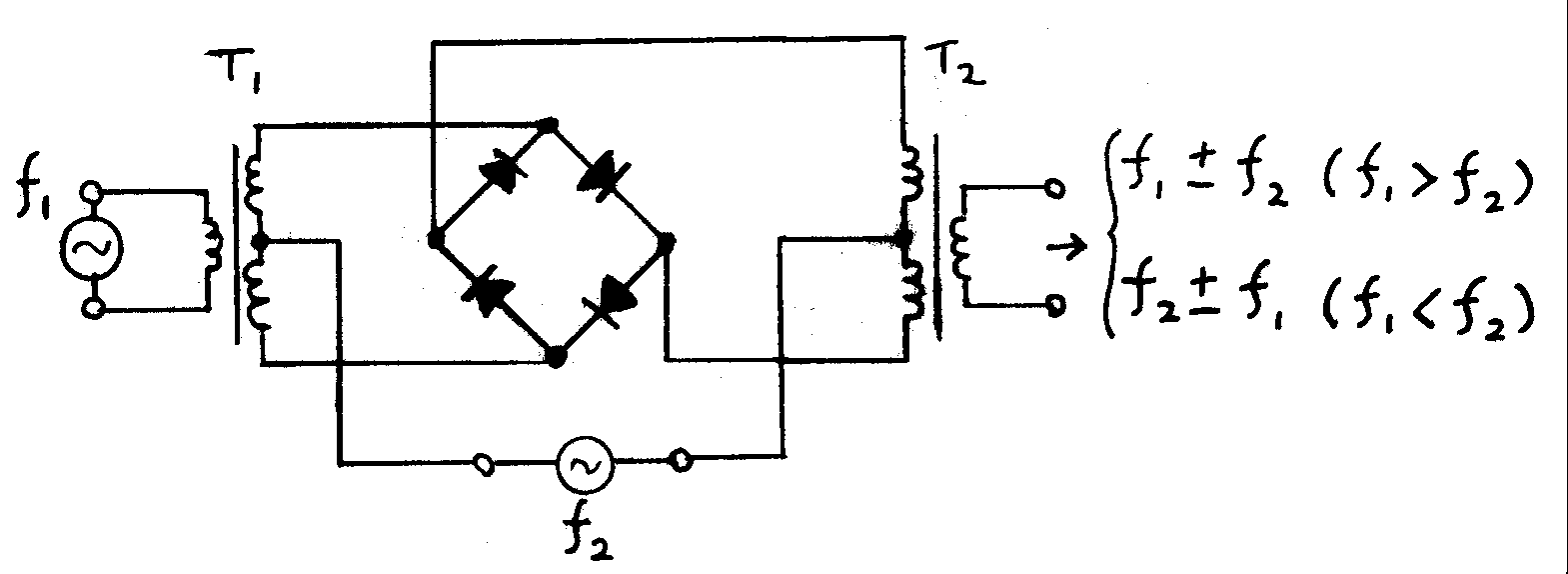
Frequency Mixer
In electronics, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is an electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and difference of the original frequencies. Other frequency components may also be produced in a practical frequency mixer. Mixers are widely used to shift signals from one frequency range to another, a process known as heterodyning, for convenience in transmission or further signal processing. For example, a key component of a superheterodyne receiver is a mixer used to move received signals to a common intermediate frequency. Frequency mixers are also used to modulation, modulate a carrier signal in Transmitter, radio transmitters. Types The essential characteristic of a mixer is that it produces a component in its output which is the product of the two input signals. Both active and passive circuits can realize mixers. Passive mixers use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Superheterodyne Receiver
A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original carrier frequency. It was invented by French radio engineer and radio manufacturer Lucien Lévy. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle. Precursors Early radio Early Morse code radio broadcasts were produced using an alternator connected to a spark gap. The output signal was at a carrier frequency defined by the physical construction of the gap, modulated by the alternating current signal from the alternator. Since the output frequency of the alternator was generally in the audible range, this produces an audible amplitude modulated (AM) signal. Simple radio detectors filtered out the high-frequency carrier, leaving the modulation, which was passed on to the user's headphones as an audible signal of do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components are etched onto a small, flat piece ("chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Integrated circuits are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and televisions, to perform various functions such as processing and storing information. They have greatly impacted the field of electronics by enabling device miniaturization and enhanced functionality. Integrated circuits are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete components, allowing a large transistor count. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design have ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |