|
Copper Silicide
Copper silicide can refer to either or pentacopper silicide, . Pentacopper silicide is a binary compound of silicon with copper. It is an intermetallic compound, meaning that it has properties intermediate between an ionic compound and an alloy. This solid crystalline material is a silvery solid that is insoluble in water. It forms upon heating mixtures of copper and silicon. Applications Copper silicide thin film is used for passivation of copper interconnects, where it serves to suppress diffusion and electromigration and serves as a diffusion barrier. Copper silicides are invoked in the Direct process, the industrial route to organosilicon compounds. In this process, copper, in the form of its silicide, catalyses the addition of methyl chloride to silicon. An illustrative reaction affords the industrially useful dimethyldichlorosilane Dimethyldichlorosilane is a tetrahedral, organosilicon compound with the formula Si(CH3)2Cl2. At room temperature it is a colorless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRC Handbook Of Chemistry And Physics
The ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'' is a comprehensive one-volume reference resource for science research. First published in 1914, it is currently () in its 103rd edition, published in 2022. It is sometimes nicknamed the "Rubber Bible" or the "Rubber Book", as CRC originally stood for "Chemical Rubber Company". As late as the 1962–1963 edition (3604 pages) the ''Handbook'' contained myriad information for every branch of science and engineering. Sections in that edition include: Mathematics, Properties and Physical Constants, Chemical Tables, Properties of Matter, Heat, Hygrometric and Barometric Tables, Sound, Quantities and Units, and Miscellaneous. Earlier editions included sections such as "Antidotes of Poisons", "Rules for Naming Organic Compounds", "Surface Tension of Fused Salts", "Percent Composition of Anti-Freeze Solutions", "Spark-gap Voltages", "Greek Alphabet", "Musical Scales", "Pigments and Dyes", "Comparison of Tons and Pounds", "Twist Drill and St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical potential. It is possible to diffuse "uphill" from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, like in spinodal decomposition. The concept of diffusion is widely used in many fields, including physics (particle diffusion), chemistry, biology, sociology, economics, and finance (diffusion of people, ideas, and price values). The central idea of diffusion, however, is common to all of these: a substance or collection undergoing diffusion spreads out from a point or location at which there is a higher concentration of that substance or collection. A gradient is the change in the value of a quantity, for example, concentration, pressure, or temperature with the change in another variable, usually distance. A change in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyldichlorosilane
Dimethyldichlorosilane is a tetrahedral, organosilicon compound with the formula Si(CH3)2Cl2. At room temperature it is a colorless liquid that readily reacts with water to form both linear and cyclic Si-O chains. Dimethyldichlorosilane is made on an industrial scale as the principal precursor to dimethylsilicone and polysilane compounds. History The first organosilicon compounds were reported in 1863 by Charles Friedel and James Crafts who synthesized tetraethylsilane from diethylzinc and silicon tetrachloride.Silicon: Organosilicon Chemistry. Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry Online, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New Jersey, 2005. However, major progress in organosilicon chemistry did not occur until Frederick Kipping and his students began experimenting with diorganodichlorosilanes (R2SiCl2) that were prepared by reacting silicon tetrachloride with Grignard reagents. Unfortunately, this method suffered from many experimental problems. In the 1930s, the demand for silicones increased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Chloride
Chloromethane, also called methyl chloride, Refrigerant-40, R-40 or HCC 40, is an organic compound with the chemical formula . One of the haloalkanes, it is a colorless, odorless, flammable gas. Methyl chloride is a crucial reagent in industrial chemistry, although it is rarely present in consumer products, and was formerly utilized as a refrigerant. Occurrence Chloromethane is an abundant organohalogen, anthropogenic or natural, in the atmosphere. Marine Laboratory cultures of marine phytoplankton (''Phaeodactylum tricornutum'', ''Phaeocystis'' sp., ''Thalassiosira weissflogii'', ''Chaetoceros calcitrans'', ''Isochrysis'' sp., ''Porphyridium'' sp., ''Synechococcus'' sp., ''Tetraselmis'' sp., ''Prorocentrum'' sp., and ''Emiliana huxleyi'') produce CH3Cl, but in relatively insignificant amounts. An extensive study of 30 species of polar macroalgae revealed the release of significant amounts of CH3Cl in only ''Gigartina skottsbergii'' and ''Gymnogongrus antarcticus''. Biogenesis T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organosilicon Compounds
Organosilicon compounds are organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds. Organosilicon chemistry is the corresponding science of their preparation and properties. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an ''inorganic'' compound. History In 1846 Von Ebelman's had synthesized Tetraethyl orthosilicate (Si(OC2H5)4). In 1863 Friedel and Crafts managed to make the first organosilieon compound with C-Si bonds which gone byound the syntheses of orthosilicic acid esters. The same year they also described a «polysilicic acid ether» in the preparation of ethyl- and methyl-o-silicic acid. The early extensive research in the field of organosilicon compounds was pioneerd in the beginning of 20th century by Frederic Kipping. He also had coined the term «silicone» (akin to ketones) in relation to these materials in 1904. In recognition of Kipping's achiev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Process
The direct process, also called the direct synthesis, Rochow process, and Müller-Rochow process is the most common technology for preparing organosilicon compounds on an industrial scale. It was first reported independently by Eugene G. Rochow and Richard Müller in the 1940s.. The process involves copper-catalyzed reactions of alkyl halides with elemental silicon, which take place in a fluidized bed reactor. Although theoretically possible with any alkyl halide, the best results in terms of selectivity and yield occur with chloromethane (CH3Cl). Typical conditions are 300°C and 2–5bar. These conditions allow for 90–98% conversion for silicon and 30–90% for chloromethane. Approximately 1.4 Mton of dimethyldichlorosilane (Me2SiCl2) is produced annually using this process.Elschenbroich, Christoph Organometallics VCH, Weinheim, Germany: 1992. . Few companies actually carry out the Rochow process, because of the complex technology and has high capital requirements. Since the si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion Barrier
A diffusion barrier is a thin layer (usually micrometres thick) of metal usually placed between two other metals. It is done to act as a barrier to protect either one of the metals from corrupting the other.. Adhesion of a plated metal layer to its substrate requires a physical interlocking, inter-diffusion of the deposit or a chemical bonding between plate and substrate in order to work. The role of a diffusion barrier is to prevent or to retard the inter-diffusion of the two superposed metals. Therefore, to be effective, a good diffusion barrier requires inertness with respect to adjacent materials. To obtain good adhesion and a diffusion barrier simultaneously, the bonding between layers needs to come from a chemical reaction of limited range at both boundaries. Materials providing good adhesion are not necessarily good diffusion barriers and vice versa. Consequently, there are cases where two or more separate layers must be used to provide a proper interface between substrates. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
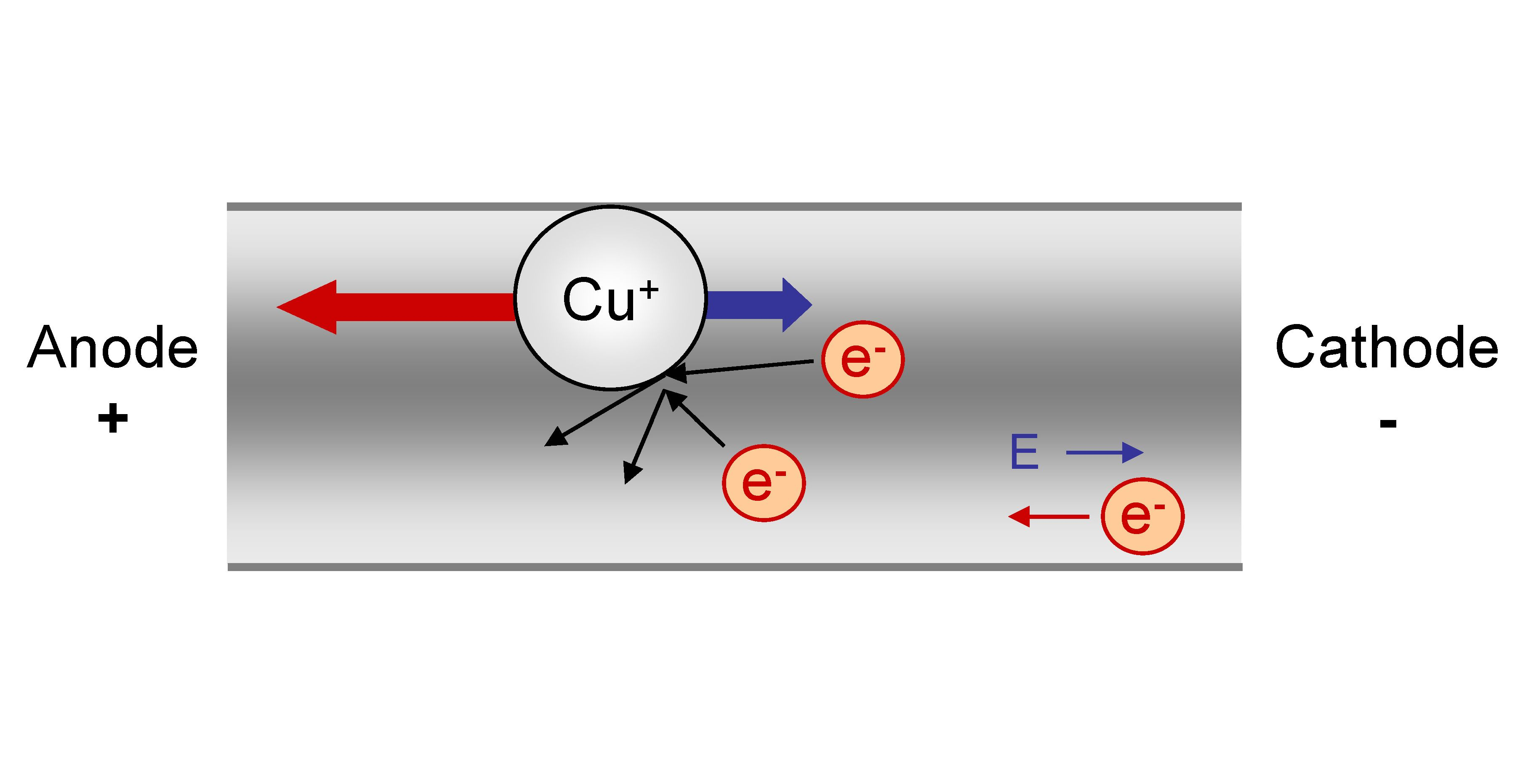
Electromigration
Electromigration is the transport of material caused by the gradual movement of the ions in a conductor due to the momentum transfer between conducting electrons and diffusing metal atoms. The effect is important in applications where high direct current densities are used, such as in microelectronics and related structures. As the structure size in electronics such as integrated circuits (ICs) decreases, the practical significance of this effect increases. History The phenomenon of electromigration has been known for over 100 years, having been discovered by the French scientist Gerardin. The topic first became of practical interest during the late 1960s when packaged ICs first appeared. The earliest commercially available ICs failed in a mere three weeks of use from runaway electromigration, which led to a major industry effort to correct this problem. The first observation of electromigration in thin films was made by I. Blech.I. Blech: ''Electromigration in Thin Aluminum Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Interconnects
In semiconductor technology, copper interconnects are interconnects made of copper. They are used in silicon integrated circuits (ICs) to reduce propagation delays and power consumption. Since copper is a better conductor than aluminium, ICs using copper for their interconnects can have interconnects with narrower dimensions, and use less energy to pass electricity through them. Together, these effects lead to ICs with better performance. They were first introduced by IBM, with assistance from Motorola, in 1997. The transition from aluminium to copper required significant developments in fabrication techniques, including radically different methods for patterning the metal as well as the introduction of barrier metal layers to isolate the silicon from potentially damaging copper atoms. Patterning Although some form of volatile copper compound has been known to exist since 1947, with more discovered as the century progressed, none were in industrial use, so copper could not be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Compound Of Silicon
Binary compounds of silicon are binary compound, binary chemical compounds containing silicon and one other chemical element. Technically the term silicide is reserved for any compounds containing silicon bonded to a more Electronegativity#Electropositivity, electropositive element. Binary silicon compounds can be grouped into several classes. Salt (chemistry), Saltlike silicides are formed with the electropositive s-block metals. Covalent silicides and silicon compounds occur with hydrogen and the elements in groups 10 to 17. Transition metals form metallic silicides, with the exceptions of silver, gold and the group 12 elements. The general composition is MnSi or MSin with n ranging from 1 to 6 and M standing for metal. Examples are M5Si, M3Si (Cu, V, Cr, Mo, Mn, Fe, Pt, U), M2Si (Zr, Hf, Ta, Ir, Ru, Rh, Co, Ni, Ce), M3Si2 (Hf, Th, U), MSi (Ti, Zr, Hf, Fe, Ce, Th, Pu) and MSi2 (Ti, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, Re). The Kopp–Neumann law applies as: Cp(M,Si,) = xCp(M) + yCp(Si) As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passivation (chemistry)
Passivation, in physical chemistry and engineering, refers to coating a material so it becomes "passive", that is, less readily affected or corroded by the environment. Passivation involves creation of an outer layer of shield material that is applied as a microcoating, created by chemical reaction with the base material, or allowed to build by spontaneous oxidation in the air. As a technique, passivation is the use of a light coat of a protective material, such as metal oxide, to create a shield against corrosion. Passivation of silicon is used during fabrication of microelectronic devices. In electrochemical treatment of water, passivation reduces the effectiveness of the treatment by increasing the circuit resistance, and active measures are typically used to overcome this effect, the most common being polarity reversal, which results in limited rejection of the fouling layer. When exposed to air, many metals naturally form a hard, relatively inert surface layer, usually an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Film
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from fractions of a nanometer (monolayer) to several micrometers in thickness. The controlled synthesis of materials as thin films (a process referred to as deposition) is a fundamental step in many applications. A familiar example is the household mirror, which typically has a thin metal coating on the back of a sheet of glass to form a reflective interface. The process of silvering was once commonly used to produce mirrors, while more recently the metal layer is deposited using techniques such as sputtering. Advances in thin film deposition techniques during the 20th century have enabled a wide range of technological breakthroughs in areas such as magnetic recording media, electronic semiconductor devices, integrated passive devices, LEDs, optical coatings (such as antireflective coatings), hard coatings on cutting tools, and for both energy generation (e.g. thin-film solar cells) and storage ( thin-film batteries). It is also being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_【_Pictures_taken_in_Japan_】_(cropped).jpg)

_250_nm_by_250_nm_image_of_one-atom-thick_silver_islands_grown_on_palladium_(111)_surface.png)