|
Cytokinin
Cytokinins (CK) are a class of plant hormones that promote cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots and shoots. They are involved primarily in cell growth and differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and leaf senescence. There are two types of cytokinins: adenine-type cytokinins represented by kinetin, zeatin, and 6-benzylaminopurine, and phenylurea-type cytokinins like diphenylurea and thidiazuron (TDZ). Most adenine-type cytokinins are synthesized in roots. Cambium and other actively dividing tissues also synthesize cytokinins. No phenylurea cytokinins have been found in plants. Cytokinins participate in local and long-distance signalling, with the same transport mechanism as purines and nucleosides. Typically, cytokinins are transported in the xylem. Cytokinins act in concert with auxin, another plant growth hormone. The two are complementary, having generally opposite effects. History The idea of specific substances requir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Hormone
Plant hormone (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, from embryogenesis, the regulation of organ size, pathogen defense, stress tolerance and through to reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in higher plants. Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristics The word hormone is derived from Greek, meaning ''set in motion''. Plant hormones affect gene expre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeatin
Zeatin is a cytokinin derived from adenine, which occurs in the form of a ''cis''- and a ''trans''- isomer and conjugates. Zeatin was discovered in immature corn kernels from the genus '' Zea''. It promotes growth of lateral buds and when sprayed on meristems stimulates cell division to produce bushier plants. Occurrence Zeatin and its derivatives occur in many plant extracts and are the active ingredient in coconut milk, which causes plant growth. 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine is a zeatin precursor. Application Zeatin has a variety of effects including: # Promotes callus initiation when combined with auxin, concentration 1 ppm. # Promotes fruit set. Zeatin 100 ppm + GA3 500 ppm + NAA 20 ppm, sprayed at 10th, 25th, 40th day after blossom. # Retards yellowing for vegetables, 20 ppm, sprayed. # Causes auxiliary stems to grow and flower. Zeatin can also be applied to stimulate seed germination and seedling growth. Zeatin has also been shown to promote the resistance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeatin
Zeatin is a cytokinin derived from adenine, which occurs in the form of a ''cis''- and a ''trans''- isomer and conjugates. Zeatin was discovered in immature corn kernels from the genus '' Zea''. It promotes growth of lateral buds and when sprayed on meristems stimulates cell division to produce bushier plants. Occurrence Zeatin and its derivatives occur in many plant extracts and are the active ingredient in coconut milk, which causes plant growth. 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine is a zeatin precursor. Application Zeatin has a variety of effects including: # Promotes callus initiation when combined with auxin, concentration 1 ppm. # Promotes fruit set. Zeatin 100 ppm + GA3 500 ppm + NAA 20 ppm, sprayed at 10th, 25th, 40th day after blossom. # Retards yellowing for vegetables, 20 ppm, sprayed. # Causes auxiliary stems to grow and flower. Zeatin can also be applied to stimulate seed germination and seedling growth. Zeatin has also been shown to promote the resistance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Senescence
Plant senescence is the process of aging in plants. Plants have both stress-induced and age-related developmental aging. Chlorophyll degradation during leaf senescence reveals the carotenoids, such as anthocyanin and xanthophylls, which are the cause of autumn leaf color in deciduous trees. Leaf senescence has the important function of recycling nutrients, mostly nitrogen, to growing and storage organs of the plant. Unlike animals, plants continually form new organs and older organs undergo a highly regulated senescence program to maximize nutrient export. Hormonal regulation of senescence Programmed senescence seems to be heavily influenced by plant hormones. The hormones abscisic acid, ethylene, jasmonic acid and salicylic acid are accepted by most scientists as promoters of senescence, but at least one source lists gibberellins, brassinosteroids and strigolactone as also being involved. Cytokinins help to maintain the plant cell and expression of cytokinin biosynthesis gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetin
Kinetin (/'kaɪnɪtɪn/) is a type of cytokinin, a class of plant hormone that promotes cell division. Kinetin was originally isolated by Carlos Miller and Skoog ''et al.'' as a compound from autoclaved herring sperm DNA that had cell division-promoting activity. It was given the name kinetin because of its ability to induce cell division, provided that auxin was present in the medium. Kinetin is often used in plant tissue culture for inducing formation of callus (in conjunction with auxin) and to regenerate shoot tissues from callus (with lower auxin concentration). For a long time, it was believed that kinetin was an artifact produced from the deoxyadenosine residues in DNA, which degrade on standing for long periods or when heated during the isolation procedure. Therefore, it was thought that kinetin does not occur naturally, but, since 1996, it has been shown by several researchers that kinetin exists naturally in the DNA of cells of almost all organisms tested so far, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetin
Kinetin (/'kaɪnɪtɪn/) is a type of cytokinin, a class of plant hormone that promotes cell division. Kinetin was originally isolated by Carlos Miller and Skoog ''et al.'' as a compound from autoclaved herring sperm DNA that had cell division-promoting activity. It was given the name kinetin because of its ability to induce cell division, provided that auxin was present in the medium. Kinetin is often used in plant tissue culture for inducing formation of callus (in conjunction with auxin) and to regenerate shoot tissues from callus (with lower auxin concentration). For a long time, it was believed that kinetin was an artifact produced from the deoxyadenosine residues in DNA, which degrade on standing for long periods or when heated during the isolation procedure. Therefore, it was thought that kinetin does not occur naturally, but, since 1996, it has been shown by several researchers that kinetin exists naturally in the DNA of cells of almost all organisms tested so far, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenylurea
1,3-Diphenylurea is a phenylurea-type compound with the formula (PhNH)2CO (Ph = C6H5). It is a colorless solid that is prepared by transamidation of urea with aniline. DPU is a cytokinin Cytokinins (CK) are a class of plant hormones that promote cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots and shoots. They are involved primarily in cell growth and differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and le ..., a type of plant hormone that induces flower development. It occurs in coconut milk. The cytokinin effect of DPU is relatively low, but other more potent phenylurea-type cytokinins have been reported.Effect of cytokinin-active phenylurea derivatives on shoot multiplication. T. Genkov and I. Ivanova, Bulg. J. Plant Physiol., 1995, 21(1), pages 73–83link to article at researchgate References External links * Cytokinins Ureas {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine signaling, autocrine, paracrine signaling, paracrine and endocrine signaling as Immunomodulation, immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some growth factor#cytokine, overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as Endothelium, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axillary Bud
The axillary bud (or lateral bud) is an embryonic or organogenic shoot located in the axil of a leaf. Each bud has the potential to form shoots, and may be specialized in producing either vegetative shoots (stems and branches) or reproductive shoots (flowers). Once formed, a bud may remain dormant for some time, or it may form a shoot immediately. Overview An axillary bud is an embryonic or organogenic shoot which lies dormant at the junction of the stem and petiole of a plant. It arises exogenously from outer layer of cortex of the stem. Axillary buds do not become actively growing shoots on plants with strong apical dominance (the tendency to grow just the terminal bud on the main stem). Apical dominance occurs because the shoot apical meristem produces auxin which prevents axillary buds from growing. The axillary buds begin developing when they are exposed to less auxin, for example if the plant naturally has weak apical dominance, if apical dominance is broken by re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae. Wild potato species can be found from the southern United States to southern Chile. The potato was originally believed to have been domesticated by Native Americans independently in multiple locations,University of Wisconsin-Madison, ''Finding rewrites the evolutionary history of the origin of potatoes'' (2005/ref> but later genetic studies traced a single origin, in the area of present-day southern Peru and extreme northwestern Bolivia. Potatoes were domesticated there approximately 7,000–10,000 years ago, from a species in the ''Solanum brevicaule'' complex. Lay summary: In the Andes region of South America, where the species is indigenous, some close relatives of the potato are cultivated. Potatoes were introduced to Europe from the Americas by the Spanish in the second half of the 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae. Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, including the Baltic Sea, as well as off the west coast of South America. Three species of ''Clupea'' (the type genus of the herring family Clupeidae) are recognised, and comprise about 90% of all herrings captured in fisheries. The most abundant of these species is the Atlantic herring, which comprises over half of all herring capture. Fish called herring are also found in the Arabian Sea, Indian Ocean, and Bay of Bengal. Herring played an important role in the history of marine fisheries in Europe, and early in the 20th century, their study was fundamental to the development of fisheries science. These oily fish also have a long history as an important food fish, and are often salted, smoked, or pickled. Herring are also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
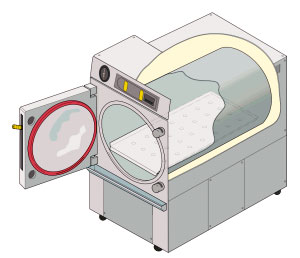
Autoclave
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites. Many autoclaves are used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to pressurized saturated steam at for around 30-60 minutes at a pressure of 15 psi (103 kPa or 1.02 atm) depending on the size of the load and the contents. The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the steam digester was created by Denis Papin in 1679. The name comes from Greek ''auto-'', ultimately meaning self, and Latin ''clavis'' meaning key, thus a self-locking device. Uses Sterilization auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |