|
Coupling (electronics)
In electronics, electric power and telecommunication, coupling is the transfer of electrical energy from one Electronic circuit, circuit to another, or between parts of a circuit. Coupling can be deliberate as part of the function of the circuit, or it may be undesirable, for instance due to coupling to stray fields. For example, energy is transferred from a power supply, power source to an electrical load by means of conductive coupling, which may be either resistor, resistive or direct coupling. An Alternating current, AC potential may be transferred from one circuit segment to another having a Direct current, DC potential by use of a capacitor. Electrical energy may be transferred from one circuit segment to another segment with different Characteristic impedance, impedance by use of a transformer; this is known as impedance matching. These are examples of capacitive coupling, electrostatic and electrodynamic induction, electrodynamic inductive coupling. Types Electrical cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification and rectification, which distinguishes it from classical electrical engineering, which only uses passive effects such as resistance, capacitance and inductance to control electric current flow. Electronics has hugely influenced the development of modern society. The central driving force behind the entire electronics industry is the semiconductor industry sector, which has annual sales of over $481 billion as of 2018. The largest industry sector is e-commerce, which generated over $29 trillion in 2017. History and development Electronics has hugely influenced the development of modern society. The identification of the electron in 1897, along with the subsequent invention of the vacuum tube which could amplify and rectify small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitive Coupling
Capacitive coupling is the transfer of energy within an electrical network or between distant networks by means of displacement current between circuit(s) nodes, induced by the electric field. This coupling can have an intentional or accidental effect. In its simplest implementation, capacitive coupling is achieved by placing a capacitor between two nodes. Where analysis of many points in a circuit is carried out, the capacitance at each point and between points can be described in a matrix form. Use in analog circuits In analog circuits, a coupling capacitor is used to connect two circuits such that only the AC signal from the first circuit can pass through to the next while DC is blocked. This technique helps to isolate the DC bias settings of the two coupled circuits. Capacitive coupling is also known as ''AC coupling'' and the capacitor used for the purpose is also known as a ''DC-blocking capacitor''. A coupling capacitor's ability to prevent a DC load from interfe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna Noise Temperature
In radio frequency (RF) applications such as radio, radar and telecommunications, noise temperature of an antenna is a measure of the noise power density contributed by the antenna to the overall RF receiver system. It is defined as "The temperature of a resistor having an available thermal noise power per unit bandwidth equal to that at the antenna’s output at a specified frequency."IEEE Std 145-2013, IEEE Standard for Definitions of Terms for Antennas, IEEE In other words, antenna noise temperature is a parameter that describes how much noise an antenna produces in a given environment. This temperature is not the physical temperature of the antenna. Moreover, an antenna does not have an intrinsic "antenna temperature" associated with it; rather the temperature depends on its gain pattern, pointing direction, and the thermal environment that it is placed in. Mathematics In RF applications, noise power is defined using the relationship P_ = kTB, where k is Boltzmann's constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
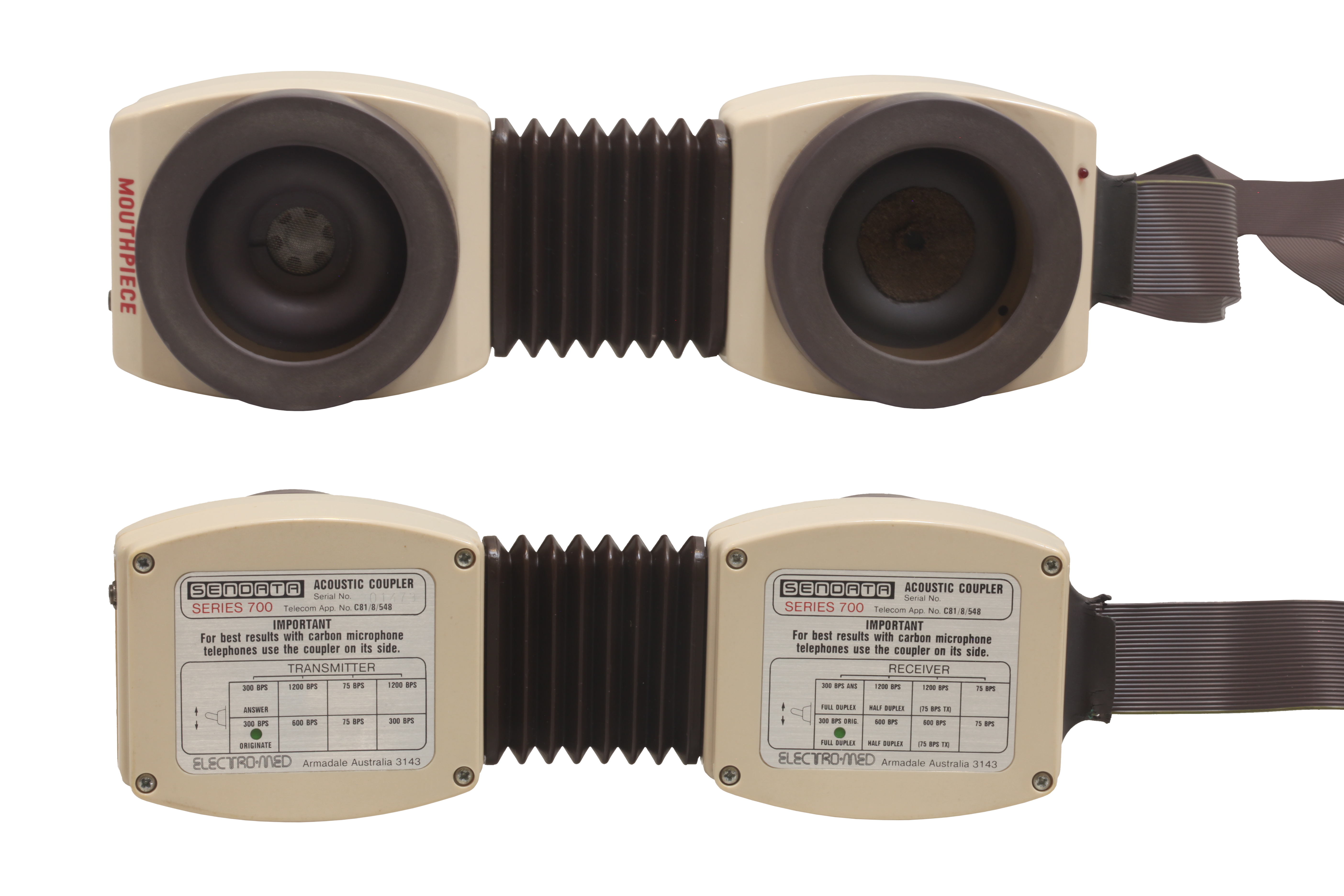
Acoustic Coupler
In telecommunications, an acoustic coupler is an interface device for coupling electrical signals by acoustical means—usually into and out of a telephone. The link is achieved through converting electric signals from the phone line to sound and reconvert sound to electric signals needed for the end terminal, such as a teletypewriter, and back, rather than through direct electrical connection. History and applications Prior to its breakup in 1984, Bell System's legal monopoly over telephony in the United States allowed the company to impose strict rules on how consumers could access their network. Customers were prohibited from connecting equipment not made or sold by Bell to the network. The same set-up was operative in nearly all countries, where the telephone companies were nationally owned. In many households, telephones were hard-wired to wall terminals before connectors like RJ11 and BS 6312 became standardized. The situation was similar in other countries. In Australi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave Power Transmission
Wireless power transfer (WPT), wireless power transmission, wireless energy transmission (WET), or electromagnetic power transfer is the transmission of electrical energy without wires as a physical link. In a wireless power transmission system, a transmitter device, driven by electric power from a power source, generates a time-varying electromagnetic field, which transmits power across space to a receiver device, which extracts power from the field and supplies it to an electrical load. The technology of wireless power transmission can eliminate the use of the wires and batteries, thus increasing the mobility, convenience, and safety of an electronic device for all users. Wireless power transfer is useful to power electrical devices where interconnecting wires are inconvenient, hazardous, or are not possible. Wireless power techniques mainly fall into two categories, near field and far-field. In '' near field'' or ''non-radiative'' techniques, power is transferred over sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Shielding
In electrical engineering, electromagnetic shielding is the practice of reducing or blocking the electromagnetic field (EMF) in a space with barriers made of conductive or magnetic materials. It is typically applied to enclosures, for isolating electrical devices from their surroundings, and to cables to isolate wires from the environment through which the cable runs (). Electromagnetic shielding that blocks radio frequency (RF) electromagnetic radiation is also known as RF shielding. EMF shielding serves to minimize electromagnetic interference. The shielding can reduce the coupling of radio waves, electromagnetic fields, and electrostatic fields. A conductive enclosure used to block electrostatic fields is also known as a '' Faraday cage''. The amount of reduction depends very much upon the material used, its thickness, the size of the shielded volume and the frequency of the fields of interest and the size, shape and orientation of holes in a shield to an incident electromagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Compatibility
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the ability of electrical equipment and systems to function acceptably in their electromagnetic environment, by limiting the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy which may cause unwanted effects such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) or even physical damage in operational equipment. The goal of EMC is the correct operation of different equipment in a common electromagnetic environment. It is also the name given to the associated branch of electrical engineering. EMC pursues three main classes of issue. Emission is the generation of electromagnetic energy, whether deliberate or accidental, by some source and its release into the environment. EMC studies the unwanted emissions and the countermeasures which may be taken in order to reduce unwanted emissions. The second class, susceptibility, is the tendency of electrical equipment, referred to as the victim, to malfunction or break down in the presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Interference
Electromagnetic interference (EMI), also called radio-frequency interference (RFI) when in the radio frequency spectrum, is a disturbance generated by an external source that affects an electrical circuit by electromagnetic induction, electrostatic coupling, or conduction. The disturbance may degrade the performance of the circuit or even stop it from functioning. In the case of a data path, these effects can range from an increase in error rate to a total loss of the data. Both man-made and natural sources generate changing electrical currents and voltages that can cause EMI: ignition systems, cellular network of mobile phones, lightning, solar flares, and auroras (northern/southern lights). EMI frequently affects AM radios. It can also affect mobile phones, FM radios, and televisions, as well as observations for radio astronomy and atmospheric science. EMI can be used intentionally for radio jamming, as in electronic warfare. History Since the earliest days of ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Waves
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz (GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (shorter than a grain of rice); at 30 Hz the corresponding wavelength is (longer than the radius of the Earth). Like all electromagnetic waves, radio waves in a vacuum travel at the speed of light, and in the Earth's atmosphere at a close, but slightly lower speed. Radio waves are generated by charged particles undergoing acceleration, such as time-varying electric currents. Naturally occurring radio waves are emitted by lightning and astronomical objects, and are part of the blackbody radiation emitted by all warm objects. Radio waves are generated artificially by an electronic device called a transmitter, which is connected to an antenna which radiates the waves. They are received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver, which p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
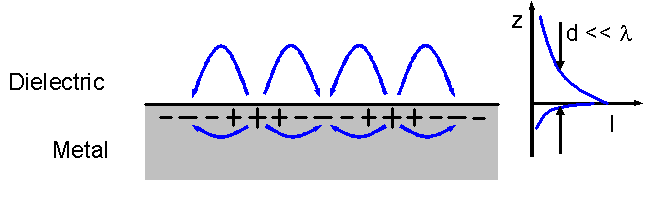
Evanescent Wave Coupling
In electromagnetics, an evanescent field, or evanescent wave, is an oscillating electric and/or magnetic field that does not propagate as an electromagnetic wave but whose energy is spatially concentrated in the vicinity of the source (oscillating charges and currents). Even when there is a propagating electromagnetic wave produced (e.g., by a transmitting Antenna (radio), antenna), one can still identify as an evanescent field the component of the electric or magnetic field that cannot be attributed to the propagating wave observed at a distance of many wavelengths (such as the far field of a transmitting antenna). A hallmark of an evanescent field is that there is no net energy flow in that region. Since the net flow of electromagnetic energy is given by the average Poynting vector, this means that the Poynting vector in these regions, as averaged over a complete oscillation cycle, is zero. Use of the term In many cases one cannot simply say that a field is or is not "evanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitive Coupling
Capacitive coupling is the transfer of energy within an electrical network or between distant networks by means of displacement current between circuit(s) nodes, induced by the electric field. This coupling can have an intentional or accidental effect. In its simplest implementation, capacitive coupling is achieved by placing a capacitor between two nodes. Where analysis of many points in a circuit is carried out, the capacitance at each point and between points can be described in a matrix form. Use in analog circuits In analog circuits, a coupling capacitor is used to connect two circuits such that only the AC signal from the first circuit can pass through to the next while DC is blocked. This technique helps to isolate the DC bias settings of the two coupled circuits. Capacitive coupling is also known as ''AC coupling'' and the capacitor used for the purpose is also known as a ''DC-blocking capacitor''. A coupling capacitor's ability to prevent a DC load from interfe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductive Coupling
In electrical engineering, two conductors are said to be inductively coupled or magnetically coupled when they are configured in a way such that change in current through one wire induces a voltage across the ends of the other wire through electromagnetic induction. A changing current through the first wire creates a changing magnetic field around it by Ampere's circuital law. The changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF or voltage) in the second wire by Faraday's law of induction. The amount of inductive coupling between two conductors is measured by their mutual inductance. The coupling between two wires can be increased by winding them into coils and placing them close together on a common axis, so the magnetic field of one coil passes through the other coil. Coupling can also be increased by a magnetic core of a ferromagnetic material like iron or ferrite in the coils, which increases the magnetic flux. The two coils may be physically con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)