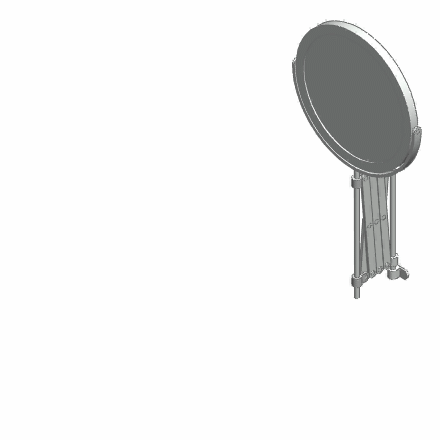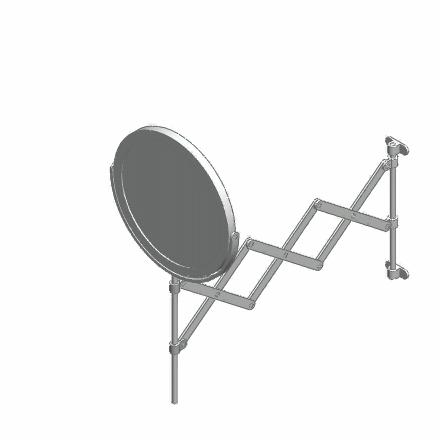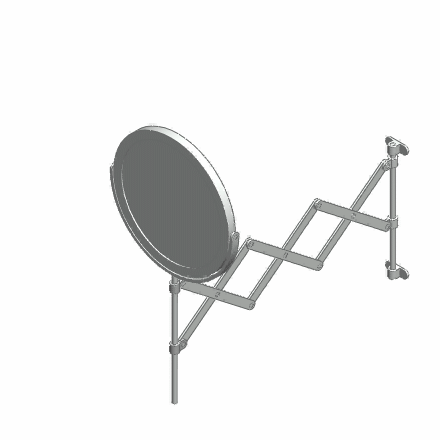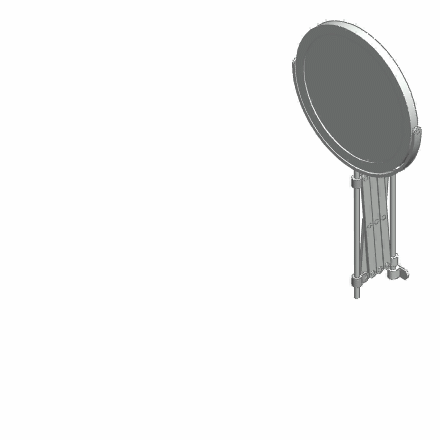|
Deployable Structure
A deployable structure is a structure that can change shape so as to significantly change its size. Examples of deployable structures are umbrellas, some tensegrity structures, bistable structures, some Origami shapes and scissor-like structures. Deployable structures are also used on spacecraft for deploying solar panels and solar sails. Space-based deployable structures can be categorized into three primary classes: the first is the articulated structure class wherein rigid members contain sliding contact joints or are folded at hinge points and pivot to deploy, often locking into place. The second class consists of on-orbit assembly where a device is fabricated and/or mechanically joined in space to form the structure. The final class is high strain structures (often composed of High_strain_composite_structure, High strain composites) wherein the device is dramatically flexed from one configuration to another during deployment. Gallery File:Scissor Tower.gif, Scissor-type s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Control Tower P1220950
Field may refer to: Expanses of open ground * Field (agriculture), an area of land used for agricultural purposes * Airfield, an aerodrome that lacks the infrastructure of an airport * Battlefield * Lawn, an area of mowed grass * Meadow, a grassland that is either natural or allowed to grow unmowed and ungrazed * Playing field, used for sports or games Arts and media * In decorative art, the main area of a decorated zone, often contained within a border, often the background for motifs ** Field (heraldry), the background of a shield ** In flag terminology, the background of a flag * ''FIELD'' (magazine), a literary magazine published by Oberlin College in Oberlin, Ohio * ''Field'' (sculpture), by Anthony Gormley Organizations * Field department, the division of a political campaign tasked with organizing local volunteers and directly contacting voters * Field Enterprises, a defunct private holding company ** Field Communications, a division of Field Enterprises * Field Museu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four-bar Linkage
In the study of Mechanism (engineering), mechanisms, a four-bar linkage, also called a four-bar, is the simplest closed-Kinematic chain, chain movable linkage (mechanical), linkage. It consists of four Rigid body, bodies, called ''bars'' or ''links'', connected in a loop by four Kinematic pair, joints. Generally, the joints are configured so the links move in parallel planes, and the assembly is called a ''planar four-bar linkage''. Spherical and spatial four-bar linkages also exist and are used in practice. Planar four-bar linkage Planar four-bar linkages are constructed from four links connected in a loop by four one-degrees of freedom (mechanics), degree-of-freedom joints. A joint may be either a revolute joint – also known as a pin joint or hinged joint – denoted by R, or a prismatic joint – also known as a sliding pair – denoted by P. A link that is fixed in place relative to the viewer is called a ''ground link.'' A link connecting to the ground by a revolute joint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compliant Mechanism
In mechanical engineering, a compliant mechanism is a flexible mechanism that achieves force and motion transmission through elastic body deformation. It gains some or all of its motion from the relative flexibility of its members rather than from rigid-body joints alone. These may be monolithic (single-piece) or jointless structures. Some common devices that use compliant mechanisms are backpack latches and paper clips. One of the oldest examples of using compliant structures is the bow and arrow. Compliant mechanisms manufactured in a plane that have motion emerging from said plane are known as lamina emergent mechanisms or LEMs. Design methods Compliant mechanism design continues to be an active area of research in the mid 2020s. Many methods have been developed for compliant mechanism design, broadly in two categories: Kinematics approaches Kinematic synthesis regards compliant mechanisms as discrete combinations of rigid and compliant elements. Pseudo-Rigid Body Mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slider-crank Linkage
A slider-crank linkage (also commonly referred to as a crank-slider linkage) is a four-link mechanism with three revolute joint, revolute joints and one prismatic joint, prismatic (sliding) joint. The naming convention of slider-crank and crank-slider is generally used to refer to the functional [input]-[output] of the linkage. In a crank-slider, the rotation of the crank (mechanism), crank drives the linear movement of the slider, and in a slider-crank, the expansion of gases against a sliding piston in a cylinder can drive the rotation of the crank. There are two types of slider-cranks: in-line and offset. # In-line: An in-line slider-crank has its slider positioned so the line of travel of the hinged joint of the slider passes through the base joint of the crank. This creates a symmetric slider movement back and forth as the crank rotates. # Offset: If the line of travel of the hinged joint of the slider does not pass through the base pivot of the crank, the slider movemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Motion
Parallel may refer to: Mathematics * Parallel (geometry), two lines in the Euclidean plane which never intersect * Parallel (operator), mathematical operation named after the composition of electrical resistance in parallel circuits Science and engineering * Parallel (latitude), an imaginary east–west line circling a globe * Parallel of declination, used in astronomy * Parallel, a geometric term of location meaning "in the same direction" * Series and parallel circuits#Parallel circuits, Parallel electrical circuits Computing * Parallel (software), a UNIX utility for running programs in parallel Language * Parallelism (grammar), a balance of two or more similar words, phrases, or clauses * Parallelism (rhetoric) Entertainment * Parallel (manga), ''Parallel'' (manga) * Parallel (2018 film), ''Parallel'' (2018 film), a Canadian science fiction thriller film * Parallel (2024 film), ''Parallel'' (2024 film) an American science fiction thriller film * Parallel (video), ''P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outline Of Machines
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to machines: Machine – mechanical system that provides the useful application of power to achieve movement. A machine consists of a power source, or engine, and a mechanism or transmission for the controlled use of this power. The combination of force and movement, known as power, is an important characteristic of a machine. Essence of machines * Applied mechanics * Machining, Machinist * Mechanical engineering * Mechanics * Mechanism (engineering) History of machines * Antikythera mechanism * Automatic lathe * Enigma machine * Early flying machines * History of the bicycle * History of computing hardware * History of the sewing machine * History of perpetual motion machines * Industrial Revolution * History of mechanical engineering * Paper machine * Second Industrial Revolution * Simple machine * Tabulating machine * Threshing machine * Vending machine * Washing machine Machine the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine (mechanical)
A machine is a physical system that uses Power (physics), power to apply forces and control Motion, movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecules, such as molecular machines. Machines can be driven by Animal power, animals and Human power, people, by natural forces such as Wind power, wind and Water power, water, and by Chemical energy, chemical, Thermal energy, thermal, or electricity, electrical power, and include a system of mechanism (engineering), mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement. They can also include computers and sensors that monitor performance and plan movement, often called mechanical systems. Renaissance natural philosophers identified six simple machines which were the elementary devices that put a load into motion, and calculated the ratio of output force to input force, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linkage (mechanical)
A mechanical linkage is an assembly of systems connected so as to manage forces and Motion, movement. The movement of a body, or link, is studied using geometry so the link is considered to be Rigid body, rigid. The connections between links are modeled as providing ideal movement, pure rotation or Sliding (motion), sliding for example, and are called joints. A linkage modeled as a network of rigid links and ideal joints is called a kinematic chain. Linkages may be constructed from open chains, closed chains, or a combination of open and closed chains. Each link in a chain is connected by a joint to one or more other links. Thus, a kinematic chain can be modeled as a graph in which the links are paths and the joints are vertices, which is called a linkage graph. The movement of an ideal joint is generally associated with a subgroup of the group of Euclidean geometry, Euclidean displacements. The number of parameters in the subgroup is called the degree of freedom (mecha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinematics
In physics, kinematics studies the geometrical aspects of motion of physical objects independent of forces that set them in motion. Constrained motion such as linked machine parts are also described as kinematics. Kinematics is concerned with systems of specification of objects' positions and velocities and mathematical transformations between such systems. These systems may be rectangular like Cartesian coordinate system, cartesian, Curvilinear coordinates like polar coordinates or other systems. The object trajectories may be specified with respect to other objects which may themselve be in motion relative to a standard reference. Rotating systems may also be used. Numerous practical problems in kinematics involve constraints, such as mechanical linkages, ropes, or rolling disks. Overview Kinematics is a subfield of physics and mathematics, developed in classical mechanics, that describes the motion of points, Physical object, bodies (objects), and systems of bodies (group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
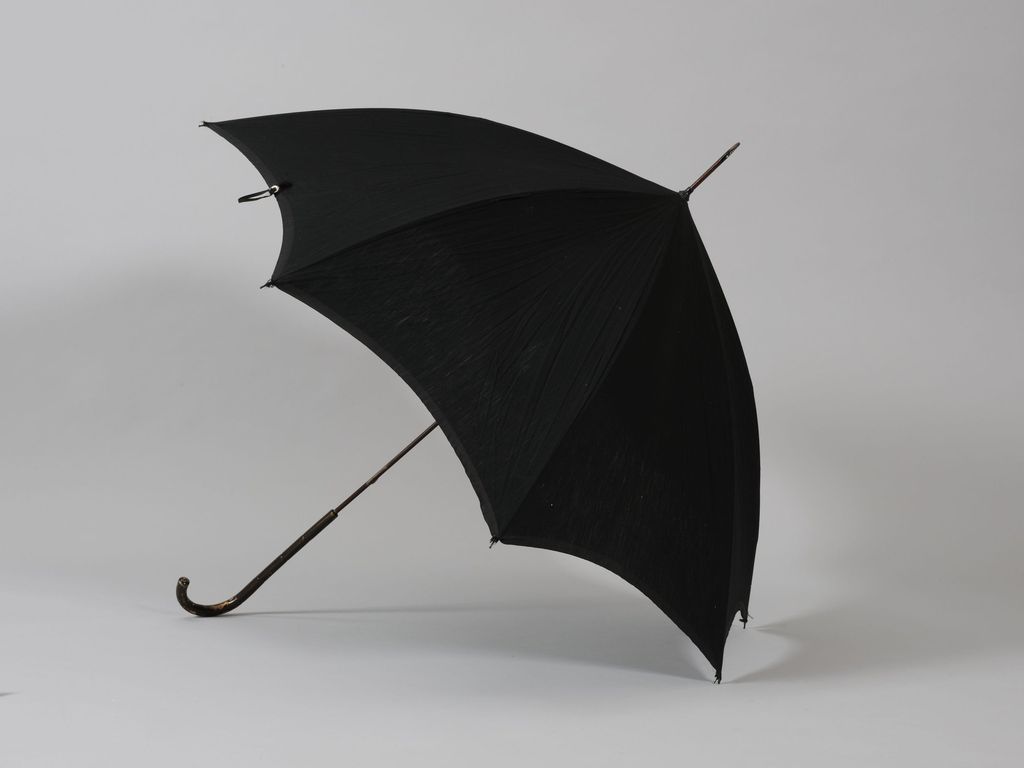
Umbrella
An umbrella or parasol is a folding canopy supported by wooden or metal ribs that is mounted on a wooden, metal, or plastic pole. It is usually designed to protect a person against rain. The term ''umbrella'' is traditionally used when protecting oneself from rain, while ''parasol'' is used when protecting oneself from sunlight, though the terms continue to be used interchangeably. Often the difference is the material used for the canopy; some parasols are not waterproof, and some umbrellas are transparent. Umbrella canopies may be made of fabric or flexible plastic. There are also combinations of parasol and umbrella that are called ''en-tout-cas'' (French for "in any case"). Generally speaking, parasols and umbrellas are small, handheld, personal use items. Golf umbrellas are the biggest hand-portable umbrellas available. There are two types of umbrellas: completely collapsible umbrellas, which can be folded up into a small enough bag because of the supporting metal pole's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |