|
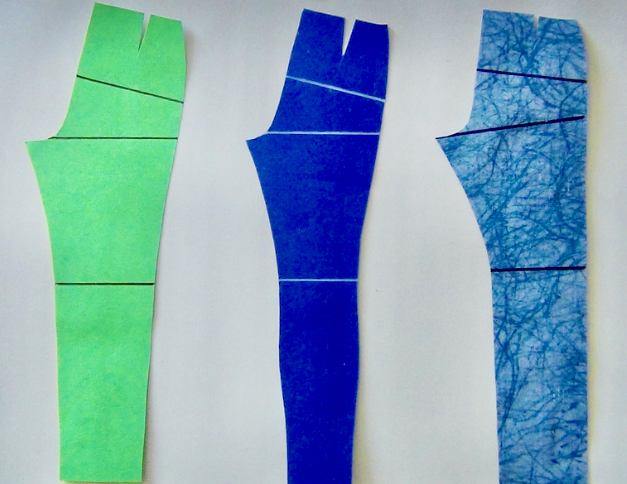
Cut (clothing)
Cut in clothing, sewing and tailoring, is the style or shape of a garment as opposed to its fabric or trimmings. The ''cut'' of a coat refers to the way the garment hangs on the body based on the shape of the fabric pieces used to construct it, the position of the fabric's grain line A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legumes ..., and so on. See also * Ease (sewing) * Pattern (sewing) * Clothing terminology Sewing {{clothing-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clothing
Clothing (also known as clothes, apparel, and attire) are items worn on the body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin sheets of materials and natural products found in the environment, put together. The wearing of clothing is mostly restricted to human beings and is a feature of all human societies. The amount and type of clothing worn depends on gender, body type, social factors, and geographic considerations. Garments cover the body, footwear covers the feet, gloves cover the hands, while hats and headgear cover the head. Eyewear and jewelry are not generally considered items of clothing, but play an important role in fashion and clothing as costume. Clothing serves many purposes: it can serve as protection from the elements, rough surfaces, sharp stones, rash-causing plants, insect bites, by providing a barrier between the skin and the environment. Clothing can insulate against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sewing
Sewing is the craft of fastening or attaching objects using stitches made with a sewing needle and thread. Sewing is one of the oldest of the textile arts, arising in the Paleolithic era. Before the invention of spinning yarn or weaving fabric, archaeologists believe Stone Age people across Europe and Asia sewed fur and leather clothing using bone, antler or ivory sewing-needles and "thread" made of various animal body parts including sinew, catgut, and veins. For thousands of years, all sewing was done by hand. The invention of the sewing machine in the 19th century and the rise of computerization in the 20th century led to mass production and export of sewn objects, but hand sewing is still practiced around the world. Fine hand sewing is a characteristic of high-quality tailoring, haute couture fashion, and custom dressmaking, and is pursued by both textile artists and hobbyists as a means of creative expression. The first known use of the word "sewing" was in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailor
A tailor is a person who makes or alters clothing, particularly in men's clothing. The Oxford English Dictionary dates the term to the thirteenth century. History Although clothing construction goes back to prehistory, there is evidence of tailor shops in Ancient Greece and Rome, as well as tailoring tools such as irons and shears. The profession of tailor in Europe became formalized in the High Middle Ages through the establishment of guilds. Tailors' guilds instituted a system of masters, journeymen, and apprentices. Guild members established rules to limit competition and establish quality standards. In 1244, members of the tailor's guild in Bologna established statutes to govern their profession and required anyone working as a tailor to join the guild. In England, the Statute of Artificers, passed in 1563, included the profession of tailor as one of the trades that could be entered only by serving a term of apprenticeship, typically seven years. A typical tailor sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: Domestic purposes onsumer textilesand technical textiles. In consumer textiles, aesthetics and comfort are the most important factors, but in technical textiles, functional properties are the priority. Geotextiles, industrial textiles, medical textiles, and many other areas are examples of technical textiles, whereas clothing and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trim (sewing)
Trim or trimming in clothing and home decorating is applied ornament, such as gimp, passementerie, ribbon, Ruffle (sewing)s, or, as a verb, to apply such ornament. Before the industrial revolution, all trim was made and applied by hand, thus making heavily trimmed furnishings and garments expensive and high-status. Machine-woven trims and sewing machines put these dense trimmings within the reach of even modest dressmakers and home sewers, and an abundance of trimming is a characteristic of mid-Victorian fashion. As a predictable reaction, high fashion came to emphasize exquisiteness of cut and construction over denseness of trimming, and applied trim became a signifier of mass-produced clothing by the 1930s. The iconic braid and gold button trim of the Chanel suit are a notable survival of trim in high fashion. In home decorating, the 1980s and 1990s saw a fashion for dense, elaborately layered trimmings on upholstered furniture and drapery. Today, most trimmings are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat (clothing)
A coat typically is an outer garment for the upper body as worn by either gender for warmth or fashion. Coats typically have long sleeves and are open down the front and closing by means of buttons, zippers, hook-and-loop fasteners, toggles, a belt, or a combination of some of these. Other possible features include collars, shoulder straps and hoods. Etymology ''Coat'' is one of the earliest clothing category words in English, attested as far back as the early Middle Ages. (''See also'' Clothing terminology.) The Oxford English Dictionary traces ''coat'' in its modern meaning to c. 1300, when it was written ''cote'' or ''cotte''. The word coat stems from Old French and then Latin ''cottus.'' It originates from the Proto-Indo-European word for woolen clothes. An early use of ''coat'' in English is coat of mail (chainmail), a tunic-like garment of metal rings, usually knee- or mid-calf length. History The origins of the Western-style coat can be traced to the sleeved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grain Line
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legumes. After being harvested, dry grains are more durable than other staple foods, such as starchy fruits (plantains, breadfruit, etc.) and tubers ( sweet potatoes, cassava, and more). This durability has made grains well suited to industrial agriculture, since they can be mechanically harvested, transported by rail or ship, stored for long periods in silos, and milled for flour or pressed for oil. Thus, the grain market is a major global commodity market that includes crops such as maize, rice, soybeans, wheat and other grains. Grains and cereal Grains and cereal are synonymous with caryopses, the fruits of the grass family. In agronomy and commerce, seeds or fruits from other plant families are called grains if they resemble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ease (sewing)
In sewing and patternmaking, ease is the amount of room a garment allows the wearer beyond the measurements of their body. For example, if a man has a 40-inch chest measurement, a jacket with a 40-inch chest would be very tight and would constrict movement. An ease of 3 or 4 inches might be added to the pattern (making a 43-44 inch chest), or more to enhance comfort or style. Ease is not generally included in sizing measurements. To use the example again, a man with a 40-inch chest will likely buy a jacket advertised as size 40, but the actual measurements of the garment will almost always be somewhat larger. Ease is most important for woven garments cut on the straight or crossgrain, because fabric in this orientation has little or no stretch. This is in contrast to woven garments cut on the bias and knit garments, both of which can stretch to accommodate movement. A sloper pattern or block pattern is a simple pattern with very little or no ease made for the purpose of fitting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern (sewing)
In sewing and fashion design, a pattern is the template from which the parts of a garment are traced onto woven or knitted fabrics before being cut out and assembled. Patterns are usually made of paper, and are sometimes made of sturdier materials like paperboard or cardboard if they need to be more robust to withstand repeated use. The process of making or cutting patterns is sometimes compounded to the one-word Patternmaking, but it can also be written pattern(-)making or pattern cutting. A sloper pattern (home sewing) or block pattern (industrial production) is a custom-fitted, basic pattern from which patterns for many different styles can be developed. The process of changing the size of a finished pattern is called grading. Several companies, like Butterick and Simplicity, specialize in selling pre-graded patterns directly to consumers who will sew the patterns at home. Commercial clothing manufacturers make their own patterns in-house as part of their design and produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clothing Terminology
Clothing terminology comprises the names of individual garments and classes of garments, as well as the specialized vocabularies of the trades that have designed, manufactured, marketed and sold clothing over hundreds of years. Clothing terminology ranges from the arcane (watchet,M. Channing Linthicum, ''Costume in the Drama of Shakespeare and his Contemporaries'' (Oxford, 1936), pp. 28-9. a pale blue color name from the 16th century), and changes over time in response to fashion which in turn reflects social, artistic, and political trends. Categories At its broadest, clothing terminology may be said to include names for: * Classes of basic garments: shirt, coat, skirt, dress, suit, underwear, swimsuit * Length, for skirts and dresses: micro-mini, mini, tea length, ballerina length, full length, midi, maxi * Contemporary and historical styles of garments: corset, frock coat, t-shirt, doublet * Parts of garments: sleeve, collar, lapel * Styles of these: juliette s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)